Financial Management Concepts and Their Application – Focus on Activity Based Costing
The process or the technique of determining the cost of a service or a product is called cost accounting system. The costs are assigned to cost objects only after collected and classified by the cost accounting system. It is used to estimate the cost involved in developing, designing, purchasing, producing, servicing, distributing and selling different services or products. The heart of cost accounting system is cost allocation and Activity Based Costing (ABC) can be considered as a type of cost allocation. In this essay, different approaches to cost allocation and activity based costing are described. The methods used for cost allocation and activity based costing. Activity based costing received focus when attempts were made to improve the methods of cost allocation. The different ways of implementing cost allocation and ABC approaches in for- profit organizations (corporations) and in real world business enterprises (Akyol and Bayhan, 2005).
Like any other approach involved in business activities cost allocation and activity based costing also have their strengths and weaknesses and a detailed study of these factors ensures the successful implement of these account systems. The costs associated with these account practices are very crucial and they must be considered very carefully in terms of benefits earned by implementing cost allocation and ABC approaches. These systems could be viable only if they are implemented efficiently and they gain efficiency and profitability.
The study further discusses about the main objectives of cost allocation and ABC approaches and the relation between various factors like resources, costs, cost drivers and activities. It also signifies the methods of cost allocation like direct allocation, step- down allocation and reciprocal allocation. Activity Based Costing (ABC) has been discussed elaborately for allocating costs to services or products and the different steps involved in the process. The recommendations made in this paper could be used by the users as guideline for charging the fixed and variable costs of one department to other department of the organization (Peter B.B. 1997).
Cost Allocations and Activity Based Costing (ABC)
The process or the technique of determining the cost of a service or a product is called cost accounting system. The costs are assigned to cost objects only after collected and classified by the cost accounting system. Therefore, the process by which some costs or groups of costs are linked with one or more cost objectives, like divisions, departments and products, is basically called cost allocation. Generally, cost objectives which are responsible for causing costs are allocated costs. Costs are linked with cost objectives by selecting appropriate cost drivers. A cost driver is called cost allocation base when it is used for allocating cost. Major costs are allocated, such as cost of raw material for a manufacturing firm or cost of building material for a construction firm are allocated to departments, projects and jobs on an item basis by utilizing cost drivers like quintals of raw materials or tonnes of building materials consumed where as other costs, considering individually, may not be so significant that they need to be allocated individually (Peter B.B. 1997).
They are pooled and then they are allocated together. Hence, a cost pool may be defined as a set of single costs allocated to cost objectives utilizing an individual cost driver. For instance cost of everything which are measured in square meters and occupy space like rent of the building, cost of utilities and janitorial services can be pooled together for allocation. Or all the operating expenses of the registrar’s office of a university can be pooled together and it can be allocated to the respective colleges as per the quantity of students enrolled with each department.
In brief, the costs caused by the same factor should be given in the same pool. Those factors are called cost driver. In practice, many terms are used by the companies for describing cost allocation. Such terms can be attributing, trace, allocate, reallocate, distribute, assign, burden, load, reapportion, apportion, etc. For describing allocation of costs to cost objectives any of the above mentioned terms could be utilized interchangeably (Cooper and Kaplan, 1988).
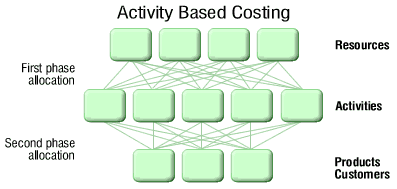
The type of methodology used to measure the cost and the performance of different activities, cost objects and resources is known as the Activity Based Costing (ABC) and it is one of the most important aspects of the organizations engaged in specially manufacturing or service. For the traditional accounting systems based on costs it is regarded as the best alternative epitome of the accounting system. Presently, the organizations engaged in manufacturing and service sector are forced by the global competition for increasing productivity and reducing associated costs and for this they have to be greatly automated and more integrated and flexible.
They can only sustain in this competitive world if they adapt to a mechanism of calculating costs which is more than accurate. Activity based costing is regarded as the best alternative of the traditional methods of cost accounting and it is used now a days for assigning costs, using various cost drivers, to activities, further for allocating costs to products on the basis of use of these products for these activities. ABC is used to reduce the stake of distortion and gives information about costs accurately by utilizing various activities as cost drivers (Akyol , and Bayhan, 2005).
According to activity based costing, the total cost of a product or a service is calculated by adding the cost of all value added activities involved in the production with the cost of the raw material. It can be explained in different words as the activity based costing method is used to link the cost of activities performed for usages of the resources of the organization (inputs) to the final outputs like services, customers and above all products. Purchasing, engineering, technology, design, quality control and production are prime activities required for a product and each of these activities use resources of various types, for example the working hours of the supervisors or engineers. The activities performed by these resources are measured by cost drivers (Peter B.B. 1997).
The costs that can be associated directly to the product, as per traditional systems of cost accounting, are labor and direct materials. As per activity based accounting system, there are two types of activities – a. value added activities and b. non- value added activities and generally non- value added activities are reduced for improving the performance. ABC is quite useful in calculating costs accurately but it involves extra effort and expenditure for collecting the information required for cost analysis. These difficulties which come across in designing a cost model can be reduced by using a tool properly designed (Peter B.B. 1997).
Cost allocation and ABC approaches in for-profit firms (corporations)
Cost allocation and cost accounting systems are very crucial for any organization and in case of for- profit firms it become vital for the financial managers to be very careful about all the financial consequences within the organization or outside the organization. No any organization can make profit if their managers don’t consider the cost allocation factor seriously. The objective of cost allocation is to;
- compute valuations of assets and income and
- justify costs and attain reimbursement
For computing valuations of assets and income, cost allocation is done to projects and products for measuring costs of goods sold and inventory. The purpose of these allocations is to provide frequent service to financial accounting. Managers often use the resulting costs for performance appraisal, motivating employees and other managers and planning.
Most of the time prices depend on costs and an accepted bid is to be justified subsequently. This could be understood by citing the example of Boreal which is the largest company of Canada supplying scientific equipments and apparatuses to schools. It has a diverse line of products, hence the process of costing product is comparatively complex. Recently, a combination of several costing techniques for determining the cost of inventory and making allocations was used. The company has many departments for production and for each commodity the activities of production vary from each other. Three guidelines were kept in mind for making allocations:
- Fair allocation
- Verifiable and rational allocation
- Its impact must be known on people using or working with it
.The current input costs and changes in operating costs were reflected by the revised Inventory Costing System. These information were used for making cost allocations(Akyol , and Bayhan, 2005).
ABC approach proved to be beneficial for the company for following reasons:
- Recalculating selling price
- Calculating selling prices of different offers including mixture of products or quantity of products
- Deciding about whether to produce a product in- house or to purchase from market
- Calculating taxes
- Calculating profits
The importance of allocations is quite visible in the above example and furthermore it has many intended uses (Peter B.B. 1997).
Different ways of implementing Cost allocation and ABC approaches in real-world business enterprises
In real world business enterprise the ways of implementing cost allocation and ABC approaches are different and they depend on the need and requirement of the enterprise. There is no any defined way of implementing cost allocation and ABC approaches in the real world business enterprise which can be implemented universally. The following example of a transmission company (PJM) illustrates the understanding of the ways of cost allocation. It classifies various methods of transmission cost allocation used in the United States and the world. The following five categories don’t stand alone but give a general idea about cost allocation (Cooper and Kaplan, 1988).
The costs of transmission can be allocated:
- Between generation and load
- Amount of usage
- Generation or peak consumption
- Basis of flow
- Basis of monetary impact
These allocations can be implemented by following methods:
Direct Method – As per the name suggests, by direct method, any other service departments are ignored when the cost is being allocated for the department directly to the operating (revenue – producing) department. It can be explained as, the services provided by facilities management to personnel may be ignored as it is a kind of support provided to personnel by facilities management. The cost allocated for facilities management depend on the square meters area used by the production department only. Similarly, the costs of personnel department are allocated to the production department only depending on the number of workers working with it (Akyol , and Bayhan, 2005).
Step- Down Method – It is recognized in the step – down method that the activities of different services are supported by activities of other service departments including production department also. In this method, the allocations are made in a sequence. It starts with the service department providing the greatest service in terms of costs to the largest number of other service departments. It ends with the service department providing the least service in terms of costs to the least number of other service departments. For example, in this method, the cost would be allocated to facilities management before it is allocated to personnel department because facilities management provides more support to the personnel as compared to the support provided by personnel to the facilities management. Once the costs are allocated to facilities management, no costs are allocated back to personnel even if some services are provided to the facilities management by the personnel. The costs of personnel allocated to the production department include the costs allocated by facilities management for personnel (Peter B.B. 1997).
Reciprocal Allocation Method – In the reciprocal allocation method the cost is allocated after recognizing that the services are provided to each other by different service department including production department. This method is considered as the most ideal and correct method due to its ability to cost the relationship between different departments completely for the cost allocation to the service departments.
For example, as shown in the above methods, in this method the costs of the facilities management are allocated to the personnel department and the costs of the personnel department are allocated to the facilities management department before they are allocated to the department of production. The costs of the services are allocated first which are provided between two service departments (Cooper and Kaplan, 1988).
It can be noted that the costs can be affected greatly by the method of allocation selected. For example, using a direct method of allocation can make an operation more expensive in comparison to other methods like step- down method or reciprocal allocation method. Similarly, finishing can be an expensive operation if non- direct method of cost allocation is used.
Analysis of ABC’s potential strengths and weaknesses within a company
A number of indirect overhead manufacturing costs can be turned into direct costs by using activity based costing systems. Direct costs mean the costs recognized specially with selected cost objectives. ABC enables managers to select appropriate cost drivers and activities to recognize numerous overhead manufacturing costs and cost objectives as simply as traditional accounting systems enable them to recognize direct material costs and direct labor costs.
ABC based systems classify most of the costs as direct cost which is not the case in traditional accounting systems. ABC system gives great confidence to managers as far as costs of services and products are concerned because they have more information (Özbayrak, Akgün and Türker, 2004).
On the other hand ABC systems are comparatively complex and expensive to traditional systems and it is not affordable by all companies. ABC systems are used by both manufacturing and service industries because of the following reasons:
- Margins are shrinking due to increasing competition and companies ought to know their accurate margins for their services or products
- Increasing complexity in the businesses has diversified products, services and even customers. The consumption of resources of the company also varies across customers and products
- Introduction of new technologies are increasing the share of indirect costs and presently in manufacturing world indirect costs are more important. Automated machines are replacing direct labors.
- Life cycles of products are shortened by changing technology and it has become difficult for companies to spare time for making price or cost adjustments once error are found
The costs of developing and operating systems are reduced substantially by the use of computers (Cooper and Kaplan, 1988).
Steps needed to ensure a successful implementation of ABC
An Activity based costing system requires four steps for its designing and successful implementation:
- Determination of key activities, cost objectives and resources to be used is to be known and analyzed by the managers. They also need to identify the output measures (cost drivers) for each activity and resource.
- A map is needed to be drawn by managers which should be based on process and be able to represent the activity – flow and resources supporting cost objects
- The third step requires collection of operating data and cost
The last and final step requires calculation and interpretation of the new information based on ABC. A computer is required for the last step because of the complexity involved in activity based costing systems. The process of using ABC information for improvement of operations is known as Activity Based Management (Cooper and Kaplan, 1988).
The associated costs & benefits
The three main purposes of cost allocation are:
- Motivation
- Measurement of asset and income
- Justification of cost or cost- plus contracts
By considering the above mentioned benefits of ABC system the cost involved in its implementation becomes regardless as the system enables to make calculations accurately which is very important for determining the profits. The cost involved in the implementation of ABC system is so high that it is beyond the reach of small enterprise but the benefits are so important that big enterprise cannot manage without it (Özbayrak, Akgün and Türker, 2004).
Efficiency gains
Activity concepts are utilized by Activity Based Costing systems which enables it to link successfully the costs of product to the knowledge of production. For example, what is the process of producing a product or service, what is the time required for the performance of an activity, and finally what is the amount of money required for performing the activity? These all questions are answered efficiently by ABC system of accounting (Cooper and Kaplan, 1988).
Profitability implications
ABC systems are used for inventory of products and determination of income. This is done by using the physical units or method of relative-sale-value. It is becoming popular gradually due to its ability of assigning costs to various activities within an organization, tracing costs to products or services depending on cost drivers measuring the reasons for the costs of the activity. It helps in improving profitability of the organization by quality improvement and waste elimination.
It also increases profitability by focusing on quality, reducing inventory, making production cycle short and by flexibly using human resources and operating assets. As these factors are non- value added activities and it results in reducing operating costs and increasing profitability (Özbayrak, Akgün and Türker, 2004).
Conclusion and recommendations
The traditional systems of accounting are gradually becoming irrelevant in the present competitive business world when things are changing very fast. Traditional costing system under costs the product because they are not able to consider the hidden costs involved in production. ABC systems enable to cost accurately and hence to calculate profitability accurately. Sometimes traditional methods over cost the product due to their incapability of calculating costs accurately and the price of the product become incompatible in the competitive market.
In nut shell it can be said that businesses have to adopt the Cost Allocation and ABC systems to sustain in the competitive business world. It is an expensive practice but keeping its utilities in mind the cost becomes negligible because it enables businesses to calculate profitability accurately without which business has no meaning.
References
Akyol D.E., Tuncel G. and Bayhan M. 2005. “World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology”, Vol 3
Peter B.B. 1997. “Activity-Based Costing An Emerging Foundation for Performance Management”
Özbayrak M., Akgün M. and Türker A.K., 2004. “Activity-based cost estimation in a push/pull advanced manufacturing system,” International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 87, pp; 49–65
Cooper R., and Kaplan R.S. 1988. “How cost accounting distorts product costs,” Management Accounting, vol. 69, pp; 20–27
Kim G., Park C.S. and Kaiser M.J. 1997. “Pricing investment and production activities for an advanced manufacturing system,” Engineering Economist, vol. 42, no. 4, pp; 303-324
Gunasekaran A. and Sarhadi M. 1998. “Implementation of activity-based costing in manufacturing,” International Journal of Production Economics, vol.56-57, pp; 231-242
Ben-Arieh D. and Qian L.2003. “Activity-based cost management for design and development stage,” International Journal of Production Economics, vol.83, pp; 169-183
Lewis R.J. 1995. “Activity-based models for cost management systems,” Quorum Books, Westport, CT
Köker U. 2003. “Activity-based costing: Implementation in a sanitaryware company,” M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Industrial Engineering, University of Dokuz Eylül
Cokins G. 1997. “Activity-based cost management making it works,” McGraw-Hill. Inc.
Elliot, B. & Jamie E. 2004. “Financial accounting and reporting”, Prentice Hall, London, p. 3,
Goodyear and Earnest L.1993. “Principles of Accountancy”, Goodyear-Marshall Publishing Co., p.7
Singh W. and Ramnik. AICPA committee on Terminology. Accounting Terminology Bulletin No. 1 Review and Résumé.
Friedlob, Thomas G. & Plewa, Franklin J.1996. “Understanding balance sheets,” pp; 1
Carruthers, Bruce G., & Espeland, W. N.1991. “Accounting for Rationality: Double-Entry Bookkeeping and the Rhetoric of Economic Rationality”, American Journal of Sociology, Vol. 97, No. 1, pp: 40-41,44 46,