Decision Making, Leadership Development and Business Ethics at Boeing
Title: Decision Making Leadership Development. The Boeing Company is an American organisation which has been manufacturing aircraft, rockets and satellite for a considerable period of time. In the early 21st century, it had faced several problems regarding its ethical policy. With reference to the case i.e. Boeing: How Low Can They Flow? It has been ascertained that at the end of 2003, the board of directors sacked its chief financial officer Michel Sears and Vice President Darleen Druyun for their unethical approaches towards the organization. Accordingly, the study intends to comprehensively explore the case in terms of certain crucial parameters including effect of the issues faced by Boeing on its stakeholders along with offering optimal solution to address the situation among others.
With regard to discrepancies ascertained, the department of justice accused Michel Sears and Darleen Druyun on the basis of unauthorized discussion with a supplier during the contract review process about employment opportunity. Specifically, it had happened during the contract between Boeing and United States’ Air Force during the deal of 767 airborne refueling tankers. As per the investigation, it has been revealed that Druyun had lobbied with the political parties for competing Airbus’s bid for a military tanker contract.
After exposing the scandal, Druyun admitted that she had considered this high priced tanker deal as a gift before she started working with them. Apart from this, it was also exposed that Sears and Druyun had interconnections in between their family. The entire set of information had been exposed through the memo which had been written by the Air force e general counsel. After exposing the evidence in front of Boeing’s management, Sears and Druyun had tried to cover-up their unethical activities’ clue. On the other hand, Boeing had started reinvestigation about them thoroughly. After conspiracy both of them had been penalized financially and also sent to prison for rehabilitation. Moreover, the chairman of Boeing Philip Condit had mentioned that the responsibility of the organization was to prevent the unethical operations.
At the same time, a former executive of Boeing Larry Satchell had also been charged earlier during 1999s due to the conspiracy to violate United State (US) procurement laws. It also happened during the Condit’s period. During his tenure, several issues that occurred had enforced Boeing to become highlighted in front of media. Difference between the male and the female employees’ salaries had been one of the key incidents among them. As a result, The Office of Federal Contract Compliance Program (OFCCP) under the U.S. Labour Department had charged Boeing and Condit had paid to settle that issue. In addition, in terms of airplanes cost recovering purpose, it had also come into focus. Even in case of personnel issues such as marriage and relationship, Condit had created conflict in Boeing. During the end of 2003, he had resigned from the post of chairman of Boeing. During his era, several personalities had complimented Boeing organization inversely.
After him, Harry Stonecipher had taken the responsibility of Boeing. During his period, Boeing had come up with couple of ethical programs to ensure the organizational discipline. The new chairman Lewis Platt had declared the zero tolerance policy for unethical behaviour. During that period in 2004, Stonecipher had taken extra responsibility for his employees at Boeing. Subsequently, in the year 2005, he had resigned from the post of Chief Executive Officer (CEO). Platt, the chairman of Boeing, stated that Stonecipher was having an extramarital affair with a Boeing female employee. Besides, he had also criticized about Stonecipher. In the middle of 2005, James McNerney had been appointed as the CEO of Boeing. After his joining, firstly McNerney had settled the Lockheed Martin’s stolen paper issue, due to which U.S. Air Force had suspended Boeing. McNerney through this settlement wanted to ensure the protection of unethical behaviour at Boeing. After a long time, in 2008, Boeing had attempted to enter into a large deal with Air Force to build refuelling tanker, but it was not successful. At that stage, U.S. Air Force had made an alliance with Northrop Grumman. Finally, it was observed that in the year 2011, U.S. Air Force confirmed the deal with Boeing, as it was lucrative one than that of Airbus.
Discussion of the Stakeholders Affected
According to the analysis of Boeing’s ethical conduct of its employees, it has been found that there were certain complexities that emerged for the stakeholders. The decisions of the stakeholders can affect an organization in both ways. Consequently, it can be also asserted that good practice in case of decision making in an organization can influence the work environment in a positive manner. In accordance with French Philosopher-mathematician Blaise Pascal (1623-62), the ethical decision making is related with the six steps. Those are mentioned below:
- Perception
- Analysis
- Synthesis
- Choice
- Action
- Learning
These are the factors that can be deemed as best practices through which the stakeholders can protect the ethical conduct of an organization. In this case, aircraft manufacturing company Boeing’s stakeholders’ such as employees, suppliers and consumers among others had been affected in several ways. In order to find those reasons, first of all, it was observed that there was an unauthorized discussion about employment opportunity. Besides, it has been also observed that during 1999s when Boeing had differentiated the salary of its male and female employees’, they were also noticeably affected. Moreover, the unethical approaches of the former CEOs Condit and Stonecipher with the internal organizational employees’ of Boeing can be termed as a key factor affecting the vital stakeholders of the company i.e. employees at large. Furthermore, due to the Lockheed Martin’s stolen paper issue, key stakeholders had been also affected in a bigger way and in order to settle that issue the organization had paid a substantial amount.
How the Company or Individual Should Prioritize Stakeholders
For maintaining the goodwill of the organization and good crisis management, prioritizing the key stakeholders is needed mostly. In order to find the stakeholders prioritizing process, it has been observed that it can be ethically maintained through BSR five steps approaches. This approach is emphasised below:
Engagement Strategy. In order to prioritize key stakeholders such as employees, suppliers and consumers among others first of all Boeing needs to set its vision. In addition, it needs to define the criteria for engagement mechanism and it must have to keep focus on short and long term goals. Moreover, it should also ensure the equality of stakeholders. Furthermore, identifying the opportunity to achieve the goals and planning for the future engagement ought to be key facets.
Stakeholder Mapping. It is a collaborative process, through research, debate and discussion, it helps to determine the key list of stakeholders. It can be segmented into four divisions. These include identifying, analyzing, mapping and prioritizing.
Preparation. It brings knowledge to fulfillment of a plan or project. It helps to ensure the engagement with stakeholders which in turn facilitates to conduct the entire process successfully.
Engagement. After the preparation in case of Boeing for its stakeholders, it needs to thoroughly work through the planning stages. This is the moment when facilitation truly counts.
Action Plan. In case of engagement failure, it will help to avoid the pitfall. This step helps to develop a plan whose aim is to find the engagement with the stakeholders through communication.
This is the process through which Boeing can ensure the priority of stakeholders (Morris and Baddache, “Back to Basics: How to Make Stakeholder Engagement Meaningful for Your Company”).
What Is The Optimal Solution?
According to the analysis, it has been observed that there were multiple difficulties faced by Boeing. Even it has been also seen that within 18 months Boeing had appointed the third CEO for its unethical activities inside the organization. In order to prevent the ethical indiscipline, organisational decision-makers need to prioritize all challenging values and standards of organization behaviour. A common set of ethical standards can be developed to guide decisions when conflicting obligations, cost-benefit trade-offs, and challenging value choices are to be seen. These aspects are illustrated below:
- Problem Awerness
- Problem Definition
- Decision Making
- Action Plan Implementation
- Follow Through
These are the optimum solutions which can prevent Boeing from unethical conduct and ensure leadership development in case of decision making (McGraw-Hill, “Ethical Problem-solving and Decision Making”).
Figure 1: The Rational Problem Solving Process/ Optimal Solution
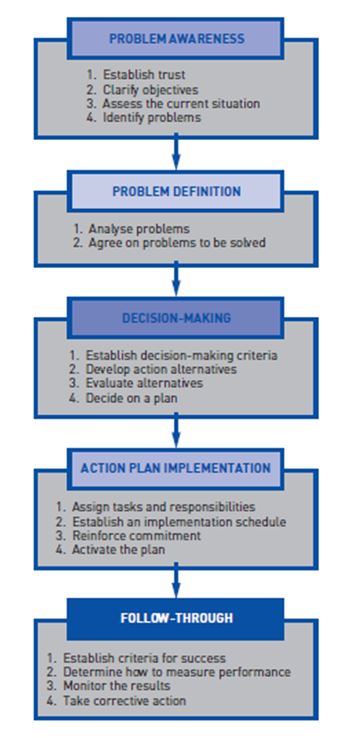
Source: (Mcgraw-Hill, “Ethical Problem-Solving And Decision Making”).
An Optimal Solution?
This optimal solution can help Boeing to resolve the lingering multifaceted problems and eliminate the discrepancy between actual and desired outcomes. The prime responsibility of the decision making authority is to identify the actual problems and in order to do that gathering problem awareness is required. Through communication and monitoring process, it can be done. It will be useful because after identifying the issue trust needs to be established for assuring that the causes of disputes can be resolved. Clarifying the objective can also help to understand the problem otherwise it will be difficult to identify the core issues. Evaluating the current turbulent situation is also helpful for Boeing to identify the problem, because comparing the predetermined performance and earlier performance will enable to directly define the difference. Moreover, it can be asserted that identifying the problem can facilitate to understand the entire viewpoint.
On the other hand, through problem definition, problems can be analysed and it will also help to determine whether Boeing has agreed to solve the problem or not. However, decision making is also a very crucial task. It can help to establish a decision depending upon the situation. Besides, it can also aid Boeing to decide a way from various alternatives by evaluating those alternatives. Finally, it can facilitate to choose a better alternative plan.
Even action plan implementation is very essential for a firm as in initial phase it helps to assign the tasks and responsibilities in keeping with short-term objectives. During this process, it will also facilitate to schedule those tasks in an organized manner. This approach related to Boeing can directly and indirectly enable to fortify the organizational situation along with ensuring the level of commitment of key organisational stakeholders. Furthermore, it can also help to active the plan of resurrection of Boeing from the faced difficulties perfectly.
Consequently, the conclusive part in this solution approach is follow-through. It can help Boeing to evaluate its own decision making system. Through determining the actual performance and measuring the results, Boeing can take desired actions. It is almost like a feedback process through which Boeing can review its own leadership policies and ethical conducts for future period.
How Are the Various Stakeholders Effected and Why?
From the analysis of The Boeing Company’s case, it has been apparently observed that, various stakeholders are affected due to a number of key reasons. In order to discuss those unethical issues, first of all, it has been found that Boeing had suffered because its former CEO Sears and Vice President (VP) Druyun had been engaged in an unauthorized discussion about employment opportunity and during that time Druyun had lobbied with the political parties for competing Airbus’s bid for a military tanker contract.
Moreover, during Condit’s leadership, conflict had been raised in terms of male and female salaries discrepancy. Consequently, U.S. Labour Department had charged Boeing. In addition, he had also involved with an unethical issue for engaging in a relationship with the female employee of Boeing. As an effect, both of them i.e. Condit and the female employee involved had been fired from the organization.
Even after Condit’s period, the unethical approaches had continued in Boeing. Stonecipher had joined with several promises but he was unsuccessful to accomplish them. Within a short span, it had been exposed that Stonecipher was having an extramarital affair with a Boeing’s female employee. This kind of undesirable conduct by an organisation head affected different stakeholders of Boeing including its other employees as the image of the company got tarnished by a considerable extent. Moreover, Lockheed Martin’s stolen paper issue had been also happened at the same time; due to which U.S. Air Force had suspended Boeing from any short of business deals. This factor was a major setback for the company and its key stakeholders such as suppliers as they were deprived of placing their prominence in a competitive market.
Proactive Steps The Company Could Take To Avoid Similar Issues In The Future
With regard to avoiding these kinds of unethical conducts in the future, Boeing should take few precautions. Firstly, it should choose the right person as a leader who always intends to uphold strong ethical conduct as his/her main priority. Prior leadership experience should be provided greater emphasis to lead the organisation through complex and uncertain business environment. Besides, Boeing has to be stricter about its ethical conducts in terms of business dealings. In case of business deals with the suppliers or clients, Boeing should not only rely on one person instead it should give the responsibility to the top management council, where the decision will be taken by the discussion of the council members. Consequently, in case of employee selection, Boeing should follow the approaches laid down by best practices. Additionally, in case of women related scandals, it should react strictly to settle the issues and set examples for future ensuring zero tolerance. These are the key precautions Boeing should consider for future conducts to avoid the unethical scenarios in case of leadership development.
Works Cited
“Ethical Problem-Solving and Decision Making.” McGraw-Hill. n.d. Web. 22 Apr. 2014.
Morris, Jonathan, and Farid Baddache. Back to Basics: How to Make Stakeholder Engagement Meaningful for Your Company. 2012. Web. 22 Apr. 2014.
Other Relevant Blog Posts
Business Management Dissertations
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to decision making, leadership development and business ethics at Boeing in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.