Portfolio Analysis and Evaluation of Project Management Techniques
Portfolio Analysis Project Management Techniques – The techniques and tools are significant for the effective project management. The Project management techniques are specifically making the overall management of the projects effective and easier. The project managers, software of project management and a range of project management aspect take their own techniques and tools that are likely to helpful for the projects to save the maximum cost and time. The problems can also occur in the project management. These problems related to the management of the project must be tackling effectively to complete the project on time without any delay.
All of the problems and their substitute solutions set up some fundamentals of change in the project that must acclimatize. Projects are normally conventional to perform these changes the management of the project is responsible for the successful project completion. So, it is also important to know that each project is exclusive as far as the problems that occur are concern and the main concern and resources needed for it, the atmosphere in which it functions, and the attitude of the project manager to control and guide all of the activities of project. As a result, the project should be planned to fit all of the requirements of organization and the nature of the problems that needed to solve under the project (Seyr, 2019).
The techniques and tools to be used in the project also depends on the organizational structure because depending on the nature of the organization the project available project personnel, resource, priorities, laws, and other possibility can also change. Implementing effective techniques of the project management reduce the disturbance of regular resources of the business activities by placing under a particular control on all technologies, skills required to understand the project. The analysis of the portfolio level is a significant part of organization a derivatives portfolio. The common types of portfolio analysis are Aggregated Cash Flows, Total Value, Value-at-Risk, Stress testing and Risk Sensitivity all of which are essential for effective portfolio analysis.
Portfolio analysis in project management is a quantitative method for optimal portfolio selection that can balance between make the most of the return and reduce the risk in various indecisive environments. In this report there would be discussion regarding the tools and techniques and problems solving method in the project management (Rever, 2007).
Critical Analysis of Tools and Techniques
The project management is very demanding task with numerous complex responsibilities. Opportunely, there are a lot of techniques and tools are available to assist in tasks accomplishment and responsibilities execution. For example, some may need a computer with effective software, while in some of the projects the tasks can be management manually. Project managers need to select some techniques and tools for the project management that are more compatible with the style of management. There are some of the tools and techniques that can be applied to project management to optimize the overall operations of the project (Jackline, 2014).
PERT Technique in Portfolio Analysis
The PERT (Program evaluation and review technique) is a control and planning tool used for controlling and defining the responsibilities necessary for the accomplishment of project and is essential in effective portfolio analysis. The PERT charts are frequently used in the project. The PERT is an extensively used technique for development and large-scale projects coordination (Calmèset. al., 2021). PERT is essentially a tool for the management control and planning. It is also known as road map for particular project or program in which the most important elements have been totally recognized, with their equivalent interrelations’. The PERT charts are time and again built for a lot of projects, the end date is permanent and service provider has flexibility of front-end. A fundamental PERT-style planning element is to recognize the critical activities.
Following are the main steps involve in PERT planning:
- Identify the particular milestones and activities. The activities are the project tasks. The milestones in the process are events that mark the start and the ending of all activities.
- Verify the appropriate activities sequence. This step is connected with above one because the sequence of activity is obvious for tasks. Other responsibilities in the project may need some investigation to resolve the accurate classification in which they must be carried out.
- Build network diagram. By using the information of the activity sequence, a diagram of the network can be drawn that show the series of parallel and successive activities. Arrowed lines in the diagram stand for activities and circles symbolize the milestones of the project.
- Estimation time essential for all activities. Weeks are normally used time unit for completion of the activity, but reliable time unit can be utilized. An individual feature of PERT is its aptitude to handle the uncertainty in completion of the activity. For all activities, the model typically comprises three-time approximation:
- Most likely time – time of the completion with highest possibility.
- Optimistic time – shortest time to complete an activity.
- Pessimistic time – longest time for an activity to complete.
Critical Path Technique
The critical path method is project management technique for planning of all process and defines the non-critical and critical tasks of the project with objective of preventing problems of time-frame and bottlenecks of project process. The critical path method is preferably suitable for projects that consist of a lot of activities that interrelate in a composite manner(Cohen, 2018).
For critical path method implementation, there are quite a few steps that are as follows:
- Define all of the required tasks and organize them in ordered list.
- Create a diagram or flowchart that shows the relationship between different tasks in the project.
- Recognize the non-critical and critical relationships between tasks.
- Find out the projected execution or completion time for all tasks.
- Devise or Locate substitute for the critical paths
In case a critical path is not right away obvious, it might be helpful to find out 4 timelines for all activities (Ray, 2018):
- EF – Earliest Finish time
- LF – Latest Finish time
- ES – Earliest Start time
- LS – Latest Start time
All of these times can measure by using the anticipated time for the activities. The initial finish and start times of activity are find out by forward working via network and formative the earliest time on which an activity can finish and start bearing in mind its predecessor actions.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts in the projects are used to demonstrate task assignments of the calendar time in months, weeks and days. This tool utilizes graphic representations to demonstrate elapsed, start and finishing point times of task in any project. The Gantt charts are perfect for progress tracking in the project management. The days required to finish a particular task that achieve a goal can compared with the number that is either estimated or planned. The real workdays, from the start to conclude, are plotted underneath the days scheduled. In the project processes this information help in targeting the possible failure points or timeline slippage. These are also said to be the chats that serve as an important tool of budgeting and can demonstrate dollars spent versus dollars owed (Rever, 2007).
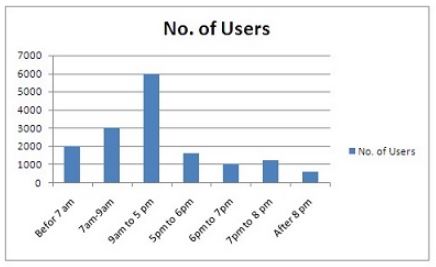
Histogram
Histograms are said to be the tool that use in the project to make understanding of the project easier for the project team. It is a kind of bar charts that portray variables distribution over time. This symbolizes the mean distribution. This diagram can use different shapes depending on the distribution condition. The histogram used to calculate something next to time for example the histogram plotted with variable on the x-axis and time on the y-axis. The following histogram demonstrates company’s website number of hits on different day time. The x-axis demonstrates number of customers or users active on website and time of the day shows on the y-axis (Osha. gov, 2018).
Flowcharts
In the project management flowcharts are rational steps in logical organization to achieve an objective. By using the geometrical objects, the flow charts are drawn as rhombus, rectangular, activities, parallelogram, and points of decision in a process. Flowcharting in the project can also help to identify where on project the problems of quality occur and how problems take place. There are said to be a lot of tools are there today in market for flow charts drawing, for example MS Visio, project management software etc. These techniques and tools are supportive for project manager to incorporate it and understand it and convey a quality product (Hiles, Andrew, 2010).
Problem Solving
In the project management a lot of problems also raise and it is important to deal with them effectively in order to minimize the risk of project failure and complete the project on time. There are some of the problems solving techniques to be used by the project management for better project accomplishment (Nowak et. al., 2020)
1. Brainstorming. The first step in the project management to solve any problems is brainstorming, it means to think of different possibilities and techniques of solving the problems and what impact does selecting particular techniques would have on project.
2. Patience. It is also very important to not get panic over the problems, in some of the cases the project management become frustrates with the problems occurring that can further increase the tension. It is essential for the project management team to be patient at the time problem occur. A patient approach would also help keep away from any error that further increase the problem additional issues would also raise.
3. Apollo Root Cause Analysis. This is said to be the technique in the project management that acknowledge that the majority of the outcomes have numerous causes, and find out actions and conditions that might contribute to problem occurs.
3. Data collection. By collecting more information related to the problems and way of its solution, project team members can develop more appropriate response.
4. Consider the effect anticipated solutions for the problems in the project may have as a whole on project.
5. Pareto Analysis. It is the generalized economy rule that 80 percent of the outcomes are get through 20 percent of work. It can also say that 80 percent of problems are caused by just 20 percent of root causes. Pareto was an economist who first comes up with this rule and the analysis produce a table of incidence of every cause and plot it on a bar representing cumulative total(Bragg, 2003).
6. Process evaluation. Some of the Problems in the project management can be approach by dividing the systems into segment that can be investigate for the problem source.
7. Fishbone diagrams. These diagrams look like a fish skeletal structure and chart causes to recognize effects while defect analysis. There are different questions are there used to build Fishbone diagram cause and effect based on whether question related to the problem deals with services. By imagine all cause and connected effect; managers can easily recognize the problems source.
Risk Management in Portfolio Analysis
The risk management objective is to make certain security never redirect the attempt from the established goals of the business. It is also said to be the process that comprise the recognition, prioritization and assessment of risk to manage the impact probability. Here are some of the risk management techniques to use in the project management (Clarizen, 2018).
Identification
The reorganization is the initial process idea that is to describe and uncover risks that might affect the project outcome. The major question to ask here is the reason behind the lack goal specification and thinking of risk is misperception. Recognizing a problem and discussing it is key to risk management process beginning(Allan, 2002).
Qualitative Risk Portfolio Analysis
The Qualifying risks an analysis is the method that is used to quality any risk that can occur during the project under this method involves making a list of the potential risks, with ranking them. For risks assessing from qualitative aspect following are some actions to be used (Clarizen, 2018):
- Probability and matrix and impact assessment: Rating and analyzing risks using possibility and its impact on like schedule, performance and cost.
- Risk categorization: Risks grouping by general root causes to build up effective reaction.
- Risk urgency: The risk ranking from the matrix probability mutual with importance can help place priorities of these risks.
- Expert judgment: Expert opinion from people in field or with alike experience project can also help in the accomplishment of the project.
Quantitative Risk Portfolio Analysis
These are said to be the methods that deal with definitive probabilistic and measuring techniques of project management. The major risk is risk of money losing and qualitative systems cannot be use to count the overall cost of the project. The following are some of the ways that can be used to minimize the risk associated with the project (Rever, 2007):
- Schedule and Cost risk analysis: Cost scheduling and estimates are used as values of input that are randomly selected for the iteration.
- Expected Monetary Value analysis: Measuring the average scenarios outcome that may or may not occur.
- Probability distributions: It can be used in the simulation and modeling to correspond to the values uncertainty in things like the task labor and costs.
- Analysis of Sensitivity: This is very simple method to find out how the risk is affects the project of any organization.
There are a huge number of methods to “count” the project risk throughout the process analysis. Once measurement has happened, the planning final stages have to begin.
Conflict Management
Smooth/Accommodate Conflict Management
The accommodate conflict management emphases agreement areas rather than difference areas; giving way one’s position to others needs to preserve relationships and harmony between the project team (Jackline, 2014).”
This method also is acquainted with the professional relationships’ importance towards the success of project. As far as the long-term projects are concern, strengthening and persevering becomes very important for the project team. Nevertheless, the members of the project team are continually emphasized on differences, on the project making more of the progress becomes very complicated (Rever, 2007).
Agreement areas to give emphasis to will also vary based on the situation. It can also be said that the project shared commitment and impacts of disagreement on others team members. The project management also needs to position agreement areas that surfaced throughout the project stages. Effectively using accommodating and smoothing requires considerate of the conflict between parties. For instance, are parties really distress about a project work being late. As a project manager, it is very important for successful accomplish the project to eliminate any kind off risk from the project (Rever, 2007).
Quality Management
The quality assurance process is connected with the nonstop analysis and development of process. Before this all levels of the quality must be verified, it is very important to have correct data; as there is an old saying, “garbage in, garbage out.” For that reason, the project team have to conduct a methodical analysis of measurement system to authenticate the integrity and accuracy of system of measurement and data. There are said to be a lot of components of the good measurement system (Clarizen, 2018):
- Precision – data is measuring precisely that is supposed to calculate
- Reproducibility – unlike appraisers same measuring item get the similar outcome
- Accuracy – the true value reflected by the data the property to be measured
- Repeatability – following measurements by same evaluator have to be the same
Effort and time have to be made by the project team and project manager to make sure the credibility and accuracy of the system of measurement. The future decisions credibility depends on vital step of the quality assurance. The overall process analysis is said to be the quality assurance key aspect. This process analysis also comprises all of the topics of value-added analysis and root-cause analysis.
Many of the project managers are well-known with the root-cause analysis, in particular use of fishbone diagram or cause and effect. This is very important to know that there is root-cause analysis is to take in five main categories: methods, people, measurement system, materials, machines, and setting when inspecting the sources of the problems occur in the project management. This is also very easy to focus on the greater part of improvement corrective and efforts measures on people. After all, administration decides on the procedures, methods, processes and materials so be confident about the investigation of the root causes in all of the above categories (Jackline, 2014).
Conclusion
Summing up the discussion it can be said that it is important to know that each project is exclusive as far as the problems that occur are concern and the main concern and resources needed for it. Implementing effective techniques of the project management reduce the disturbance of regular resources of the business activities by placing under a particular control on all technologies. PERT is essentially a tool for the management control and planning. It is also known as road map for particular project or program in which the most important elements have been totally recognized, with their equivalent interrelations.
The critical path method is preferably suitable for projects that consist of a lot of activities that interrelate in a composite manner. The Gantt charts are perfect for progress tracking in the project management. The days required to finish a particular task that achieve a goal can compared with the number that is either estimated or planned. The histogram used to calculate something next to time for case in point the histogram plot with variable on the x-axis and time on the y-axis. There are some of the problems solving techniques to be used by the project management for better project accomplishment. Some of the Problems in the project management can be approach by dividing the systems into segment that can be investigate for the problem source. Rating and analyzing risks using possibility and its impact on like schedule, performance and cost.
References
Allan, A. (2002). Innovation Management: Strategies, Implementation, and Profits. Oxford University Press.
Bragg, S. M. (2003). Essentials of Payroll: Management and Accounting. John Wiley & Sons.
Calmès, Christian, and Raymond Théoret. “Portfolio analysis of big US banks’ performance: the fee business lines factor.” Journal of Banking Regulation 22, no. 2 (2021): 112-132.
Clarizen, T. (2018, February 19). What Are Some Good Risk Management Techniques?
Cohen, E. (2018, April 18). How to Use the Critical Path Method for Complete Beginners.
Hiles, Andrew. (2010). The Definitive Handbook of Business Continuity Management. John Wiley & Sons.
Jackline. (2014). Quality Management Tools and Techniques.
Nowak, M., Mierzwiak, R., Wojciechowski, H., & Delcea, C. (2020). Grey portfolio analysis method. Grey Systems: Theory and Application.
Osha. gov. (2018). Process Safety Management Guidelines for Compliance.
Ray, S. (2018). Understanding Critical Path in Project Management.
Rever, H. (2007). Quality in project management–a practical look at chapter 8 of the PMBOK® guide.
Seyr, B. F. (2019). Portfolio Analysis in the Field of Strategic Knowledge Management. GAZDASÁG ÉS TÁRSADALOM, 2018(3–4), 54-66.
Portfolio Analysis Relevant Links
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to Portfolio Analysis and Evaluation of Project Management Techniques] in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.