Application of Risk Management: In the Perspective of a Workplace Health and Safety Manager
Introduction
The objective of this paper is to discuss the problem related to workplace health and safety. Workplace health and safety hazards are mostly preventable provided proper precautions are taken in proper time to avoid costly losses of life and property. A hazard can be anything causing injury or disease, e.g. a health hazard, a safety hazard or an environmental hazard. The paper discusses about an organization dealing in petrochemicals. It proceeds with the identification of hazards related to the industry and designing a system to manage the heat problem.
Application of Risk Management
Starting in 1987 the US petrochemicals is a Texas Corporation operating in over 30 countries now. The company is operating successfully in meeting the demands of its customers across the globe which is beneficial for the company itself in many ways. The company is known for its timely delivery at an edge cutting price. The company has earned a worldwide reputation for its workplace health and safety management. Common workplace health and safety hazards include: transportation accidents, slipping and falling, communicable diseases, toxic events, chemical and gas exposure, workplace violence, electrocution, getting struck by objects, explosion, repetitive motion, hearing loss and ergonomic injuries, heat stress, etc.
Heat Situation is the most common incident at any chemical industry and the US Petrochemical is not an exception and there is a well-defined and established system to manage risk at the US Petrochemicals which is discussed in detail in the following paragraphs (Crockford and Neil, 1986).
Identification of hazard
At the US Petrochemicals there are various ways for identifying hazards at workplace:
Inspection: A regular walk through the workplace with a hazard checklist is a direct way of identifying many hazards. The inspection should be for physical things as well as the systems of work and work procedures. The action can be taken immediately if any straight forward problem is detected. Sometimes simple matters like non-functioning of risk control or it is not being used or not things not kept at appropriate place, be detected which don’t need formal risk assessment and immediate action can be taken to control or eliminate the risk. Sometimes the inspection walk-through detects a situation of immediate and substantial danger to working people (Hubbard and Douglas, 2009).
Finding and applying available information: There are many sources of information which can be made readily available for particular industry or job or type of activity. Many organizations which work for the health and safety of the people publish both hard and soft copies of information on a wide range of OHS topics and industries. Industry unions and associations can provide substantial information about industrial and job hazards, this is essential to the workplace health and safety manager.
Testing and measuring: Often measurements are required to decide about any action specially in case of hazards like noise and atmospheric contaminants. For estimating general noise levels simple comparisons can be made. Measuring and testing provide accurate information about the hazard. Simple machines like noise meters, atmospheric testing machine can be used for the purpose.
Surveys of employees and others at the workplace: Information about occupational stress, workplace bullying, muscle or skeletal aches and pains which may be signal for potential hazard, can be obtained from the people by conducting surveys at the workplace.
Analysing records and data: Another way of identifying hazard is to analyse data and records. Records and data of incidents and injuries are valuable source of information about hazards. Some organizations mostly large ones even have records or data which show trends of injury or incident. There are many safety authorities which publish data and records about the common sources of injury for different industries. Data can also be shared from other similar industries which have it.
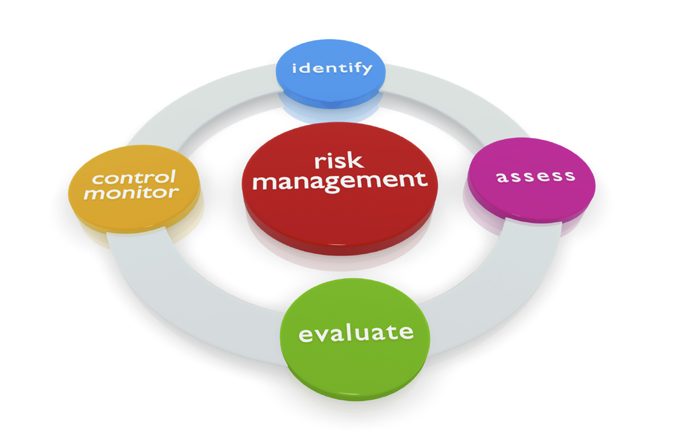
Risk Assessment
The process of developing understanding and knowledge of risks and hazards to take suitable decision to control them is called risk assessment. Existence of understanding and knowledge and understanding of risks and hazards minimizes the necessity of risk assessment. At the US Petrochemicals the objective of risk management is to determine;
- What is the level of harm that can occur
- How will the harm occur
- What are the chances of occurring harm
A risk assessment should be tailored to the organization and the situation in which it is to be conducted. It may be elaborate and formal or simple as structured discussion. It should be done when the knowledge and understanding about a risk or hazard is limited or there is uncertainty about its outcome or everything that may go wrong is estimated or there is uncertainty about the impact of hazards upon each other to produce greater or new risks (Deloach J. 2012).
Risk Control
The risk control strategies vary as per the need of the organization and the situation. The strategies mentioned below can be used in an appropriate combination or independently. Normally they are used in a combination at the US petrochemicals. They are as follows:
Eliminating Risk – Elimination of risk is the most effective action which can be taken to control risk. This can be done by eliminating the hazard which may not be possible. In such cases as many risks associated with the hazards as possible can be eliminated (British Occupational Hygiene Society Technical guide).
Avoiding risk: Risk avoidance means to avoid activities which may lead to possibility of loss. This is a calculated decision which may also mean to avoid earning profits because no risk no gain.
Preventing Loss: For unavoidable risks, the methods of ‘prevent the loss’ should be used. Preventing the loss means breaking the sequence of events which cause loss.
Reducing Loss: For unavoidable losses, the methods of ‘minimize the severity of injury or financial impact’ should be used. These methods include activities of pre-loss reduction or post loss reduction.
Reducing risks– Practically it is not possible in many cases to eliminate hazards or risks but steps can be taken for changing the risk to reduce it. It is the most effective way because it is comparatively less reliant on people performing faultlessly. It can be done by substituting the risk with a lesser risk, by changing the process of work, using technology and isolating people from exposure.
Duplication/Separation: The aim of the risk control techniques is to minimize high losses and not to prevent, avoid or reduce any single operation or asset. Separation means isolating one exposure from others, e.g. a business can occupy different buildings at different locations instead of one big building. Duplication means utilizing spares or backups, e.g. a business can store the spares or backup data at different location.
Transferring Risk: Transferring risk means making such contracts with parties, other than insurance companies, such as vendors, service providers, suppliers and contractors which include transferring risk to them. This is also termed as contractual risk transfer.
Changing exposure of people to risk– The behavior of the people or the way they expose themselves to the risk can be changed to control the risk. This does not change the risk but controls it by protecting the people. This can be done by improving the skills of the people which will limit the chance of failure, by limiting the time of exposure and by providing protective equipment to them.
Controlling the risk in heat situation– For heat situation some different and specialized steps are taken like reducing or removing the sources of heat if possible, controlling the temperature, providing mechanical aids for reducing work rate, regulating the duration of exposure to heat by providing breaks or rest facilities, preventing dehydration, providing protective clothing and equipment and by providing special training about heat stress.
Implementing control strategies and assigning responsibility
The responsibility of a workplace health and safety manager is not only to establish only a system to control risk or hazard but also to ensure its proper implementation according to a suitable approach of the organization. At the US petrochemicals there is a detailed guide for different departments of the company for the implementation of control strategies and assigning responsibilities. The guide has key questions like what does the department do, how is the department organized or managed, what is the size of the department, what are the numbers of hazardous processes and hazards, what are the types of risks or hazards, what levels of harm, risks or hazards do, etc. Being a large organization, the US petrochemicals has the benefit of established formal process of implementation which ensures certainty of results and consistency and this is possible due to availability of many hazardous processes, large number of employees and many layers of management (New and expectant mothers at work).
Risk Monitoring
A risk management system can only be effective if there is a structure of reviewing and reporting to ensure the effective identification and assessment of risks and hazards and proper control over it. Compliance of standards, review of standard performance and regular audit of the process is required for improvement. At the US Petrochemicals it is assured by the monitoring system that the controls are in place and procedures are clear to everybody to follow them adequately. Changes are made in the system with the changes in the environment and the organization. The monitoring also determines that the intended outcomes were achieved, appropriate information was collected and appropriated processes were implemented and the decisions taken were appropriate according to identification and assessment (A handbook for workplaces).
Conclusion
Workplace health and safety is a key issue for any organization and the US Petrochemicals is not an exception. The responsibility of a workplace health and safety manager is tremendous and keeps him on toes because the things in the business world are changing fast and with this organizations are also changing and it is a challenge to keep changing the risk management strategies according to the organization. The US Petrochemical is a big organization with large number of staffs and different layers of management which makes the implementation of risk management strategies accurate. The risk management involves various steps like identification of risk or hazard, assessment of risk and hazard, control of risk and hazards, implementation of strategies of risk and hazards and finally the monitoring of the process. All these steps require serious and careful attention to avoid any incident and ensure health and safety measures.
References
A handbook for workplaces, Controlling OHS hazards and risks, Edition No.1, November 2007
British Occupational Hygiene Society Technical guide, No 12 The thermal environment (Second edition) H and H Scientific Consultants Ltd 1996 ISBN 0 948237 29 5
Crockford and Neil, 1986. An Introduction to Workplace Health and Safety Management (2 ed.). Cambridge, UK: Woodhead-Faulkner, pp; 18, ISBN 0859413322.
Deloach J. 2012. Key Elements of the Risk Management Process and Workplace Health and Safety.
Dorfman and Mark S. 2007. Introduction to Risk Management and Insurance ,(9 ed.). Englewood Cliffs, N.J: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-224227-3.
Hubbard and Douglas, 2009. The Failure of Workplace Health and Safety Management: Why It’s Broken and How to Fix It. John Wiley & Sons.,pp; 46.
New and expectant mothers at work: A guide for employers HSG122 (Second edition) HSE Books 2002 ISBN 0 7176 2583 4
View Business Management Dissertations Here
I hope you enjoyed reading this post on Workplace Health and Safety. There are many other titles available in the business management and MBA dissertation collection that should be of interest to MBA students and academic professionals. There are many dissertation titles that relate to other aspects of business such as strategy, leadership, international business, mergers and acquisitions to name a few. It took a lot of effort to write this post and I would be grateful if you could share this post via Facebook and Twitter. Feel free to add your thoughts in the comments section. Thank you.

I was able to find good information from your blog posts.
Great write up on Workplace Health and Safety – Do you have dissertation on this subject, preferably 15,000 words plus.
Hi, great H&S post. Have you got any dissertations that relate to H&S in the workplace? If so, can you please upload.
Have you got any dissertations that relate to H&S in the workplace? If so, can you please upload. or send me
Hi – We do have a few H&S in the workplace dissertation available in the dissertation section. http://www.study-aids.co.uk
I wanted to thank you for this health and safety post. I definitely enjoy your blog and have been following it for over a year. It is hard to find sites that post quality material for students for free. Thanks.
No problem Donnetta. Thanks for the positive comments, it makes it all worthwhile.
Wonderful blog thank you for sharing. Rob
Thanks Rob
Thanks for every other magnificent article. The place else could anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal manner of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am at the look for such information.
I’ve been looking for HSE and workplace H&S material for some time. I will make sure I reference this material when I start my own dissertation. Thanks.