Organization Culture, Strategy and Leadership
Organization Culture, Strategy and Leadership Project – Strategy formulation is one of the responsibilities and roles of effective leadership (John & Allen 1998, p. 45). According to John & Allen (1998, p. 45-46), the perspective of strategy assumes assumptions of the task of leadership especially due the emphasis given to guiding, shaping and controlling the organization environment.
Effective strategy formulation is one of the essential elements of ensuring the business success. Failure by the business executives to exhibit effective strategy formulation could lead to the failure of the business. As such ensure effective strategy formulation within the organization requires the managers and the business executives to exhibit strong leadership skills. Strategy and leadership cannot be alienated as one influences the other (John & Allen 1998, p. 47).
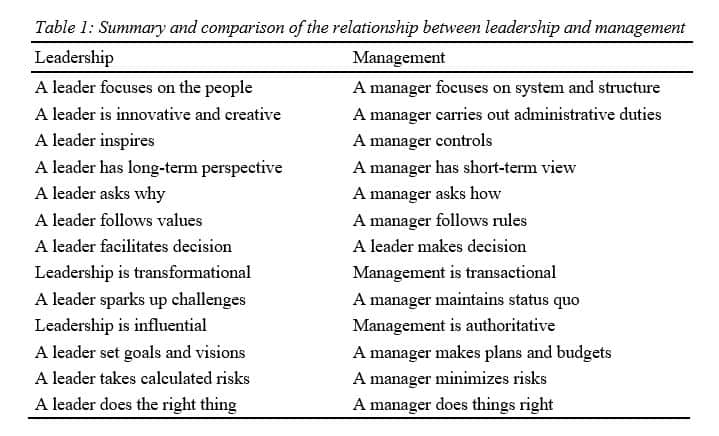
A strategy is an action or a plan designed within the organization for the purpose of achieving an overall or a major goal. On the other hand, leadership can be described as the ability to influence others towards a particular direction within the organization (Pride, Hughes & Kapoor 2010, p. 201).
This paper will analyze Wal-Mart stores generic business strategy, organization culture and formal organization structure. Wal-Mart store is multinational retail store operating a chain of hypermarkets, grocery stores, and discount department stores. Studies show Wal-Mart as the most profitable retail store in the world. Currently, Wal-Mart operates in 26 countries outside of the United States (Vosburgh 2011, p. 10).
Generic Business Strategy
A generic business strategy can be described as the strategy that is adopted by a business to gain a competitive edge over its competitors in the industry (Goldman & Nieuwenhuizen 2006, p. 22). Goldman & Nieuwenhuizen (2006, p. 23) argues that a generic business strategy is vital to the success of the business especially in a competitive industry.
Michel Porter designed three generic strategies that can be used by a business to gain a competitive advantage in the market. The porter’s generic strategy is used to describe how an organization can pursue a competitive edge within its market scope (Tanwar 2013, p.13). The modern business world is characterized by increased competition. As such to ensure business survival it is essential for the business to pursue activities that would give it a competitive advantage over the competitors within the industry.
Competitive advantage is the distinct feature of the business that gives it an edge over the competitors in the market. The more competitive business is, the better the chance for the business to survive in the current global market. According to Tanwar, R., 2013, p. 13-15) Porter identified three generic strategies which include cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.
To ensure efficient utilization of organization resources, porter argues an organization must choose only one of the three strategies. The porter’s generic strategies show the relationship between the strategies of cost reduction, market focus, and the product differentiation.
In the argument of Porter, an industry has various segments that can be exploited by the organization. To gain a competitive advantage over the rivals, a business is expected to make a choice about the kind of competitive advantage that it seeks and its scope.
The basic types of competitive advantage include product differentiation and lower cost. Making the choice on the appropriate strategy for the business requires proper leadership skills. Choosing an inappropriate strategy could lead to the loss of organization competitiveness within the industry. As such it is appropriate for the business to ensure enough resources are devoted to conducting research for the purpose of understanding the industry.
In the argument of Stankeviciute, Grunda & Bartkus 2012, p. 1201) Wal-Mart is ranked as one f the most successful retail store in the world. The company success largely is associated with its cost reduction strategies. Wal-Mart stores operate in the retail sector that is largely characterized by huge competition not only from the large stores but also from small scale traders (Stankeviciute et al. 2012, p. 1202).
Stankeviciute et al. (2012, p. 1202-1204) further argue to survive in the retail industry and to ensure organization competitiveness an organization needs to establish itself as the cost leader. The Wal-Mart use of the cost leadership strategy and its integration with the porter’s five forces has provided the company a competitive advantage in the industry enabling the company to be ranked as one of the must successful retails stores.
The adoption of cost leadership strategy by Wal-Mart has to some extend acted as the price barrier within the industry thus reducing the number of competitors. Wal-Mart has adopted various strategies to ensure the success of its core cost leadership strategy. Some of the strategies adopted by Wal-Mart to ensure cost reduction include the adoption of technology, elimination of stock holding costs and sourcing its products directly from the manufacturers’ thus eliminating wholesalers cost (Stankeviciute et al. 2012, p. 1203).
In the argument of Stankeviciute et al. (2012, p. 1203-1205) Wal-Mart has also adopted waste reduction measures by investing in a stock management system that helps monitor stock levels in real time. The stock management system has been instrumental in minimizing waste costs. Wal-Mart adoption of cost leadership as its generic business strategy has enabled the company to achieve its low-cost price strategy.
Adopting a cost leadership strategy is essential to business since it enables a business to charge a relatively low price compared to the price of the competitors. Charging a low price can act as a barrier to entry of new competitors and can also drive away the existing competitors due to continued sustained loses. In the case for Wal-Mart cost leadership strategy has enabled the business to control a large market share in the industry and create a competitive advantage for the company.
To maximize its sales, Wal-Mart also discounts its products since it has a significant cost advantage over its rivals in the industry. To ensure effective cost-leadership strategy a close cooperation between all the areas of the business is required. As such effective leadership is required in all the functional areas of the business (Stankeviciute et al. 2012, p. 1205).
Organization Culture
In the recent past, there has been a growing concern in the manner in which organizations conduct business. One of the components that have been identified as essential in growing the business is the organization culture. According to Schein (2010, p. 96), organization culture is the shared experiences, norms, and beliefs within the organization.
As a leadership concept, organization culture can influence the success or the failure of an organization. It is the responsibilities of the business leaders to impose the right culture in the organization. In the argument of Schein (2010, p. 97) organization culture is influenced by various factors. One of the factors influencing organization culture is leadership.
To a large extent, organization culture is influenced by the business leadership. The attitude of the business leaders can determine whether the business will succeed or fail. As such leader’s attitude could form the basis of the organization culture. Often employees within the organization look up to their leaders for direction and guidance.
Therefore, the way the leaders interact with their employees and solve the day-to-day challenges forms a basis of the organization culture (Sadri& Lees 2001, p. 854). The organization culture is also likely to be created by what leaders reward and punish, pay attention to and allocate resources.
According to Sadri & Lees (2001, p. 854), the organization culture influences the organization strategy. An organization is more likely to be successful if the organization culture has a close relation with the business strategy. The business leaders should thus ensure that the organization has the right culture that supports the business strategy. The organization culture influences the manner in which things are done in the organization. Organizational culture is, therefore, central to the operations of the business and its success (Klein 2011, p.23).
The success of Wal-Mart has been attributed to the organization culture. Wal-Mart has been described as having a strong and pervasive culture that gives the company a competitive advantage in the market. The culture of Wal-Mart is attributed to have been formed by the founder Sam Walton.
Wal-Mart has managed to retain its organization culture elements since it started operating. The organization culture of Wal-Mart is created around the brand and the image of the company. According to Klein (2011, p.24), the organization culture of the organization can be assessed by having an understanding of its behaviors and artifacts, shared perspectives, awareness and the unconscious assumptions of the business.
Studies indicate that the organization culture has an influence on the performance of the organization (Davies 2007, p.6). It is therefore highly likely that successful businesses are supported by a strong organization culture. Various studies conducted on Wal-Mart stores indicate that the company has a strong organization culture which is the driving force of its success. The organization culture of Wal-Mart has contributed to the company recognition by both the insiders and the outsiders of the company (Jacques, et al. 2003, p. 514).
According to Davies (2007, p.9-14) Wal-Mart organization culture is characterized by; first, strong leadership- Wal-Mart has adopted both the transformational and the transactional leadership styles. The transformational leadership is described as the type of leadership that changes the life of the community and people in the area in which the leader operates.
Transformational leadership has been at the center of Wal-Mart. Wal-Mart has been able to change the life of the people and society within its area of operation through its various corporate social activities as well as its low pricing strategy. On the other hand, transactional leadership has given the company vision and strategy.
Transactional leadership is the type of leadership that is responsible for the strategy execution and the daily running of the business operations. Second, low price products- Wal-Mart culture has been formed around offering low price products since the inception of the company. The low-price strategy has given the company a competitive edge in the industry, which makes it the largest retailer store in the world (Schneider 1998, p.295).
Over the years despite the worsening economic situations Wal-Mart has offered its customers low price products in line with its culture. Its low pricing strategy has contributed to the company recognition around the world. The low-price culture has also contributed to the organization effectiveness and efficiency as it aims to lower the cost of its operations so as to continue providing its customers with low price products.
Third, innovation- Wal-Mart has been at the center of innovation over the years (Schneider 1998, p.296). The company innovative strategies have enabled the company to continue providing high-quality, low-priced products. In line with its innovative culture, Wal-Mart continues to adopt the use of new technology in its business. Recently the company adopted the use of stock management system.
The company has also adopted technology in communication with the aim of reducing its cost. Fourth, entrepreneurship and risk taking- over the year’s Wal-Mart has ventured into business and markets that would be considered risky. The continued venture in different countries shows the entrepreneurial spirit of the company.
The entrepreneurship has been part of the Wal-Mart culture since the inception of the company as the company has since been expanding its areas of operations and market. In the current global market, organization entrepreneurship is an essential skill in ensuring the organization competitiveness and retention of its current market share.
Failure of the business leaders to understand the value of corporate entrepreneurship and engage in it could lead to the organization loss of market share and competitiveness. As such where the entrepreneurship is part of the organization culture it is highly likely that the business will be a success, as a case for Wal-Mart. Fifth, customer relations- another important element of the Wal-Mart organization culture is its customer relations. Wal-Mart strives to ensure customers satisfaction in its operations.
The Wal-Mart customer relations have been an essential element in creating customer loyalty. Customer loyalty is essential as it ensures the company can retain its market share and attract new customers as well. Sixth, outcome orientation- as part of Wal-Mart culture, employees are encouraged to achieve the desired outcome. As a way of motivating the employees to achieve their targets, employees are often involved in setting the company goals.
This culture has enabled the company not only to meet the target but also supersede these targets. Employee participation creating a sense of belonging in the company thus increases their productivity (Schneider 1998, p.296). Wal-Mart could thus be argued to have a strong organization culture which has been instrumental in its success.
Formal Organization Structure
The formal organization structure of the organization defines the activities such as supervision, coordination and task allocation to different officers of the organization. The organization structure is important in allocating responsibilities and enhancing accountability in the organization. The organization structure as acts a control procedure in the organization and helps reduce possible conflicts.
According to Rosen (2004), Wal-Mart has adopted a hierarchical functional organizational structure. The organization structure of Wal-Mart hence has two feature; hierarchy and function-based. As such Wal-Mart has adopted a hybrid organizational structure. The adoption of a hybrid organization structure has some of the following benefits to the company, shared vision and mission, improved interactions among departments, speed in decision implementation, minimizes complexity and flexibility.
The Wal-Mart organization structure defines the business operations of the company. The organization structure also does define the relationship of the different officers and departments within the company as well as defining the duties and responsibilities of the company officers. As such the Wal-Mart organization structure is instrumental in creating the formal company culture. The Wal-Mart organization structure also defines the limitations of how the organization would address a particular issue (Rosen 2004).
Formal organization culture is essential in the day-to-day operations of the business as it creates a way of addressing the daily operations and how people respond to daily challenges an interact. The formal organization culture of Wal-Mart has impacted on the success of the company by ensuring different departments work in harmony and with minimal conflicts. It has also been instrumental in ensuring that different employees at various levels of the organization are accountable for their actions. Where employees are made accountable for their actions, it is highly likely they will be more productive and efficient.
A strong formal organization culture could contribute to the organization competitiveness in the industry. As such the organizational structure adopted by Wal-Mart has been influential in the success of the company by not only defining roles and responsibilities but also creating the formal culture of the organization (Rosen 2004).
Conclusion
The current global market is quite competitive and as such the success of the organization will largely depend on effective strategy formulation and effective leadership. The ability of the organization to choose an appropriate generic business strategy would prove to be the point of difference between different players in the market.
The generic business strategy adopted by the organization determines the direction of the organization as well as its ability to effectively compete in the market. The businesses executives have the responsibility to integrate the generic business strategy with the organization culture as well as the formal organization structure.
Integration of the generic business strategy with the organization culture and structure creates an enabling environment for the organization to achieve its goals. The business leaders should ensure the adoption of the appropriate culture within the organization that can support the business strategies as well as the organization structure.
References
Davies, D.J., 2007. Wal-Mao: The discipline of corporate culture and studying success at Wal-Mart China. China Journal, (58), p.1-27.
Goldman, G., & Nieuwenhuizen, C. (2006). Strategy: sustaining competitive advantage in a globalised context. Cape Town, Juta.
Jacques, P. et al., 2003. Wal-Mart or World-Mart? A Teaching Case Study. Review of Radical Political Economics, 35(4), p.513-533.
John, R., & Allen, M. (1998). Global business strategy. London [u.a.], Thomson.
Klein, A., 2011. Corporate culture: its value as a resource for competitive advantage. Journal of Business Strategy, 32(2), p.21-28.
Pride, W. M., Hughes, R. J., & Kapoor, J. R. (2010).Business. Australia, South-Western/Cengage Learning.
Rosen, E.I., 2004. The Quality of Work at Wal-Mart.Conference on Wal-Mart: Template for 21st Century Capitalism.
Sadri, G. & Lees, B., 2001. Developing corporate culture as a competitive advantage. Journal of Management Development, 20(10), p.853-859.
Schein, E. H. (2010). Organizational culture and leadership. San Francisco, Jossey-Bass.
Schneider, M.J., 1998. The Wal-Mart Annual Meeting : From Small-Town America to a Global Corporate Culture.Human Organization, 57(3), p.292-299.
Stankeviciute, E., Grunda, R. & Bartkus, E.V., 2012. Pursuing a Cost Leadership Strategy and Business Sustainability Objectives: Wal-Mart Case Study. Economics and Management, 17(3), p.1200-1206.
Tanwar, R., 2013. Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies.Journal of Business and Management, 15(1), p.11-17.
Vosburgh, R., 2011. WAL-MART STORES. Supermarket News, p.10.
Relevant Organization Culture Posts
Business Management Dissertation Topics
MBA Dissertation – Chinese Business Culture
The Impact and Influence of Organisational Culture on Innovation Management
Cultural Diversity Dissertation
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to organization culture, strategy and leadership in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.