The Importance of Recruiting
At the heart of every Human Resource Management (HRM) practice is a deep-seated concern regarding how human capital can be managed to derive the best results for any organization. One of the most critical functions and processes in HR is recruitment and selection. The importance of Human Capital and the impact it portends for companies and business organizations cannot be understated – it is the most crucial asset in every organization. As such, it follows that the mechanisms and procedures employed by organizations in recruiting talent among its ranks are an accurate presentation of how an organization intends to implement its mission and achieve its vision.
This paper examines the importance of this process in recruitment and selection, especially in the modern work environment. It does this by evaluating the standard frameworks of recruitment and selection before it explores the common trends as practiced in the modern era. It then examines the challenges faced by HR professionals within this context and concludes by highlighting some recommendations to address these challenges.
Recruitment and Selection – Getting it Right
The importance of the recruitment process in any organization is evident – recruiters ensure that an organization succeeds in achieving its goals and objectives by availing the best candidates whose competence and skills make them the best suited for the job. In this sense, recruiters are the filters that select the most appropriate candidates for organizational success. In the modern business environment—one that is continually evolving—the need to hire individuals who are knowledgeable, loyal, adaptable, dependable and skilled has become even stronger. As such, the recruitment and selection process is one of the core responsibilities of Human Resources (HR) in most organizations. This is because it is widely regarded as a process that fundamentally affects the potential for revenue growth and hence the profit margins of any profit-driven organization in comparison to other tasks like leadership development, onboarding, retention and talent management (Bhatia, 2013).
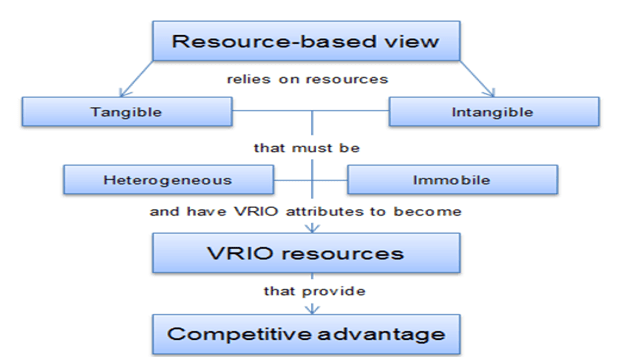
The theoretical framework under which this topic will be discussed in this paper is based on two theories – the human capital theory and Resource-Based View theory (RBV). The human capital theory contends that humans are the most important asset of any organization and that their market skills are a form of capital which essentially makes humans a type of investment (Buta, 2015). This point of view is critical especially in developing an understanding of the incentives as well as the structure of earnings and wages. The Resource-Based View theory is premised on the notion that an organization can develop a competitive advantage by creating a human resource capital which is unique to its organizational demands and which cannot be imitated by other organizations (Rothaermel, 2012). The representation is a graphic representation of the Resource-Based View theory framework.
In this paper, the task is to position the recruitment and selection process as a pivotal component of organizational success.
The Recruitment and Selection Process
Human talent is without a doubt, one of the most sought-after commodities in the 21st century workplace. Therefore, the process of searching, isolating and recruiting these talents is at the heart and soul of all organizations. Within the professional realm of Human Resources, recruitment is defined as the ‘process of searching out and attracting qualified job applicants’ (The Strategic Importance of Recruitment, 2012). Naturally, this begins with identifying the position that needs to be filled and ends when an adequate number of candidates have submitted their application forms or resumes. The strategic plan of the organization dictates the identification of job openings. In some instances, these needs can arise unexpectedly due to factors such as terminations, natural attrition, or resignations.
Once the need for hiring has been identified, the next step is to select an appropriate method that will facilitate an effective recruitment process. Some organizations prefer to recruit from within while others prefer to widen their selection pools by going outside the organization’s talent pool. Each of these methods has their advantages and disadvantages. For example, when an organization hires from within, it enhances the morale, commitment, and performance of its employees. However, when a company’s existing pool of talent does not meet the required standards, it is common for such companies to search outside. Studies show that most entry-level jobs are mostly filled by candidates sourced externally (The Strategic Importance of Recruitment, 2012). Because of the advances in technology that inform HR processes, online recruitment is increasingly becoming a popular strategy for getting external talents. Job fairs and co-operative education programs are equally powerful recruitment methods.
Once the recruitment process had ended, the next step selection involves choosing the most suitable candidate from the pool of recruiting. Methods of selection usually vary from one organization to the other depending on their demands and culture. Regardless, this process is usually complex and involves a lot of decision making. The structure of the selection process typically depends on a lot of things such as the urgency, number of potential candidates, and so on. Irrespective of the structure of the selection process, the main objectives of selection tests are: (a) prediction, (b) diagnosis, and; (c) situational behavioral assessments. (Opayemi & Oyesola, 2013).
The Selection Process
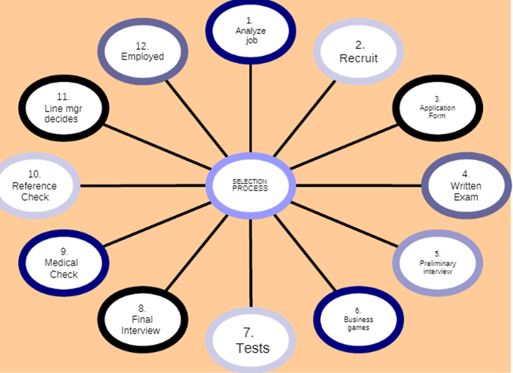
The overall selection process can be made up of several stages. This is exemplified in the diagram shown below. It is, however, instructive to understand that the steps in a selection process vary depending on many factors that will be discussed herein.
According to Alsabbah and Ibrahim (2013), Kamran, Dawood, and Hilal (2015), the structure of the selection process differs from one organization to the other and mostly depends on a company’s needs. In most cases, however, the selection process comprises several stages which are:
Evaluation – the evaluation stage entails applicants submitting their applications usually in application forms. The information contained in these forms include the name of the candidate, age, education, experience, expected salary, hobbies, and references, etc. the applicants who apply are the called shortlisted candidates.
Preliminary interview – in this stage, the shortlisted candidates are invited for the interview. Their personal interests, career goals, objectives for applying, and general attitudes are evaluated. Those who meet the basic standards proceed to the next stage.
Selection tests – in this stage, the candidates are subjected to written examinations. Different types of selection tests can be used depending on the nature of the job, responsibilities, and the number of applicants. Some of the typical selection tests are intelligence, personality, attitude, interest and professional examinations. Qualification and skills are also assessed in this stage. The goal is to select candidates who meet the minimum requirements.
Selection interview – this interview usually is more comprehensive compared to the preliminary interview. In this stage of the selection process, the candidates are subjected to face-to-face interactions where critical aspects such as speech delivery, intelligence, motivation, and the capacity to understand a problem are evaluated. The candidates are interviewed on questions directly related to the job to gauge their suitability. These interviews can be structured, semi-structured or unstructured.
Reference check – this is a background information check usually done to confirm the information provided by the candidates are true.
Decision-making – this is usually the final step in which candidates who have succeeded in the above steps are presented with appointment letters. These letters contain information on job description, salary, benefits, accountability, authority, and etcetera.
Validity and Credibility of Selection Tests
The validity and credibility of the selection tests go a long way in determining the caliber of employees that will be hired. The overall goal is to hire employees who are the best fit in relation to the job and for this reason, it is imperative that the selection tests are rigorously analyzed using up-to-date credibility tests. In this regard, the reliability of selection tests can be examined using three different methods (Opayemi & Oyesola, 2013):
- Over time – the outcome should be the same throughout the testing period.
- Across different sample – the outcome from a group of employees ought to be the same during the testing period.
- Across different rates – this test compares the results from two (or more) independent raters. A consistent rating throughout the testing period indicates that the selection test is reliable.
Similarly, validity tests simply evaluate the correctness of the selection test. The practice is that the candidates who emerge with the best results should be able to perform equally as well in real working environments. In other words, validity tests measure job relatedness. The commonly used validity tests are: (a) content validity, (b) concurrent validity, (c) predictive validity, and; (d) construct validity (Bertua, Anderson, & Salgado, 2005). The details of these validity tests are beyond the scope of this discussion and therefore will not be discussed herein.
The Importance of Recruitment and Selection
Since a comprehensive summary of the recruitment and selection process has been provided in the preceding paragraphs, this paper now focuses on the importance of the recruiting and selection process. As such, the proceeding analysis will categorize the four significant implications for the recruitment and selection process into (i) costs, (ii) retention, (iii) productivity and loyalty, and; (iv) legal issues.
Cost
A common perception among HR professionals is that a lot of money and effort goes into managing employees and this sometimes leads into a situation where organizations end up over-staffing or understaffing for its organizational needs. Logically when the number of employees in a department is higher relative to the need for which they were employed, then the company will incur higher operational costs in maintaining such as department (Ekwoaba, Ikeije, & Ufoma, 2015). In the long run, this will diminish the earnings of the company. Conversely, when an organization understaffs a department such that critical positions are left unattended, then the organization also faces the risks of incurring losses because of reduced revenue earnings.
Today the traditional concept of hiring where all job vacancies were treated equally has shifted to one that prioritizes the hiring process as one based on criticality. The objective of this style is to create a perfect balance between work that needs and employees in a manner that is sustainable for the company. Moreover, the process of recruitment and selection places more emphasis on selecting and ultimately hiring the candidates that exhibit the highest level of competency and skill (Ekwoaba et al., 2015). As such, the cost of hiring a candidate has a direct implication on the company, and as demonstrated in most cases, weak hiring mechanisms do place higher costs on the organization (Ekwoaba et al., 2015).
A weak hiring system is likely to bring in employees with high failure rates. This happens when a newly hired employee(s) voluntarily quits or is terminated within a few months irrespective of their performance. Weak hiring systems thus create a situation where a company can repeat the recruitment and selection process for the same position repeatedly – a scenario that increases the costs of damages incurred by the organization (Ekwoaba et al., 2015).
As technology continues to be more and more integrated into the management of businesses, most companies are going the extra mile into not only using job recruiters who possess business acumen, astute judgement, and an ability to foresee the crucial factors that will likely impact the growth requirements of their organizations, but also supplementing their effort with talent management and recruitment software to facilitate the efficacy of the recruitment and selection process (Bhatia, 2013). The use of tried and tested technology is thus a practical recommendation that is expected to reduce the inefficiencies of human-led recruitment and selection processes significantly.
Productivity and Loyalty
These two entities are linked – an employee who feels connected to the organization will work hard to help it achieve its objectives. On this basis, it is the recruiter’s responsibility to ensure that they get as much details from potential employees in order to sufficiently analyze their strengths and weaknesses. These pieces of information can be obtained from the candidates if the recruitment and selection process employs strategic mechanisms for achieving this goal. In general, loyal employees demonstrate a track record of competitiveness, innovation, excellence which cumulatively results in increasing the profitability of the business.
Legal Issues
The most common legal problem that arises from recruitment and selection processes is discrimination. Discriminatory practices often have dire consequences on the reputation of an organization and sometimes can also have financial implications. In the United States, for instance, the department of labor expressly prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, sex, political affiliation, and many other features that have often been used in facilitating discriminatory practices (Saez, 2018). In the end, recruiters are required to implement checks and balances to ensure that their methods are beyond reproach. For example, most organizations advertise only the basic requirements for the job. In recent years, the practice of listing language proficiencies and physical capabilities has gradually been phased out unless they are inherently vital in the position (Heneman III, Judge, & Kammeyer-Muller, 2015). Some organizations also encourage the recruitment and selection process to be run by more than one recruiter.
Practices and Trends in HR
The standard practice in many HR functions seems to be that most organizations do not concern themselves with the Return on Investment (ROI) especially when it comes to their human capital. Most organizations are guilty of perpetuating a recruitment process that does not measure the impact that its employees have on the organization. This is compounded by the trend among organizations not to document or make reports on their recruitment process. Furthermore, there is no accountability on HR regarding the opportunities missed and the costs incurred during the recruitment (Cascio, 2016). But as focus on strategic activities of HR departments continue to increase, an ever-increasing number of organizations are becoming more interested in calculating ROI on recruitments. As such, the activities and functions of HR are increasingly being assessed in a bid to quantify their outcomes and results.
Admittedly, calculating the ROI on recruitment is not an easy process because of the high numbers of variables involved. But since it portends critical implications on the activities of the whole organization, this is a task that every recruitment manager needs to perform. To achieve this, the manager should (Thoo & Kaliannan, 2013):
- Define the objectives of the recruitment in terms of the results that should be achieved.
- Devise mechanisms to accurately measure critical aspects of the recruitment process such as time of hire, the effectiveness of recruitment source, and the cost-of-hire.
- Establish a precise estimate of the costs of the recruitment project.
- Calculate the intangible and tangible benefits the organization will accrue, including payback period, from the recruitment.
- Ensure that recruitment managers are well trained.
The ability to evaluate the recruitment process in terms of ROI is fundamental for organizations that desire to strengthen their HR processes. This is because it significantly improves the recruitment function and develops a strategic human capital advantage for the company (Thoo & Kaliannan, 2013). But even as employers pile the pressure on HR professionals for increased accountability, experts contend that recruiting trends are getting more and more competitive. The main trends that have dominated talent acquisition in recent years are branding, repairing the potential candidate’s experience, maximizing talent analysis, and venturing into untapped sources (Maurer, 2016). They are also aware that getting real talent is getting harder and this is forcing companies to reinvent their strategic approaches to talent acquisition. The year 2015 beckoned the beginning of thoughtful attitudes in recruitment, but this approach will only pay off for companies and organizations that focus on important success determinants.
Employers are expected to improve their branding if they are to attract highly qualified job seekers who themselves are becoming increasingly selective about companies. The onus is on employers to make themselves attractive to potential employees, and this means availing as much information as they can about the organization, its culture as well as corporate values. Some organizations have taken this a notch higher- they are using employees’ photos to showcase their culture, training opportunities, and key benefits associated with working with them (Maurer, 2016). This practice is supported by the notion that employees are the best brand ambassadors any organization and as such, their stories do much more compared to the company’s mission statement.
Another trend that is expected to continue is the use of talent analytics. Talent acquisition professionals are under increasing pressure to demonstrate ROI in the recruitment process. This has forced them to move away from traditional methods of recruitment that were primarily based on instincts and instead focus on techniques that can convert everyday data into actionable information that can guide decision-making (Maurer, 2016). With the advent of HR data scientists, data science in HR has become a fundamental aspect of the recruitment process.
Most companies are going beyond routine operational measurements like cost-per-hire, source-of-hire, and time-to-fill to mine more in-depth metrics on talent (Morgan, 2018). Some organizations have turned to data analytics to analyze competitors’ talent pools with the aim of finding the candidates with the skill-set that they want and which can be convinced to join their organizations. The use of talent data analytics essentially captures the whole-person analysis in determining whether potential employees have the experience, competencies, drivers, and traits to bring additional value to an organization.
Employers have widened the scope of their talent search by venturing into new sources. Cross-industry hiring, for instance, is believed to make persons who have worked in various fields acquire experience that could come in handy. These types of employees also carry with them a wealth of cultural diversity that is especially appealing for new companies (Maurer, 2016). Nevertheless, internal hiring is likely to be embraced going forward because of the advantages it has over external hiring. According to Bryne Mulrooney, the CEO of a company that specializes in recruitment, internal sourcing has a shorter hiring-to-productivity time and considerably lowers staffing costs, which in the long run translates into better financial performance. This system also promotes talent development – a feature that keeps employees motivated as they become more valuable to the organization as the knowledge they acquire compounds with time (Maurer, 2016). The consensus is that the hiring process has changed fundamentally and in addition to personality and aptitude, experience is increasingly being seen as one employee feature that can be adjusted.
Repairing the candidate experience is another trend that most organizations are quickly catching up on. They try to create positions that can be filled with candidates with the right combination of skills and competence. Failure to maintain contacts with employees, minimal engaged by recruitment during the recruitment process, and tedious and lengthy application process do leave candidates and employees feeling unappreciated.
Elaine Orler, the CEO of a talent acquisition consultancy firm based in San Diego, opines that every touch point starting from the application process to the interactions with the schedulers to interviewers’ preparedness to turnaround time, creates an impression in the candidate about the employer (Maurer, 2016). The well-coordinated these experience are the higher the acceptance rates of a firm considering that highly skilled candidates will most likely be juggling job offers from different companies. In short, recruiters are expected to give candidates white-glove treatment whether they succeed for the job or not for it increases the interest of the candidate to apply when another opening comes up.
Technology is slowly but gradually being integrated into the talent acquisition processes. Cross-platform expansion and technology consolidation are becoming increasingly streamlined as organizations shift from multiple vendor systems to conflating their tracking systems, management of their human capital, and video conferences into one platform (Maurer, 2016). While this process is admittedly coming along at a slow pace, its impact in HR processes stands to be significant. Nonetheless, conventional talent management suites have also been expanding and increasing their recruiting potential. But while the recruitment and selection would seem, in principle, to be a straightforward HR process, the reality is much different in practice. The following section outlines some of the common challenges faced by HR recruiters and the possible solutions that have been proven to help in alleviating some of these problems.
Common Challenges in HR Recruitment and Selection
The recruitment process is widely seen as a procurement activity designed to identify and hire the best candidates for a job. On the part of recruiters, this directs attention to their expertise, business perspective, and ability to make decisions that are beneficial to both the organization and the individual. The challenges start from the type of recruitment method to use – whether to use internal or external talent pools. The ever-evolving job market dynamics with regards to technologies, recruitment sources, competition and etcetera compounds the range of problems that HR professionals encounter. Furthermore, in a job market that is already saturated, recruiters are constantly faced with new challenges that they ultimately need to overcome in order to get the best candidates in line with the requirements of the organization. While these problems are unmistakably unique to every organization, the primary challenges faced by recruiters are:
Adapting to globalization – the HR professionals are typically required to keep pace with changes happening in the within the realm of Human Resources across the world (Thoo & Kaliannan, 2013).
Minimum motivation – the view of most HR professionals is that recruitment is a thankless job because they seldom get the appreciation and recognition they believe they deserve for getting the best candidates and top performers for the company especially when the impact of these candidates is tangible across the performance spectrum (Thoo & Kaliannan, 2013).
Process analysis – most companies demand a flexible, responsive, cost-effective and adaptive recruitment process that is timely and able to cater to the company’s requirements (Thoo & Kaliannan, 2013). Nevertheless, such companies might not be investing in attaining such systems.
Strategic prioritization – HR professionals are often required to make strategic moves when performing their recruitment and selection functions. This is to enable them to exploit the opportunities that arise from the challenges that come with new systems (Thoo & Kaliannan, 2013). As such, reviewing staffing needs and prioritizing tasks in line with markets demands has in recent years emerged as a critical challenge for these professionals.
Workforce diversity – while ideally, diversity is a good aspect of an organization’s workforce, sometimes integrating people from different cultures and backgrounds do present significant challenges for HR professionals (Kamran et al., 2015). If this aspect is not managed correctly, it does escalate conflict levels in an organization and ultimately impairs the ability of the organization to achieve its goals.
Government policies – this is an external challenge that most HR departments have to acknowledge. Government policies can limit the operations of HR and certainly has implications for organizational demands and needs (Kamran et al., 2015).
Conclusion
The recruitment and selection process varies from one organization to the other, and this variance can be as a result of many factors such as the size of the company, corporate culture, objectives, and etcetera. Be that as it may, the importance of the recruitment and selection process in helping in the attainment of organizational goals and objectives has been adequately substantiated in this paper. The fundamental role of the recruitment function is to avail the best candidates for the organization, and the benefits that are associated with an effective recruitment process are numerous ranging from cost reduction, elimination of potentially catastrophic discriminatory practices, enhanced employee productivity and retention, and compliance with legal requirements.
However, recruitment is not a simple, straightforward exercise – it is hampered by a wide array of challenges that make the role of HR professionals increasingly tedious. The current trends in HR practices as discussed in this article enumerate some of these bottlenecks and the potential ramifications they portend to any organization. Furthermore, as the job market becomes more and more saturated, talent acquisition is becoming a much harder objective to meet. HR recruiters have been forced to employ somewhat unconventional methods to keep up the ever-evolving corporate landscape. And as these challenges continue, HR professionals are facing increased calls for accountability – an aspect that has created a need to adopt more empirical-based approaches in the recruitment function as more organizations demand favorable ROIs on the investments on their human capital. With this in mind, below are some of the recommendations that could significantly address the issues in HR recruitment.
Recommendations
At the elementary level, recruitment and selection process should be well-defined in order meet its critical objective – tapping the best talent. It is also vital that the response time during the whole recruitment process is reasonable relative to the time frame provided in order to minimize the chances of losing potential employees to rival companies. The methods used in this crucial process should be versatile but effective. With the advent of social media and the World Wide Web, there are numerous sources of talent pools that can be exploited by recruiters.
The conventional stage-by-stage interview like the one discussed in this paper are time-intensive and are less cost-effective. A practical interview strategy like panel interviewing would portend better returns in the short term since it is less time-consuming. However, it might not be effective in identifying the most appropriate candidate. A well-structured recruitment process that is clear on the type of candidate the organization wants and which is within the cost and time constraints may be a better alternative. The uniqueness of organizational needs and demands means that there is no one-size-fits-all strategy with regards to recruitment and selection.
Some challenges such as lack of motivation, strategic prioritization, and process analysis boil down to organizational policy. But HR professionals should be able to demonstrate that with better corporate policies, their processes can yield better ROIs for the organization. As such, HR should play a core function in the design and implementation of these policies. The integration of technology in recruitment should shift focus to empirical-based methods rather than the traditional methods which were more instinctive.
Relevant Posts
Best HRM Dissertation Topics For University Students
References
Alsabbah, M. Y., & Ibrahim, H. I. (2013). Recruitment and Selection Process and Employee Competence Outcome: An Important Area for Future Research. Human Resource Management Research, 3(3), 82-90.
Bertua, C., Anderson, N., & Salgado, J. F. (2005). The predictive validity of cognitive ability tests: A UK meta‐analysis. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 78(3), 387-409.
Bhatia, T. (2013, June 13). Recruitment and selection – The most important HR function.
Cascio, W. F. (2016). Managing Human Resources Productivity, Quality of Work Life, Profits. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Education.
Ekwoaba, J. O., Ikeije, U. .., & Ufoma, N. (2015, March). The Impact Of Recruitment and Selection Criteria on Organizational Performance. Global Journal of Human Resource Management, 3(2), 22 – 23.
Heneman III, H. G., Judge, T. A., & Kammeyer-Muller, J. (2015). Staffing Organizations. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Kamran, A., Dawood, J., & Hilal, B. S. (2015). Analysis of the Recruitment and Selection Process. Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Management Science and Engineering Management (pp. 1357 – 1375). Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Maurer, R. (2016, February 1). 5 Recruiting Trends for 2016. Retrieved November 11, 2018, from Society for Human Resource Management.
Morgan, D. (2018, November 6). Top Skills of High Performing HR Data Scientists. Retrieved November 8, 2018, from Human Resources Today.
Opayemi, A., & Oyesola, T. (2013, August). Perception of selection interview, selection test and employee performance: An empirical analysis. Journal of Public Administration and Policy Research, 5(4), 95-101.
Saez, A. (2018). Importance of Effective Recruitment & Selection. Retrieved November 10, 2018, from azcentral.
The Strategic Importance of Recruitment. (2012, November 21). Retrieved November 10, 2018, from Human Resource Students Association.
Thoo, L., & Kaliannan, M. (2013). International HR Assignment in Recruiting and Selecting: Challenges, Failures and Best Practices. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 3(4), 143 – 159.
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to recruitment and selection in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.