Cultural and Gender Differences in Information Sharing through Social Media
Dissertation Topic: Cultural and Gender Differences in Information Sharing through Social Media. The overall aim of the project is to take a closer look into the social media networking site Facebook and conduct my own research into how people generally use Facebook, the impact and implications Facebook has on a user, the thoughts on privacy with regards to Facebook and to see if a participants ethnic background has an effect on the way they use the site. I will also be analyzing both male and female participants to see if there are any significant differences with regards to their Facebook activity, what they post and what personal information they choose to share. During this study I will look closely into the attitudes of users when posting content, their own censorship and consideration for others when posting content of themselves and others.
At the end of this marketing dissertation I aim to have a clearer insight and a greater understanding into a users cultural or ethnic background and if this has any effect on the way that they use or see Facebook and if there are any outstanding correlations between variables also to see if there are any significant differences between male and female participants and how they use Facebook. Since the advancement of the Internet, Social Media has become a huge part to play in everyday life. Communication and Information sharing through different types of Social Media platforms is at its highest and more and more people are choosing to use these methods.
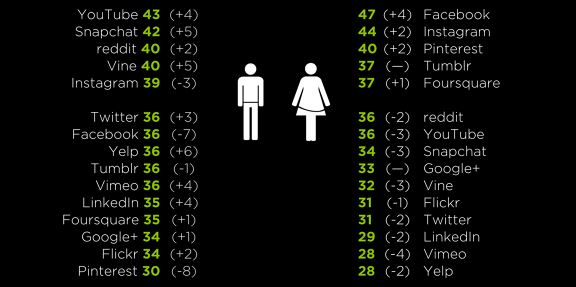
This marketing dissertation aims to use a method that will help draw out concise results on how different cultures portray themselves through Social Media. This dissertation will consist of taking a close look as to how Social Media is used by individuals and the Social Media platform that has been chosen is Facebook. The dissertation will involve a number of phases; designing the specific method to collect the data required, carrying out the method, extracting the results collected from the method, finishing off with analysis and conclusiveness of the results. The outcome of this project is to be able to clearly differentiate between cultural groups and the way information is shared through Facebook.
Dissertation Aims
- Gain an understanding between the use of Facebook among participants
- Focus on ethnic background with regards to Facebook and the differences
- Focus on the gender differences when using Facebook
- Analyse and draw up valid conclusions based on Gender, Age, and Degree type and Personal preference i.e. Privacy on Facebook
Dissertation Contents
1 – Introduction
Overall aim of the project
Problem being addressed by the project
Motivations and usefulness of the project
Aims of the project
2 – Literature Review
Privacy on Facebook
Posting content to Facebook
Facebook Activity
Gender differences on Facebook
Cultures and Facebook
3 – Methodology
Research Methods
Individual Interviews
Focus Groups
Questionnaires
Methodology Choice
Construction of questionnaire
Data capture plan
Time length
Potential Challenges
Participants
Data
4 – Methodology Analysis
Overview of data collection
Questionnaire Responses
Data capture
Implications
5 – Facebook Results Analysis
Introduction
Gender
Gender and Privacy
Levels of concern with privacy on Facebook
Concerns of posting content on Facebook
Self-Censoring on Facebook
Posting personal information to Facebook
Sharing personal preferences on Facebook
The type of information publicised on Facebook
Facebook Friends
Ethnic Groups
Purpose for using Facebook and account creation on Facebook
The laws and restrictions on Facebook in China
Publicising information to Facebook based on ethnic background
Privacy concerns based on ethnic background
How participants portray themselves on Facebook
Degree Scheme
Consideration of others
Untagging a photo on Facebook
Gender and Ethnic Background
Sharing phone numbers and email addresses on Facebook
What participants Facebook Friends can see
Selecting the audience on your Facebook account
6 – Conclusion
Highlights of the project
Data Analysis
Background research
Self-reflection
Data collection
Questions
Feedback
Lessons learned
Original Objectives
Final statement
Bibliography
Appendix
Questionnaire
View This Dissertation Here: Marketing Dissertation Cultural Differences in Information Sharing through Social Media
Other Relevant Blog Posts
Consumer Purchasing Behaviour Social Media
Example Marketing Dissertations
If you enjoyed reading this post on cultural and gender differences in information sharing through social media, I would be very grateful if you could help spread this knowledge by emailing this post to a friend, or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook. Thank you.

