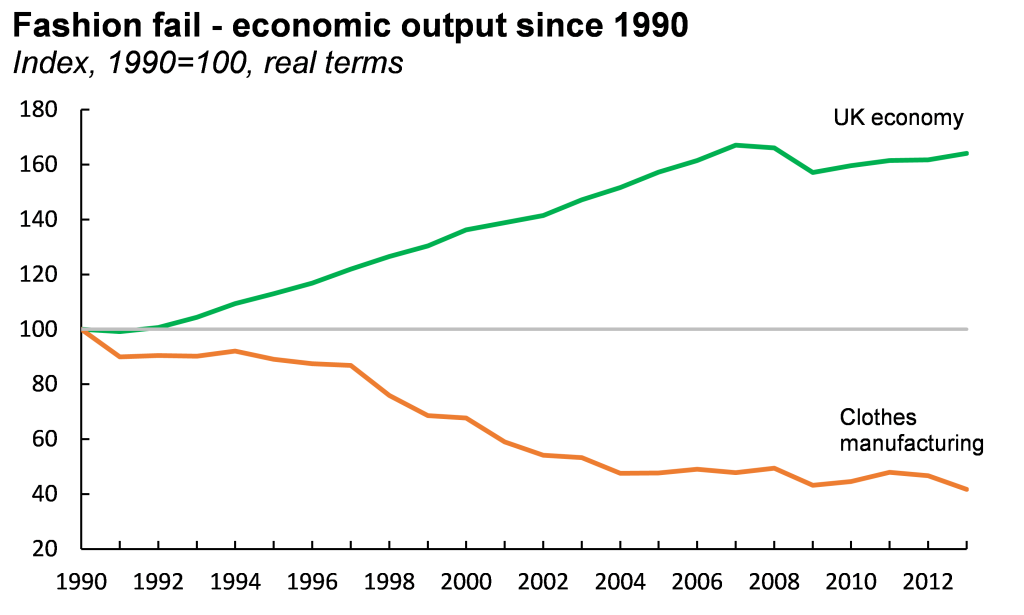
The Contribution Of Art And Fashion Industry To The National (UK) Economy
According to a report released by the British Research Council (2014), the fashion industry in Britain contributes £26 billion to the country’s economy. This is a 22 % increase from the contribution made in 2009 which added up to £21 billion. The report was released by the council during the London Fashion Week. These statistics intrigue various questions relating to the contribution of art and fashion to the economy of the country. Although art and fashion have been part of the UK’s culture for many years, their impact on a country’s economy has not been greatly considered over the years. However, in the recent years, the expansion of the global market has greatly impacted the art arena, which has further impacted the economy either positively or negatively.
Research Question: Is the art and fashion industry influential enough in the economy to attract both local and foreign investments in the long-term?
Purpose and objectives
The aim of the research is to assess the impact of the arts and the fashion industry on the economy in the UK in accordance to information revealed by the Arts Council and the British Fashion Council. The main objectives of the research will be to review and collate existing research relating to the economic impact of the arts and the fashion industry in the country. The other objective is to understand the measures and methodologies put in place for assessing the effect of creative industries, programmes, facilities and projects. Assessing the quality and comprehensiveness of the existing evidence is another objective of the research. The research also aims at informing the future agenda for effective research within the sector. It will also include evidence-founded making of policies by the Arts Council and Fashion Council. Identifying fundamental research needs that will assist in improving the research’s robustness is another scope of the research. The proposal will also include a practical resource to help the parties working in the sector.
Theoretical Framework
The Keynesian theory states that the production of goods and services by the businesses is influenced by consumers’ ability to spend. The twenty first century has experienced changes in issues relating to increase in consumer spending, hence the increase in production of various goods and services. The arts and fashion industry has not been alienated from this impact. The rapid expansion of economies that started taking place in the late twentieth century through to the twenty first century has been of great impact globally. It is believed that one of the most impacted is the arts and fashion industry.
The consumption, investment, government and net exports characterize the Keynesian theory. This research will analyse these concepts in relation to the oil and arts industry, and how they have affected the economy in the UK. The research is also sensitive to the impact of the local fashion industry on its economy. It is relevant to assess whether the most impact is evident from exports or products bought by the local consumers. The household disposable income and the general GDP are of relevance to this research. It is relevant to understand the past scenarios relating to the industry and steps that have been taken to heighten the industry to the current position. As evidently put by Keynes, the increase in consumer spending will increase the production of goods. Consequently, a decrease in consumer spending will also decrease production in the industry. It is relevant to understand the individual contribution of the various sectors in an economy. This will allow the relevant parties to make decisions relating to the present and the future of the industry in question. In this case, it will be identified whether the impact on the economy, if any, is long-term. It is relevant to understand whether it can attract investors.
Empirical / Contextual Literature Review
The Art Council England and British Fashion Council provide various reports that reveal the financial/economic impact of the arts and the fashion industry in the economy. Other economic related sources will be assessed in order to realize the share of the industry on the overall economic figure. Research will be carried out in some areas such as the Research Department of the Arts Council. The research may also include email, telephone or postal inquiries from the Culture, Media and sports Department. Other sources include the Arts Council of Northern Ireland, Arts Council of Wales, the Scottish Arts Council, among others.
After the research process, a small number of studies will be gotten, read and evaluated with the use of Draft Standards for Reporting on Statistics (Hutton, 2001). Sharp and Benefield (2001) insist that the NFER (National Foundation for educational Research) guidelines to be incorporated in order to present quality research. The researcher will also scrutinize the references in order to assess whether there are other potential materials that are relevant. The review will mainly cover research that is done in the United Kingdom. This will include England, Wales and Scotland. In order to make the research more comprehensive, statistics relating to other countries such as the USA and Australia will be included.
The research will include literature which has information concentrating on the economic contribution of the fashion and arts sectors. The inclusion of the arts sector will also lead to the inclusion of some aspects of the creative industry and culture in the UK. The research will briefly give the social-economic aspect of the industry, due to issues relating to the employment arena and the general impact of the people’s livelihoods. The materials considered are gauged on various levels. They include a widened geographical spread, diversified study foci, diversified methodologies and approaches, research quality and studies target groups. Other issues relate to issues addressed or policy area, research date in question, impact on the sector and best evidence presentation. Blake (2000) reminds researchers that a review does not have to reproduce in detail the articulated claims relating to the economic impact of the fashion or arts industry. This is because they have been covered adequately in these resources. The researchers only need to find the information relevant to their topic and then integrate it accordingly in order to answer their research question (Jermyn, 2001).
The study design that will be used is the historical approach. Babin et al (2012) states that the historical approach is one in which information is collected by reviewing the historical data presented by older reports or valid sources of information. This empirical report should not be altered. In order to place more emphasis on historical study, Gillham (2008 state that historical method is something that exceeds simple data-gathering. It involves analyzing, and confirming the information retrieved from these sources by engaging other research methods. For example, interviews will be included in this research method. The true meaning of data collected should be reported from the point of view of the objectives and the basic assumption of the project under way. The facts obtained may be accurate expressions of central tendency, deviation or correlation; but the report is not research unless discussion of these data is carried up to the level of adequate interpretation. Data must be subjected to the thinking process in terms of ordering reasoning. The design also saves on time. The researchers are also able to present factual information from the target resources using cheaper means.
Methodology
The main method will include reviewing the past and current statistical information available on the materials. However, interviews will be integrated in the research method. The interviews will be done in order to verify some of the unclear data, or place emphasis on the available information. Such technique will be used for target people who may provide more information other than the information available in the report. Since interviews are one-on-one, the researcher is able to read other forms of communication such as body language, hesitations, amongst others (Creswell, 2003). Interviews also limit the time that the information will reach the researcher.
Additionally, questionnaires will be handed to people who will not find time for interviews. It can be passed through emails or other communication channels agreed upon by the researcher and the target person. As indicated earlier, it is used to verify information that is unclear or that which has not been updated. VanderStoep & Johnston (2009) indicate that the measurement quality is highly dependent on the reliability of the instrument used to collect data. In order to follow this statement, the researcher will pre-test the questionnaires being used. Validity entails, whether the spirit of the questionnaires is in accordance with the purpose of the research. In order to confirm validity, selected questionnaires will be given to respondents in order to pre-test data collection. Once the questionnaires are returned, they will enable the accurate assessment of the validity of research instruments. The questions in the questionnaires will also be used to conduct the oral interviews. The questionnaires will not be included in the final analysis.
References
Babin, B. J., Carr, J. C., Griffin, M., & Zikmund, W. G. 2012,. Business research methods (9th ed.). Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.
Blake Stevenson Limited, 2000, “The Role of the Arts in Regeneration”, Scottish Executive Central Research Unit, Edinburgh.
Creswell, J. W. 2003, Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications
Gillham, B. 2008, Small-scale social survey methods: Real world research. London: Continuum International Pub. Group.
Hutton, L, 2001, Draft Standards for Reporting on Statistics, The Arts Council of England. 110
Jermyn, H, 2001, The Arts and Social Exclusion: A review prepared for the Arts Council of England, The Arts Council of England, Londo.
Sharp, C and Benefield, P, 2001, Literature Reviews Course Notes, NFER, unpublished.
VanderStoep, S. W., & Johnston, D. D. 2009, Research methods for everyday life: Blending qualitative and quantitative approaches. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
