Quality and Quality Management System at Barclays Group
Quality Management System at Barclays Group – The present business climate is characterised by fierce rivalry and constantly shifting client needs. A further factor driving competition is the proliferation of new technology, globalisation, and corporate consolidation (Bouranta et al., 2019). Many banking institutions are suffering economic issues because of the COVID-19 epidemic. Managers must examine their company processes in light of the negative macroeconomic climate to make investment decisions.
This report evaluates Barclays’ quality management procedures and investment decision processes (Kugbonu, 2020). Quality management trends are also examined in this paper, as well as how the QM system might be aligned with these trends. Barclays bank should incorporate these trends into its Quality Management (QM) to achieve a competitive edge in the business.
An Overview of the Situation
This bank has two divisions: Barclays International and Barclays UK. Its service subsidiary, Barclay’s execution services, supports these divisions. Over 83,000 people work for the bank, which has operations in 40 countries and employs approximately 83,500 people in its two primary markets, the United States and the UK (Diekola, 2016).
Personal banking, commercial banking, investment management, corporate banking, and internet banking are just some of Barclays’ many offerings. In addition to individual and small business banking, the bank also provides corporate and investment banking services.
TQM Principles at Barclays and its Significance TQM
Employee Engagement
The HR department’s TQM principles include employee involvement and open communication. Human capital is a key strategy for the bank in achieving its objectives (Salah, 2018). “We want to promote their health and well-being to empower and drive them to offer exceptional services” the business said in a statement.
To boost productivity, the company makes significant investments in the well-being, professional growth, and mental health of its workers. 83 per cent of the bank’s employees say they’re engaged, with 67 per cent of those surveyed responding (Nyamari, 2017).
According to employee surveys, between 74% and 78% of employees report having stress levels they can manage and a work-life balance they feel they have achieved (Parvadavardini et al., 2016). To foster a culture of innovation and creativity amongst its workers, the bank offers a variety of educational opportunities, including classes, workshops, and seminars.
Internal clients are just as crucial as external ones when it comes to a company’s success. Internal customers and external customers can both benefit from service firms’ efforts to improve the quality of the services they provide (Rafailidis et al., 2017). Human resource policies including organisational commitment, employee engagement and training are connected to optimal corporate performance and shareholder profitability. There are ways in which Barclays’ present HR policies can contribute to its long-term competitive advantage.
Communication
An annual poll of employee engagement is conducted by the corporation, allowing for two-way dialogue between top management and the workforce. Employees, consumers, investors, and stakeholders all have input in decision-making and strategy formation (Kugbonu, 2020). To help clients make well-informed financial decisions, the organisation says it is transparent about its financial offerings. The corporation engages stakeholders using surveys, social media, and other broadcast methods.
Using Kaplans and Nortons Balanced Scorecard, the company’s communication’s organisational impact may be measured (BSD). The BSD aims to improve the quality of life for both employees and the general public via better communication (Al Ghamdi et al., 2016). To create connections and satisfy consumers, Kaplan and Norton’s approach requires management to communicate. To boost performance and customer happiness, the leaders need to convey their priorities effectively.
Management
Nyamari (2017) emphasised the importance of leadership in achieving quality objectives in a business. To keep their teams focused on the pursuit of quality improvement, bank leaders instil a sense of urgency in them. Demonstrate a high level of leadership and management to lead the radical adjustments necessary for continuous improvement, Deming claims.
To increase productivity and revenues, transformational leadership may enhance the quality of the entire process (Diekola, 2016). Leadership at Barclays is responsible for establishing the bank’s long-term strategy and defining its basic principles. To help their employees achieve their goals, they are also directly involved.
Significance of TQM Principles at Barclays
An Ever-Evolving Process
This bank has a section dedicated to service and efficiency enhancement. The lean six sigma paradigm, which states that a corporation may enhance product/service quality by removing wastes along the value chain, is used by the company to accomplish continuous improvement (Bouranta et al., 2019).
Focusing on theory implies that proper precautions are taken to prevent errors and increase operational efficiency. The business says that it recycles risk-weighted assets to improve operational performance and keep costs in check while also maximising the efficient use of available resources.
To reduce inefficiencies caused by inefficient work methods, it has also used new technologies in the invoicing and documentation procedures (Salah, 2018). Banks may enhance their financial and non- financial performances as well as their operations related to supplying chain management by making investments in continuous improvement. The bank’s performance may be improved through operational efficiency and better customer service as a result of the continuous improvement projects.
Customer-Focus
For the bank, customer-focused service is a primary value proposition. Customers’ wants and connections are at the heart of all of the company’s actions and plans. Investment programmes can be adjusted to match the specific demands of each customer (Rafailidis et al., 2017). Access and tracking of investments are available online for clients. As a part of its financial education programme, the bank offers free telephone updates and money-mentoring services.
Barclays Bank also provides new goods and services to enhance the customer experience (Mahanga, 2016). For instance, consumers may save time by serving themselves and gaining access to the majority of the bank’s goods and services through the use of the bank’s mobile applications and online banking platform.
Customers from a variety of backgrounds may simply use the applications because of their basic design. In accounting and banking organisations, customer-centred services improve client happiness, customer loyalty, and customer retention levels (Parvadavardini et al., 2016).
These findings suggest that a company’s ability to retain customers may be improved by tailoring technology to match the demands of clients. In today’s highly competitive market, a company’s ability to retain and gain new customers is vital (Kugbonu, 2020).
According to the bank, a 32 per cent decrease in customer complaints may be attributed to the bank’s efforts to enhance its service delivery method. Customer service is a priority for the organisation, and it has taken the necessary steps to improve it.
The bank’s operations with reduced defect and waste creation can boost productivity and create cheaper expenses. Additionally, the bank may be able to maintain and grow its client base, resulting in greater financial success (Al Ghamdi et al., 2016). TQM’s societal advantages include customer happiness and brand approval in the marketplace.
To complement the bank’s quality plan, these TQM principles need to be adapted. Using the TQM principles, the bank may fulfil its strategic goals of diversification by implementing four proposals (Diekola, 2016).
TQM impacts competitive strategy creation and is a source of sustained competitive advantage, according to research (Nyamari, 2017). A competitive advantage may be gained through the use of the TQM paradigm, according to these studies. Using the 14 TQM principles, a firm may have a competitive edge, better financial performance, and better customer satisfaction.
This is confirmed by the company’s 2020 annual report, which notes that the improvement in customer satisfaction may be ascribed to the company’s quality measures (Mahanga, 2016). Because it concentrated on TQM principles, the bank’s financial results have improved.
The Importance of Total Quality Management Barclay’s Quality Management System (QMS)
Building a Quality Management System begins with understanding the current organisational environment, which includes things like structure and culture as well as a leadership style (Akanmu et al., 2020). Customer satisfaction was a key consideration in the development of Barclays’ quality management system.
EFQM is evident in the bank’s procedures, which have been scrutinized in depth by the bank’s auditors. To achieve excellence, the EFQM relies on five enablers and four outcomes (Carmona et al., 2016). Enablers are concerned with how a company accomplishes its work, whereas outcomes are concerned with the results it achieves. Results are generated through enabling factors, while enablers may be enhanced via the use of feedback from those results (Khan et al., 2017).
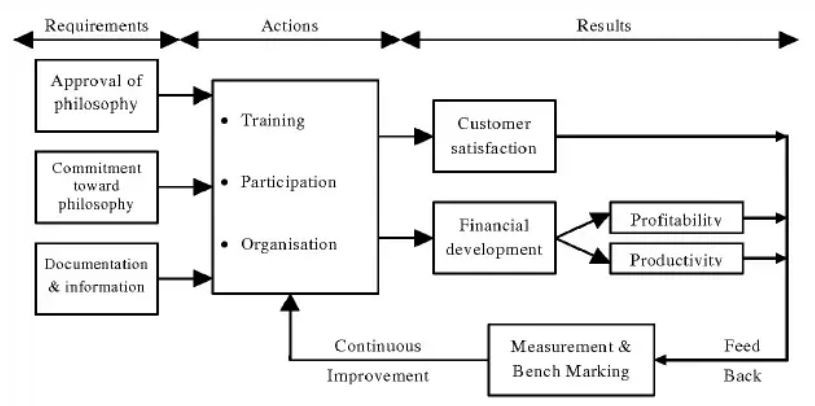
This methodology helps the company to examine its real condition according to European quality measures and determine its advantages and disadvantages in accomplishing goals (Harthy et al., 2020). Within the annual report, Barclays says it gathers and assess information on the 9 EFQM model criteria and employs the applicable improvement plan to boost each criterion’s performance. The bank’s planned quality management system (QMS) looks like this.
The EFQM model establishes the framework for QMS quality measurements to be focused on, as seen in the image above. It collects information on EFQM enablers, including employees, leadership, strategy, and products/services (Elrayeh, 2016). Customer satisfaction feedback is utilised as a quality indicator for the people criteria, whereas financial development data is employed as a metre for products and services (Waduu et al., 2019).
These quality criteria are a reflection of the leadership’s commitment to employee development, involvement, and the organization’s overall mission. Continuous improvement is possible because of this system’s design (Mahmood, 2020). The subsequent phase is to formulate quality policies, define roles and duties within the QMS, make a strategy for the management of risks and opportunities, and, as the last step, devise strategies for the regulation of change.
Elements of TQM
There are several fundamental QM components and building blocks, including ethics, integrity, trust, education, collaboration, leadership, and recognition. An employee’s code of ethics is a set of rules that he or she is expected to follow at all times while at work (Harthy et al., 2020) Customers both internal and external expect the bank to uphold a high standard of integrity.
Ethics and integrity lead to trust, which in turn determines the level of ownership and dedication to an organisation. Ethics and integrity are demonstrated through the bank’s CSR, which can be found in its society criteria in the EFQM (Odeny, 2016).
With so much face-to-face contact between customers and staff, the foundation of every successful business is solid training, collaboration, and strong leadership. TQM training helps employees acquire the skills and information they need to properly execute the concepts (Khan et al., 2017). For the bank to meet its quality goals, staff must work together as a team. Investments in quality assurance are a sign of the company’s dedication to quality management.
Quality Assessment Standards
An ISO 9001 certification indicates that the bank meets the quality standard. International quality assurance standard ISO 9001 offers precise QMS standards for the company’s leadership, planning, operating, assessment and improvement activities (Odeny, 2016). Such measurements are used by organisations to demonstrate their capacity to fulfil all applicable consumer and regulatory criteria for their products and services.
The TQM system helps banks achieve their strategic goals by satisfying the needs of their customers (Ishibashi et al., 2021). The QMS can assist the bank in achieving its strategic objectives by meeting the demands of all stakeholders. The QMS is linked to banks’ strategic goals by aligning it with stakeholder needs.
Quality Metrics for Stakeholders
The bank provides quality for all stakeholders by regularly reviewing ways to enhance metrics to satisfy their demands (Carmona et al., 2016). Various types of stakeholders’ data are gathered, including the following:
Customers
- Rates of digital involvement with clients
- Complaint scores are a measure of consumer satisfaction
- The number of bank workers who advocate working there
- Customers who would suggest the bank’s products and services to their friends and family members
- Monitoring the degree to which workers are aligned with the intended company culture is the goal of this indicator
Society
- The yearly carbon dioxide emissions
- Number of participants in the institution’s Life Skills programme; the bank hopes to increase financial capability and employability in the community
Investors
- The bank examines financial results such as revenues, market shares, operating expenses, and equity to determine how to provide attractive returns for investors (El Manzani et al., 2019). Measuring the operational costs aims to tighten budgets and increase productivity for the business.
Key Trends in Quality Management
Competition and increasing consumer expectations are the primary motivators of quality management. Stakeholder opinions of a company’s brand and overall quality/services are referred to as perceived quality (Bagur-Femenías et al., 2016). Intelligent quality management uses modern technology and smart systems to improve corporate operations, processes, and product quality (Kumar et al., 2018). The human-focus strategy leverages people to satisfy the company’s service offerings and stakeholder satisfaction.
These tendencies are important to consider since the example firm operates in a sectorof the economy that is highly competitive and marked by consistent market shifts (Barclay et al., 2017). A good example of a cloud-based technology user is the banking industry. Barclays has also adopted cloud technology to customise its clients’ digital experience to current technological advancements.
Companies that go out in front of the game or catch up quickly are more likely to have a leg up on the competition (Demir et al., 2021). That’s why it’s so important for a firm to be up to date on the latest trends to remain relevant in the marketplace.
Cloud computing, in keeping with current market demands, shows the company’s capacity to implement intelligent quality control systems (Hicks et al., 2019). Barclays also places a high value on its social duties, including reducing its impact on the environment and combating climate change. Perceived quality is directly linked to a brand’s image, regardless of its corporate social responsibility (Leung et al., 2021).
Many studies have shown that a company’s CSR policies have an impact on customer happiness and loyalty as well as its financial performance. Customers’ impressions of a company are shaped by their impressions of its perceived quality, which in turn shapes their loyalty to the brand.
Human-centeredness is seen in the bank’s culture of soliciting input from its stakeholders to enhance its business practices. Human-centred strategies lead to higher levels of employee loyalty and productivity (Nyanaro et al., 2018). There is a correlation between a company’s ability to compete in the long term and its ability to develop and retain its human resources.
Intelligent quality management systems, which monitor and forecast problems with minimum human interaction and allow real-time communication with stakeholders, can also help the bank achieve its quality targets at a cheap cost (Tahri, 2018). Barrington can use evidence-based methods to improve and make decisions.
Quality Management System Alignment Expectations with the Trends
These new trends will be easier to implement if the organisation has the right resources and competencies in place. For a smooth transfer, you need financial resources, skills, and a well-trained team behind you (Demir et al., 2021). In addition, the business may assist such adoptions by reconfiguring its approach well with current developments in Quality Management. Incorporating QM trends into new strategic goals allows it to realign its overall strategy.
Having a strategy aligned with current trends will ensure that resources are allocated accordingly (Maina, 2017). These new trends may be adopted by empowering and encouraging individuals to accept the organisational transformation. Employees can be retrained or reskilled to help them adapt to the new environment.
New quality initiatives may face difficulties in gaining stakeholder buy-in. QM often fails because of CEO disinterest. Even if intermediate management is successful, success is unlikely without upper management’s commitment (Hicks et al., 2019). Risk aversion and a lack of understanding of the relevance of Quality Management have contributed to the lack of CEO support for a created project.
Investment may be discouraged by the high cost of implementing and maintaining QM trends, particularly intelligent quality management systems (Desjardins, 2020). The administration may be reluctant to continue funding the project if it does not show a favourable return on investment.
Conclusion
The quality management procedure at Barclays has been modified to incorporate the concepts of customer orientation, leadership, continuous improvement, communication, and staff involvement (Tahri, 2018). Customers’ loyalty and retention are enhanced by the bank’s TQM, which adds favourably to its financial performance and productivity.
Investors should seriously examine TQM as an alternative source of competitive advantage in light of the competing demands in the business sector (Hudnurkar et al., 2019). For the firm to reach its greatest potential, it needs its entire support. They should help the organisation financially and with leadership skills to drive and sustain positive transformation.
References
Akanmu, M.D., Hassan, M.G. and Bahaudin, A.Y.B., 2020. A preliminary analysis modeling of the relationship between quality management practices and sustainable performance. Quality Management Journal, 27(1), pp.37-61.
Al Ghamdi, A.A., Aziz, F.S.B.A., Yusoff, R.Z. and bin Mustafa, M., 2016. The Moderating Role of knowledge management on the relationship between employees’ commitment and total quality management: A Study on the public healthcare sector in Saudi Arabia. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(4), pp.790-797.
Bagur-Femenías, L., Perramon, J. and Barquero, J.D., 2016. Does intensive social network management lead to positive effects in quality practices?. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 27(11-12), pp.1246-1260.
Barclay, L.J., Bashshur, M.R. and Fortin, M., 2017. Motivated cognition and fairness: Insights, integration, and creating a path forward. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102(6), p.867.
Bouranta, N., Psomas, E., Suárez-Barraza, M.F. and Jaca, C., 2019. The key factors of total quality management in the service sector: a cross-cultural study. Benchmarking: An International Journal.
Carmona-Márquez, F.J., Leal-Millán, A.G., Vázquez-Sánchez, A.E., Leal-Rodríguez, A.L. and Eldridge, S., 2016. TQM and business success: Do all the TQM drivers have the same relevance? An empirical study in Spanish firms. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
Demir, A., Budur, T., Omer, H.M. and Heshmati, A., 2021. Links between knowledge management and organisational sustainability: does the ISO 9001 certification have an effect?. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, pp.1-14.
Desjardins, C. and Fortin, M., 2020. From split seconds to lifetimes: the temporal fabric of fairness dynamics. In Handbook on the Temporal Dynamics of Organizational Behavior. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Diekola, A.M., 2016. The moderating effect of environmental regulation and policy on the relationship between total quality management (TQM) and organizational performance in the Malaysian food and beverage companies (Doctoral dissertation, Universiti Utara Malaysia).
El Manzani, Y., Sidmou, M.L. and Cegarra, J.J., 2019. Does IS0 9001 quality management system support product innovation? An analysis from the sociotechnical systems theory. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
Elrayeh, G.A.E., 2016. Causes of non-Implementation of ISO 9001: 2008 Quality Management System in Sudanese banks (Doctoral dissertation, Sudan University of Science and Technology).
Harthy, A.M., Aslam, N., Al Saqri, S.M., Arni, S., Nair, S. and Karim, A.M., 2020. The Use of Structural Equation Model (SEM) to Evaluate the Effectiveness of ISO 9001 Quality Management System (QMS) on the Performance of Oil and Gas Drilling Companies. International Journal of Business and Management, 15(1).
Hicks, A., Barclay, J., Chilvers, J., Armijos, M.T., Oven, K., Simmons, P. and Haklay, M., 2019. Global mapping of citizen science projects for disaster risk reduction. Frontiers in Earth Science, p.226.
Hudnurkar, M., Ambekar, S. and Bhattacharya, S., 2019. Empirical analysis of Six Sigma project capability deficiency and its impact on project success. The TQM Journal.
Ishibashi, F., Kobayashi, K., Kawakami, T., Tanaka, R., Sugihara, K. and Baba, S., 2021. Quality management system for screening esophagogastroduodenoscopy improves detection of Helicobacter pylori-negative interval gastric cancer. Endoscopy International Open, 9(12), pp.E1900-E1908.
Khan, M.I., Khan, K.I., Sheeraz, M. and Mahmood, S., 2017. Impact of quality management practices on the performance of manufacturing sectors. Abasyn Journal of Social Science, pp.1-17.
Kugbonu, J.M., 2020. Total quality management practices and customer retention at Unity Rural Bank, Ghana (Doctoral dissertation, University of Cape Coast).
Kumar, V. and Sharma, R.R.K., 2018. Leadership styles and their relationship with TQM focus for Indian firms: An empirical investigation. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management.
Leung, C.Y., Barclay, J.E., Botz, C.T., Hanf, N.K., Jasperson, J.C., Kirby, K.N., Mull, C.J., Shinde, A.S. and Vogl, M.M., 2021. Change management: A framework for measuring and implementing organisational change. Management in Healthcare, 5(4), pp.299-316.
Mahanga, M.Y., 2016. The impact of customer care on customer attraction and retantion in Tanzania: a case study of Barclays bank Dar es salaam (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Dodoma).
Mahmood, W., 2020. The influence of total quality management, school climate and job satisfaction on school performance in government schools in Pakistan (Doctoral dissertation, Universiti Utara Malaysia).
Maina, J., 2017. Effects of Environmental Factors on Performance: A Case of Barclays Bank (Doctoral dissertation, United States International University-Africa).
Nyamari, P.M., 2017. Effect of total quality management practices on operational performance of commercial banks in Mombasa County, Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi).
Nyanaro, N.N. and Bett, S., 2018. Influence of strategic planning on performance of commercial banks in Kenya: Case of Barclays Bank of Kenya. International Academic Journal of Human Resource and Business Administration, 3(2), pp.235-255.
Odeny, B.A., 2016. The Influence of service quality on performance of Barclays Bank of Kenya Limited (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi).
Parvadavardini, S., Vivek, N. and Devadasan, S.R., 2016. Impact of quality management practices on quality performance and financial performance: evidence from Indian manufacturing companies. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 27(5-6), pp.507-530.
Rafailidis, A., Trivellas, P. and Polychroniou, P., 2017. The mediating role of quality on the relationship between cultural ambidexterity and innovation performance. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 28(9-10), pp.1134-1148.
Salah, S.A., 2018. Total quality management practices and performance of commercial banks in Garissa County, Kenya. International Academic Journal of Human Resource and Business Administration, 3(1), pp.52-67.
Tahri, A., 2018. Consumer based brand equity in retail banking industry: a cross analysis of a domestic and global bank operating in the UK (HSBC vs Barclays) (Doctoral dissertation, Anglia Ruskin University).
Waduu, D.W. and Rugami, M., 2019. Total Quality Management Practices and Performance of Commercial Banks in Kilifi Town, Kenya. International Journal of Current Aspects, 3(VI), pp.1-15.
Relevant Quality Management System Posts
MBA Dissertation Dissertations
Strategic Quality Dissertation
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to quality management system at Barclays Group in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.