Employee Motivation
Employee motivation and motivation in general can be defined as a psychosomatic process that directs a person to behave and react in a way that helps them to satiate certain unfulfilled needs (Latham G., 2011). Motivation is what provides the stimuli and direction towards which employees can execute their duties (Lauby S., (2005). Motivation can be broken into three distinct categories that depend on each other for success. First of all, individual choices are driven by persistence, which reminds them of their unfulfilled needs. The choice taken will make an employee change their behavior in order to be in the right direction that would allow them to achieve those needs. Thirdly, there is the upholding of that behavior, which will go on until those needs and desires are achieved. Motivation however occurs differently in varying situations. Achieving a specific goal requires a particular motivational strategy and that same strategy cannot be used to achieve another goal.
Employee Motivation Theories
Need-Based Theories
According to Gary Latham (2011), employees draw their motivation from unfulfilled needs that they need to satisfy. Were it not for those deficiencies, then people would never have enjoyed work. The motivation to work therefore is directly equated to human needs. Once those needs are fulfilled, then the morale to work goes down. These theories were however opposed and criticized strongly by many researchers (Latham, 2011). They argued that individuals did not receive motivation to work due to fulfilling certain needs. Research conducted by these groups reveals that apart from just fulfilling their needs, many people engage themselves in jobs for enjoyment. An artist will not just draw a beautiful portrait of Zeus just to sell it and make money, but also to practice and enjoy what they do best (Latham, 2011). Examples of need-based theories include Maslow’s theory of needs, McClelland’s theory, ERG theory and Herzberg’s two factor theory. This review will only discuss the Maslow’s theory of needs and Herzberg’s two factor theory.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
This theory views motivation as a desire that changes over time and these shifts are governed by different levels of needs. These needs are the actual drivers of employees to work hard in order to achieve their goals by all means. According to Hiam Alexander (2003), these needs are organized into a certain hierarchical order that one must follow in order to reach the highest levels. While coming up with this theory, Maslow suggested that needs already satisfied can no longer motivate someone to work hard. Once they achieve their purposed needs, employees begin to drift towards fulfilling needs that are situated at a higher level in the hierarchy. This theory was however criticized strongly because one does not have to follow the order as put by Maslow in satisfying their needs. The order that Maslow proposed starts with biological and physiological needs at the base, followed by safety needs, belongingness and love needs, esteem needs and self-actualization needs.
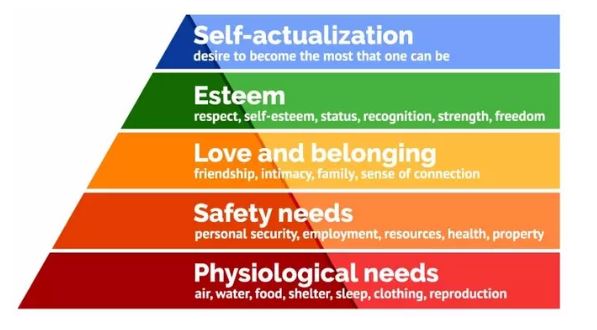
As much as Maslow tied employee motivation to hierarchical needs, Hiam believes that recognition, involvement and participation are among some of the factors that motivate a worker at the workplace.
Herzberg’s Two Factor Theory
According to Crouse Norm (2005), factors such as involvement, achievement, autonomy, participation, delegation and recognition are what increases the motivation of employees towards achieving a certain goal. Apart from that, hygienic factors such as working conditions, salary, and policies also influence the motivation of employees. As Crouse (2005) further states, poor hygienic conditions and poorly managed administrative policies lowers the morale of workers in an organization.
This theory suggests that employers should play the role of motivating their employees and is key to employee motivation. They should strive to ensure that all the factors involving working conditions go in favor of the employees – considering these factors will improve performance and bring better results for any organization. Both the two factors proposed in this theory work alongside each other.
No factor is independent on its own. Once the hygienic factors are fulfilled, the motivational factors can also be satisfied. Trying to satisfy only one set may lead to the lowering of work morale among workers, though. After doing away with the dissatisfaction in hygienic factors, employers should look forward to involving their employees in participating and developing programs. This will influence how they will perceive themselves as a part of the organization, with their due respect and recognition. This will make them improve their performance in the workplace, for they will not only increase the returns but they will also make the working environment appear more healthy and active. The model below demonstrates how Herzberg’s two factor theory is carried out.
Employee Motivation and Motivators
| Ego/Esteem | Job Enrichment |
| Self Actualization | Job Enrichment |
| Hygiene Factors | Job Enrichment |
| Social | Job Enrichment |
| Safety | Job Security |
| Physiological | Salary |
This theory was also criticized severely by Bruce Anne (2006), who argued that it did not serve the motivational needs of employees universally. Employees experience socioeconomic conditions differently and this makes them behave in variance. Herzberg’s theories assumed that the socioeconomic experiences of all employees are the same.
Process-Based Theories
Unlike need-based theories, these theories focus mainly on job aspects that motivate employees and change their behavior towards achieving their needs. According to Bruce (2006), these theories look at how employees fulfill their needs, while at the same time bargaining between behavioral choices that will suit their motivational patterns.
Cognitive Evaluation Theory
It is believed that extrinsic factors are independent from intrinsic factors in employee motivation. However, this belief does not work in contemporary organizations, because such intrinsic factors like participation and involvement are closely linked to extrinsic factors like financial incentives in the motivation of employees. This is where this theory comes handy, for it provides dependence between the external and internal factors and merges them also in the realization of an employee’s needs. Cognitive evaluation theory argues that satisfying internal factors first before proceeding to satisfy the external factors does not work. Both these factors are supposed to be satisfied at the same time for any improvement to occur in an organization.
Giving employees financial incentives and denying them an opportunity to participate and involve themselves in organizational matters such as decision-making will not motivate them fully towards achieving the goals and objectives of that organization (Latham, 2011). Some of the internal factors to be considered in employee motivation include appreciation of self-worth, employee autonomy and rewards for the achievements made. Organizations should consider such factors before coming up with job designs. The model below demonstrates various reward aspects.
Importance of Aspects of Reward
| Controlling | Informational | |
| Proposition 1 | Locus Of Causality | Feelings Of Competence |
| Proposition 2 | External/Internal | Self Determination |
Model adapted from Latham, 2011
Cognitive evaluation theory can help organizations to attract talented employees because of the commendable pay and the participation of employees in decision-making.
Goal Setting Theory
This theory was proposed by Edwin Locke and Latham in 1968. They viewed goal setting as a major basis and foundation of employee’s motivation. According to Latham (2011), the intention and objectives of an employee in a workplace is innate and that is what drives motivation. The more complex the goals become, the harder the employees work, thus improving performance. Organizations are therefore supposed to set more challenging goals for their employees in order to improve productivity. Motivation is the process that controls a person’s behavior in realizing and achieving certain goals and objectives.
As Latham further states, this theory only looks at the increasing complexity of goals with other factors remaining constant. In case there is an interruption in other contributory factors, then the challenge to achieve those goals becomes void. Apart from that, employees are supposed to accept the challenge of achieving their needs as presented to them by the goals set. Failure to accept those challenges will instead reduce the motivation towards performance.
Leaving the employees to set their own goals and objectives will result in better performance than when they are set for them by their organizations. According to Purcell John (2003), that autonomy makes employees believe in themselves and set goals that will be achieved more readily than if the goals had been set for them by others. Purcell (2003) further suggests that an employee who is restricted too much is less likely to get motivated than one that is left to participate in goal setting and decision-making processes. Contemporary organizations are supposed to therefore understand the needs of their employees before setting goals.
The Relationship between Managers and Employees
According to Ritter Joseph and Anker Richard (2002), the relationship between managers and their employees greatly affects motivation. Managers are supposed to come up with strategies that will ensure that employees remain motivated all the time. One related strategy is formulating a plan where the employee can have live forums with their supervisors and managers on a regular basis. Through those forums, managers are also supposed to recognize the behavioral patterns of their employees. Every employee has their own distinct behavior that cannot be compared to another. By understanding and appreciating the behavioral patterns of their employees, managers will be able to know which incentives and techniques to use to increase employee motivation.
Better communication between managers and their employees is also another factor that strengthens the relationship between them. Managers who rarely communicate with their employees suffer a blow when it comes to the overall outcomes of the organization. Ritter & Anker (2002) further point out that the closer the managers are to their employees, the more motivated the latter become. Regular communication between the two also makes managers understand the needs of each personal employee, thus knowing which technique to use to motivate them. According to Bruce (2006), most managers generalize the needs of their employees. This generalization is what leads to dismal performances in most organizations.
A study carried out by Sdrolias Maria, Terzidis Konstantinos and Vounatsou Maria (2005) shows that active, friendly and less strict managers are more inclined to motivate their employees towards achieving the organization’s goals and objectives. The study was conducted on eight employees of the Tech Organization in Canada. All the eight employees admitted that their manager was close to them and that he understood the individual needs of each of them.
Three employees said that they were more motivated by intrinsic factors than extrinsic ones, while the remaining five revealed that extrinsic factors carried the weight in their motivation. However, both extrinsic and intrinsic factors mattered in motivating these employees. If asked whether their manager understood them completely, all of them responded that he was a man who understood all their individual needs without generalizing.
Training as a Motivational Factor
Employee training is also another component that keeps employees motivated. According to Latham (2011), employees are supposed be trained on a more regular basis concerning the new technologies introduced in an organization. Most organizations introduce fresh changes in order to remain relevant in the market. Although such steps are taken to improve the performance of the organization, a issue arises when the employees fail to incorporate those technologies in their working systems. Many organizations will carry out a short-term internal training for their employees. According to Bruce (2006), this training technique discourages most employees because they are not given enough time to master new technologies. Instead, both internal and external training are supposed to be done. Employees should be sent out to a plethora of seminars and conferences that deal with the technology particular to the company.
This will not only give them exposure, but they will also see themselves as important players in the organization. The criteria used by some organizations to only send out only their supervisors and managers for further studies is never taken well by the employees. They see themselves as less important and this lowers their morale towards job performance thus reducing employee motivation.
Apart from technological training, organizations are also supposed to train their employees in special skills that will help them overcome difficulties and stress at the workplace. According to Bruce (2006), stress and other psychological issues like depression reduce the motivation of an employee drastically. Specialists are supposed to be brought and teach employees how they can reduce and manage their stress levels. It is difficult to realize the obstacles employees are going through unless managers develop a closer relationship with them.
A study conducted by Salmela Katariina & Numi Jari-Erik (2004) at Stanford University revealed that the non-teaching staff is motivated to work by the regular training they receive in their areas of expertise. One of the employees in the kitchen said that she strove to make the best food and serve her customers jovially. This, she said, was attributed to the program introduced by their manager to carry out a training that ran for 4 days for all the employees every month. She revealed that this not only helped her to improve her cooking styles, but it also encouraged her to be friendly and courteous to the people she served.
Teamwork as a Motivating Factor
According to Hiam (2003), teamwork is also one of the major components that determine the degree of motivation. In most companies and organizations, sales are achieved through teamwork. What determines motivation in a team is the type of task assigned and its expected outcomes. Once members gather together to fulfill a certain task, the bond and relationship among them heavily determines how that task will be accomplished. Team members are supposed to encourage one another and act as an example to others. Managers and supervisors on the other hand are supposed to evaluate and understand each team separately.
According to Latham (2011), every team in an organization has its own motivational factors which might be different from those of another team. To achieve their desired goals, managers should break down the assigned tasks into smaller and measurable units that will enable team members to easily assess the information on how they have performed. This will greatly help them in determining the amount of effort they are supposed to exert in order to complete remaining tasks. The selection and formation of teams should be done on the basis of compatibility. This step requires managers and supervisors to understand their employees well and how they can perform and react in certain situations. Even though it is useful to understand an employee on an individual basis, some employees are understood best in their various teams (Hiam, 2003).
The empirical research conducted by Latham (2011) shows that teamwork is actually one of the factors that contribute towards employee motivation. The study was conducted on employees of a bank in India. According to Latham (2011), banks are among the institutions that are generally believed to be dependent on individual efforts. This study, however, shows that bank employees feel more motivated when they work as a team and not on an individual basis. Ten bankers were interviewed and all of them agreed that consulting each other while on the job encourages one to work harder in order to achieve the set goals and objectives.
One of the respondents admitted that a career in banking is full of challenges and difficult moments. He cited some of the challenges which included serving fraudulent customers, attending to customers who had not fully complied with all the rules and even attending to clients whose money had been withdrawn by conmen. Due to these challenges, he argued that they should be given freedom to consult their workmates in order to be successful on the job. All the respondents said that their bank manager was strict and he rarely allowed them to communicate to each other, but they found themselves breaking that rule in order to seek help from their team members. All the respondents agreed that they would be more motivated to perform better if their manager allowed them to freely consult with each other while in the course of duty.

Employee Motivation – A Summary Showing the Relationship between Motivation and Job Satisfaction
Purcell (2003) points out that motivation is the key factor in determining the success of a worker. As observed from the above cases, motivated employees are more likely to meet the demands of a job than those who are not. Motivation is an innate aspect that drives one’s behavior towards achieving certain goals and objectives. Managers are supposed to understand the psychological needs of their employees before drawing work plans. Such psychological disturbances like stress and depression are likely to reduce the motivation of an employee in carrying out their duties. Employers are supposed to understand the behavior of their employees before delegating duties to them. Both the need-based and process-based theories discussed above reveal that intrinsic and extrinsic factors are supposed to be satisfied concurrently for better performance. Motivating an employee by financial incentives alone is not enough, for they will need to be recognized and appreciated as an important person in that organization.
Appreciating an employee can be done through many acts, including training and educating them on the rising issues in the organization. Employee motivation should therefore be considered as a key aspect of job satisfaction.
References
Bruce, A. (2006). How to Motivate Employees: 24 Proven Tactics to Spark Productivity in the Workplace. NY, McGraw Hill Professional.
Crouse, N. (2005). Motivation is an Inside Job: How to Really Get Your Employees to Deliver the Results You Need. Oxford, iUniverse.
Hiam, A. (2003). Motivational Management: Inspiring Your People for Maximum Performance. NY, AMACOM.
Latham, G. (2011).Work Motivation: History, Theory, Research and Practice. NJ, SAGE.
Lauby, S. (2005). Motivating Employees: Career Planning & Talent Management. Washington DC, American Society for Training and Development.
Purcell, J. (2003). Understanding the People and Performance Link: Unlocking the Black Box. NY, CIPD Publishers – Employee Motivation.
Ritter, J. & Anker, R. (2002). Good Jobs, Bad Jobs: Workers’ Evaluations in Five Countries. International Labor Review, 141(4), 331 – 358.
Salmela-Aro, K., Nurmi, J. (2004). Employees’ Motivational Orientation and Well-Being at Work. Journal of Organizational Change Management, Vol. 17 No 5, pp. 471-489.
Sdrolias, M., Terzidis, K. and Vounatsou, M. (2005), Significance, Defining Factors and Consequences of Mental Alienation of Enterprises Personnel from their Work Environment in Organizational Culture, Corporate Governance and Competitiveness. Selected Proceedings of the First International Conference on Business, Management and Economics, 16-19 June, Izmir, Turkey,Vol.2, pp.27-41.
Relevant Links
HRM Dissertation Topics
HR Performance Motivation
Theory of Motivation
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to employee motivation in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.
