Brexit and The European Union
The year 2016 is going to be remembered for long years to go for the historical term “Brexit” that meant Britain exiting from European Union. This possibility aroused since 2007, under the article 50 of treaty of European Union under European states. The final exit decision took place in June 2016 under the referendum where the votes in favor of leaving EU were 51.9%. Though there were many reasons that lead to Brexit, but some of the economic aspects are worth mentioning.
The people of Britain wanted self government system back that had existed hundreds of years ago. There were certain reasons that British citizens wanted to exit from European Union and thus held general elections to get rid of the government. The main issue behind this exit decision was that being under European Union made Britain feel like being ruled by a foreign power where they have no rights of taking their own decisions (Dagnis Jensen and Snaith, 2016). One of the key economic impacts is that Britain had been facing trade barriers under the European Union that could be well managed by this exit decision. The market prices for EU are much higher than the world market prices and that has been affecting the economy of Britain in terms that the country involved in producing more of the products that were worst and less of those it was best in producing. Furthermore this also led the customers to pay higher amounts due to tariff and trade policies of EU and thus the exit from it was the much significant decision (Weiler, 2015).
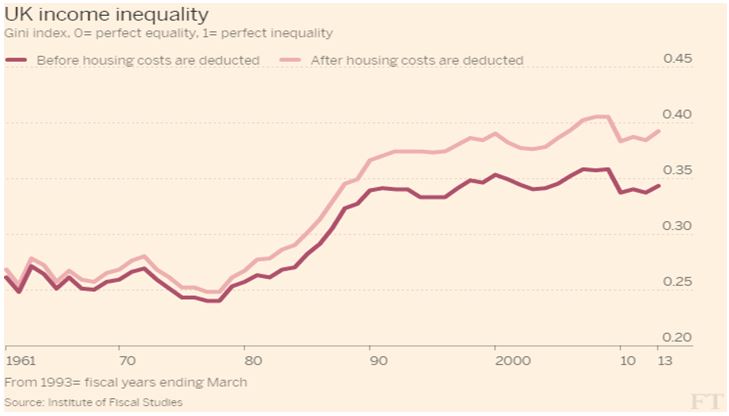
Figure 1: Income inequality in UK
Figure 1 above describes one of the key economic reasons why Britain chose to leave the European Union is inequality in Income. It describes that though the overall European economy was doing well and had larger benefits and shares, still these benefits are not being felt by population in an even and justified manner.
After this exit, the barriers both tariff and non- tariff on trade could be removed from UK that were being imposed upon by EU till now. This will in turn benefit the customers and raise their living standards due to larger decrease in import prices. In contrast to this there are certain arguments against this decision of exit of Britain from EU (Boulanger and Philippidis, 2015). The key UK producers could determine that the prices that they would get in the free market would be different they used to get inside EU, in fact it would be lesser.
The products they sell outside are no different they sell inside EU but the protection of customs union premium provided by EU would be lost that would affect these producers. It can be concluded from the above statements that the customers would be the people in benefit from this exit decision and also those firms that are willing to buy the products at the world prices, whereas the producers within the union would be disheartened as they would have to lose their share of premium under the European Union. There are further arguments describing that after Brexit, UK may opt to trade under World Trade Organization (WTO) policies (Dhingra, Ottaviano, Sampson and Reenen, 2016). In such case it would not be able to get benefits of tariff free trade as it had, being under the membership of EU. Further this would also support the companies in halting the inflow of less skilled workers from EU. It would also provide relaxation in migration policies and provide ease to the highly skilled immigrants from EU and non- EU countries to work.
Another economic perspective towards this decision of Britain is the gain that the customers and firms would have while balancing the resources and allotting them to industries which are efficient and removing from that are less or inefficient (Oliver, 2016). The key economists of the country also estimate the gain in trade of Britain after this exit to 4% rise in GDP. Despite of this there are arguments with risks of loss in job and foreign direct investment. It has been argued that the foreign investments would be reduced but it has neglected the fact that FDI is just due to better returns in foreign capital and thus the countries can invest, just the sectors would change where there are free trade policies. Further with the investments in new sectors, the jobs will also arise in those, thereby fulfilling the loss of jobs created in the European Union protected sectors.
After the result of referendum on Britain exiting EU, many economic, political and financial impacts are most likely to be seen. It would be not new and surprising to know that after the decision, London is to face a number of financial issues that would further have an impact on overall economy of the country (MacShane, 2015). The very first impact that could be seen in London would be loss of jobs. In making the decision of exit from the European Union, the future of the city of London has been one of the key concerns.
The government of London will have to involve in effective strategy formulation to manage the possible financial and economic effects of this referendum. There are possibilities of clash in market with the change in currency values that will have an overall impact over London and its market. However, it is being argued that the city will remain as the key financial centre of the world and will be successful in managing the “Brexit” situation as it has already undergone such crisis situations during the world wars too (Barrett and et.al, 2015). While London was within the European Union, it had been enjoying the title of world’s important financial centers which is now likely to get affected by various policies and regulatory aspects.
There are number of companies that have already announced that with this decision of exiting from the European Union, they would be moving their employees out of London. J.P. Morgan also in this context said that it would be relocating around 4000 of its employees out of Europe. There are many banks outside the nation, like from US that have been trading in London as to escape from the restrictions that exist outside the European markets (Swinbank, 2016).
Similarly with the news of Brexit, Deutsche Bank also said that it is going to relocate its employees. The effects of Brexit decision are to be studied for London, as it is not only the financial centre of Europe but has topped the list of world’s best city to do business due to fewer barriers. Therefore this decision will definitely be affecting its title and the overall business economy. There are many businesses dominating in London like banking, mortgage brokers, real estate firms and the overall financial industry that is much likely to be affected with this referendum. Furthermore, there are cities in EU like Paris, Frankfurt, Amsterdam and Dublin that would be most benefited with this change and have prospective of becoming the new London for the world markets (Springford and Whyte, 2014). The overall situation can also be understood with the concept of Passporting with context to EU that describes that all the European Union based financial institutions can sell their services without getting the approval of regulator.
Further after the Brexit, every such firm would need to get regulatory approvals on local basis that is a key factor driving their decision to move their business out of London. Passporting is one of the key features that have led to the success of the banking industry with EU nations due to ease of cross border transactions and investments. After this decision, London would need to develop a new regulator that would not only require cost but would also involve authentication to develop trust among the various business firms to rely upon (Danielsson, James, Valenzuela and Zer, 2014). Further authorization of new regulators would also take considerable time to establish itself that will bring a change in the overall financial and economic status for London for its exiting decision from the European Union.
There are various risks associated with all the firms working in UK that would be affected with the decision of Britain exiting the European Union. The city like London have been the financial hub of UK that would be the most affected area after the referendum result in Britain exiting the European Union. Most of the firms that are likely to be affected by this decision would be the financial institutions, banks, real estate firms, etc. Before this referendum’s result, there are many companies that have already announced their changing business plans and strategies for their firms in Britain, if the country was to leave EU (Virasami, 2016). Most of the banks and companies are already in need to leave UK, and shift their operations to other country under the European Union states. This is due to the ease of business and lesser trade barriers and tariffs under the European Union policies that might have a larger economic and financial impact on every business.
Companies like Vodafone have warned UK that it would be shifting its headquarters from London to some other country if it exited the European Union. On the same track, one of the biggest lenders of Britain, Lloyd’s Banking group had made plans to sell out the shares of the taxpayers that are prone to be affected once the decision is being made. Furthermore companies like Virgin group have plans to cut down around 3000 jobs with the Brexit. Apart from this there are companies that have put their future export and investment plans on hold after the final decision being announced. Also the lending firms have cut short their property purchasing in London (Helm, 2016).
The risks associated with the decision of Britain exiting EU are not countable or measurable but could be understood in terms of financial and economic losses. Large numbers of firms are to face the loss in market share and affect the availability of jobs as well as personnel. The risks for the companies also involve lowered profits for the firms and control over the personnel. This decision is also likely to affect the political and social scenario of the country. Immigration is a problem that is being faced by the nation and more than half of the population is immigrant of some other place. However, with this decision, the immigrants would move again in search of better opportunities and jobs. Also as studied above, after exiting EU, the regulatory approvals would become more difficult and troublesome for the firms to continue in the same way as it existed before. Though this decision is favorable for customers and buyers but producers and investors are the ones that are most likely to be affected (Williams, 2016).
The final decision of Britain exiting the European Union would completely reform the financial services industry of the country. It has been evident that the city of London had been the largest centre of financial investments in the complete European Union and has been attracting large number of banks and financial service providers. It will thus be required for UK to formulate effective polices and plans to retain all its existing business firms and develop regulatory authorities to manage the approvals after exiting from EU (Palmer, 2016).
With the step towards taking the decision of exit from EU, there are many threats and risks associated with Brexit. There are many uncertainties and challenges that British firms have to possibly face after this decision. After this, UK will have to lose its membership of European Economic Area, European Free Trade association etc. The committee handling risks have been analyzing potential risks and have coordinating to make sure they have better plans to deal with short term and long term risks. There are companies like British gas Insurance that may not have direct potential impact through Brexit but if their parent company Centrica is impacted then they might also face risks for which they need proper mitigation approaches.
Communication
There are companies that are getting involved in improving communication among the different managerial levels. They have plans to ensure each and every message and update over the Brexit issue and let all the people all over the organization know about it on consistent basis (MacShane, 2015).
Stakeholders
The risk managers have also plans to keep their stakeholders assured and manage them cautiously. They too are to be updated timely about their losses or gains with shareholdings in the firms. Also the stakeholders must have clarity of situation and the company must not make fake promises to them.
Change Management
This is one of the most important aspects to be considered in risk management approach. The firms and its employees must be completely ready to accept the possible changes that are to occur if UK leaves EU. There would be lot of changes in legal, economic and political scenario that would have an overall impact on the complete economy. These impacts could be seen not only for few days or months but for years (Springford and Whyte, 2014). Thus the managers must be aware about the next steps they are to take up for managing the changed scenario of UK after leaving the membership of EU.
There are possibilities that if Britain exits EU, there will be migration, attrition, policy changes and loss of shareholders that will change the complete business scenario for the country. Also the legal and authorizing business approvals would have to be established in a completely new form that would need the firms that intent to continue with UK, to manage the upcoming challenges.
There are many firms that have announced that they would be shifting their operations partially or fully to some other country that is an EU member state (Oliver, 2016). This is an approach that many firms have adopted in order to ensure that they do not face extreme losses or trade barriers.
It has been evident that EU states have benefits of free trade with least barriers but this would not be the situation if UK exits this membership. It has been a fact that the jobs in Britain are being safeguarded by EU as it has been a market centre for more than 500 million customers and it is Britain whose membership with EU has been the most attracting factor for FDI.
However this decision of Britain had led the firms to hire new people called effective troubleshooters that would help them in dealing with such situation after Brexit. The demand of lawyers, consultants, financial advisors and experts in the country has increased with this news flowing around for the sake of safeguarding the business from the post effects of this decision (Weiler, 2015). The organizations have started working on the reframing of trade agreements, funding problems and their solutions, staffing concerns, trade barriers and plans to deal with them. Though EU had provided free trade but the extreme interference of its policies in trade and profit sharing for the firms had made Britain to take such decision. Thus there are many firms that are still in support of this decision of Brexit, despite of the fact that this can be a potential threat to their business and funding requirements.
References
Barrett, A. and et.al, 2015. Scoping the possible economic implications of Brexit on Ireland. ESRI Research Series, 48.
Boulanger, P. and Philippidis, G., 2015. The End of a Romance? A Note on the Quantitative Impacts of a ‘Brexit’ from the European Union. Journal of Agricultural Economics, 66(3), pp.832-842.
Dagnis Jensen, M. and Snaith, H., 2016. When politics prevails: the political economy of a Brexit. Journal of European Public Policy, pp.1-9.
Danielsson, J., James, K., Valenzuela, M. and Zer, I., 2014. Model risk and the implications for risk management, macroprudential policy, and financial regulations. VoxEU. org, 8.
Dhingra, S., Ottaviano, G.I., Sampson, T. and Reenen, J.V., 2016. The consequences of Brexit for UK trade and living standards.
Helm, T., 2016. Brexit donor’s company spells out risks of quitting EU.
MacShane, D., 2015. Brexit: How Britain Will Leave Europe. IB Tauris.
Oliver, T., 2016. European and international views of Brexit. Journal of European Public Policy, pp.1-8.
Palmer, K., 2016. How businesses have reacted to Brexit so far.
Springford, J. and Whyte, P., 2014. The consequences of Brexit for the City of London. Centre for European Reform.
Swinbank, A., 2016. Brexit or Bremain? Future Options for UK Agricultural Policy and the CAP. EuroChoices, 15(2), pp.5-10.
Virasami, J.H., 2016. Brexit referendum: in-out, in-out, shake it all about.ROAR, 9, p.2016.
Weiler, J.H., 2015. Brexit: No Happy Endings; The EJIL Annual Foreword; EJIL on your iPad!!!; Vital Statistics; ICON. S Conference. European journal of international law= Journal europeen de droit international, 26(1), pp.1-7.
Williams, S., 2016. Brexit: What Companies Should Do Next.
Related Blog Post
Dissertation BREXIT UK Construction Labour Market
European Migrant Crisis Asylum
European Union Regional Economics
I hope you enjoyed reading this post on Brexit and how it affects future trading arrangements for the UK and EU. There are many other titles available in the business management dissertation collection that should be of interest to business students and academic professionals. There are many dissertation titles that relate to other aspects of business such as strategy, leadership, international business, mergers and acquisitions to name a few. It took a lot of effort to write this post and I would be grateful if you could share this post via Facebook and Twitter. Feel free to add your thoughts in the comments section. Thank you.