M-Commerce and Its Evolution
An m-commerce (mobile commerce) business model allows customers to complete every steps of the commercial transaction by utilising mobile phones rather than visiting to the physical or brick and mortar store. The experts of technology predict that the mobile wireless communications by 2020 are possibly to be available to anywhere and anyone throughout the globe at very low cost. But it is important to develop and maintain the trust and satisfaction of customers as well as reducing their risks involved in online payments and transactions. It is specifically true in case of cross-border consumption, as less familiarity with the overseas systems and policies makes it more complex for end users to comprehend their rights and easily use mobile devices for online purchasing. In this regards, the report here is inculcating about development of m-commerce by scrutinising the enabling tools, the mobile commerce impact on the business world and the evolving battle of Android and Apple IOS. Also, the online security issues and ethical and legal concerns for the sellers are discussed at the end.
Use of m-commerce technology and its effects on future retailers
Systems and devices based on mobile techniques are now a part of daily life. These systems and devices include pagers, cellular phones, two-way radios, cordless telephone, remote systems of car locking, baby crib monitors, a system of wireless networking, electronic monitoring devices for parolees and GPS (global positioning system) based maps and locators. Sometimes such systems and devices facilitate undertaking existing activities more efficiently and effectively; at other times, they also allow completely distinct and novel activities (Sahaand Mukherjee, 2003).
The advancement in wireless techniques increased the users of mobile phones and given pace to rapid development of the economy with the effective utilisation of such devices. A type of e-commerce, i.e. dealing through mobile terminals is developed, which is referred to mobile commerce. According to Sadeh (2002) m-commerce more widely characterises as the emerging services and set of applications that can be accessed by people from their smart and internet enabled cell-phones. Basically, the m-commerce occurs in a strategic platform, which is referred to a ‘mobile portal’. There fourth-generation (4G) and third-generation (3G) systems of mobile communication provides a high level of commonality of global roaming capability, which is supporting a wide multimedia and internet services and applications with higher rates of data (Sadeh, 2003).
Due to its intrinsic characteristics, like personalisation, ubiquity, dissemination and flexibility, the m-commerce promises unprecedented market potential of business, high profitability and great productivity. The crux of e-commerce revolves around the idea to reach employees, suppliers as well as customers regardless of places where they are situated. It is about transferring correct information to right place at an exact time. Such mobile commerce flexibility is made possible through the convergence of enterprise applications, internet and wireless techniques (Siau, Ee-Peng and Shen, 2001).
Also, the mobile explosion over last some years has been surprising. It is expected that in the current year around twenty billion of cell phones will be sold. It is not just there is increasing production of mobile phones rather the human being is increasingly relying upon them. In fact, in US there are nine out of 10 customers keeping their mobiles phones 24/7 in reach. It has great ramifications for the retailers, specifically for the online commerce, where 30% of US e-commerce already accounts for m-commerce and is estimated to develop 300% quicker than the traditional e-commerce. The individuals rely on their cell phones all through the day. In actual fact, 91% use their phones while accomplishing some other tasks (Kumar, 2016). Since, the human beings are becoming more reliant on the mobile devices; they are expecting to get exactly what they required in the period when they actually need it. Such mobile mind-set of customers’ presents for the retailers ‘unprecedented opportunities to engage with their clients on cell phones and which also enables the brands to give their consumers exactly what they require instantly.
However, there is a challenge for several retailers that well-known approaches to adapt desktop experiences to cell phones, i.e. an appropriate Web design fall short when it comes to contextual experiences delivery. In order to keep up with the need of their customers during their smart phone moments, retailers need to solve response limitations, for instance, by MEO (mobile experience optimisation) on the top area of their responsive websites (Rigby, 2011).
The retailers are also losing $18 billion on annual basis because of the abandonment of their shopping cart. Moreover, it has been shown by research that over 2 out of 3 users who add any item in their online shopping cart just leave without actually buying it. Even the numbers are worse on smart phones where the rates of conversion are 70% less than the desktop. But 2015 was considered as a pivotal period for the shopping by using mobiles. For instance, in the season of holiday, smart phones play an important role than ever, with 82% improvement in revenue due to the 45% increase in traffic on mobile. In fact, the mobile phone generates 57% and more traffic and nearly 30% revenue during the holidays (De Silva, 2015). Moreover, with m-commerce expected to increase more quickly than the traditional e-commerce, the more retailers will focus on executing a seamless experience of checkout in the coming period.
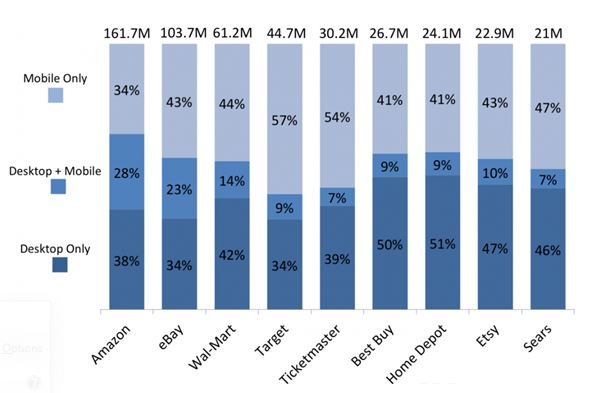
Figure 1: Monthly US visitors across retail websites. (Source: Smith, 2014)
The concept of mobile commerce will possibly emerge as a main focus of the telecommunication sector and the business organisations in the immediate future. The experience of offline shopping covers huge range of emotions by comprising several forms of social interactions with human beings (Tauber, 1972). On the contrary, the experience of online shopping might be viewed as lacking sociability and human warmth, as it attempts to be more anonymous, automated and impersonal (Wangand Emurian, 2005). The experiences attained while shopping comprise positive emotions that have been linked to several important results, like increased time spent at the store, increased spending and improved level of purchasing (Jones, 1999). Moreover, the social aspects of shopping have been considered as the main contributor towards customers’ favourable connection with the retailers.
A significant challenge is faced by the online sellers in making their virtual outlets socially rich as well as in making their services and products appear eye catching to the target customers (Kim, 2002).
In future, it would be hard to earn maximum profits and retailers will be challenged to become more smart venders. Also, they will be required to identify unique methods of reaching customers and more effective methods of measuring their marketing attempts performances. Furthermore, mobile will cease being a developing channel of marketing and will become essential for the retailer to market their brand and measure themselves. Therefore, those who will be fail to integrate and adopt today’s customers’ mind-set for mobile will become the casualties of shift in next digital paradigm (Fulgoniand Lipsman, 2016).
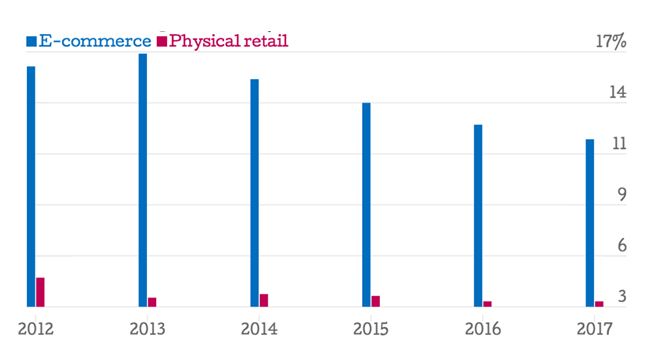
Figure 2: US retail sales growth rate by channels. (Source: McDermott, 2014)
How the battle between Android and Apple IOS will evolve in next five years
In the year 2007, Apple released iPhone based on their iOS mobile operating system. A year later after the grand reception of the revolutionary smart phones by Apple, Google launched Android mobile operating system under an open source license. Since then, Apple and Google have been engaged in a fierce competition for the mobile phone market share around the world. A broader view suggests that the battle between the two has been resulted in offering of more and more alike services. It happened due to borrowing features from each other’s and providing basic Smartphone functions like web browsing, app permissions and running, file sharing in similar ways. Though in recent times, the customer preference to select one of the two primarily depends on add on services and apps that comes along with them ranging from email, cloud services to VR and even mobile payment solutions (Tilson, Sorensen and Lyytinen, 2012).
One of the key differences between Android and iOS remains that Apple’s applications are tied to and updated at the same time as the mobile OS, whereas Google’s applications update are customizable and left on the choice of customers. Another key difference in the line is that use of Android applications across several devices such as Smartphone, laptops, tablets or desktops is smooth whether customers use these devices from the same manufacturer or not. On the other hand Apple doesn’t like their customers to switch the manufacture because Apple produces all these devices itself. Therefore, it’s easier to work across these devices if made by Apple and harder to get out of the Apple’s ecosystem.
Apple took similar approach with the iPhone as they took with their desktop operating system Macintosh. They launched a revolutionary device for a much higher price than existing products with outstanding features and capabilities. On the other hand, Android took approach similar to that of Microsoft and became like “Windows” of the smart phone operating system. The open source license enabled a lot of manufacturers to offer low-cost devices with same features as Apple. As a result, Google’s Android compete Apple’s iOS with its increased percentage of market share in year 2012.
Though, studies suggest that with respect to e-commerce transactions, Apple’s iOS is still ahead of Android in developed economies and average order value around the world. Even though, top choice of customers in m-commerce remains Apple but in reality the Android adoption has increased over the years. With respect to current annual traffic growth, Android’s rate 56% is ahead of Apple’s 33%. Also, the customers are using cell-phones and tablets to shop across mobile sites and apps that ultimately create challenge to the mobile strategies of retailers.
Consumers are also using both tablets and smart phones to shop across apps and mobile sites, which adds complexity for retailer mobile strategies. These trends suggest that, in the longer term it is expected that Android customers will become highly valuable and companies around the globe which offers m-commerce services would design their products specifically for Android customers. The online venders are required to explore such trends and change their m-commerce approach to create a strong presence on every device and platform with a reliable experience to users (Kenney and Pon, 2011).
The potential customers of mobile payments services are from the 25 to 34 years of age group, with 78% in this age group. Furthermore, the most purchased services are music, which is followed by books, travel tickets, electronic products and apparel. Study also reveals that mobile purchase choices is more dependent on convenience rather than price because users are selecting high-value items like hotels, train tickets and clothing together with the economic products. In conclusion it can be said that consumers are growing more comfortable shopping on mobile and Apple mobile payment buyers spend more time and money than Android mobile payment buyers.
Security, legal and ethical issues in m-commerce
The e-commerce implementation comprises several legal issues. These issues can be classified in varied manner, such as jurisdiction over trades, internet gambling and encryption policies. On the contrary, the ethical issues are concerned with what is considered to be wrong and right. There are many significant policy issues raise by the mobile commerce, specifically in relation to inadequate disclosure of information, unsolicited sales and minor protection. Besides this, SMS spam and unauthorised use are some additional issues (Mehra, 2015).
A high risk of crime is being carried by the wireless network. Hackers can erase and steal data and information from the cell-phone devices and disrupt the traffic on wireless network by overloading it with phone messages and information. The mobiles are also infected by virus, which cause them to randomly switch of or erase all information and addresses from it. Based on the surveys of Georgia Tech (1997 and 1998), the internet face most significant issues in relation to privacy, taxation, encryption, navigation and censorship (Niranjanamurthy and Chahar, 2013).
In particular, the privacy has long been a social and legal issue in many countries. With the increasing and broad use of e-commerce and internet, the privacy issue becomes more challenging. In this regards, an organisation known as the Electronic Privacy Information Centre is constantly working on safeguarding the privacy (ROTENBERG et al., 2003). The e-commerce security is an important portion of Information Security framework and is especially pragmatic to the constituents that creates impact on the electronic commerce including Data security, Computer Security and several other wide Information Security framework realms. The security at e-commerce has its own specific nuances and is considered as the key visible security constituents, which influence the end user by their day to day payment transactions with the organisation. Therefore, security and privacy in today’s internet era are the main consideration for e-commerce and m-commerce technologies (Massoud, n.d).
In addition to above, the privacy concerns in m-commerce have been also identified in revealing less trust in several contexts, like commerce, electronic health records, technology of e-recruitment and social networking that directly influence the response of end-users. Furthermore, the main and constant concern for the online retailers is security that restrict organisation and customers engaging via e-commerce. Also, the web e-commerce applications handle payments by electronic transactions as well as using debit and credit cards and online banking and PayPal are closely linked with the compliance issues (Mennecke and Strader, 2003).
Moreover, shopping online through websites includes several steps to buy a commodity with complete security and safety. The online mobile transactions require customers to reveal a large number of sensitive personal data to the seller by placing themselves at a great risk. Thus, comprehending and gaining trust of customers is significant for the m-commerce regular development. Also, the function of electronic payment in online shopping is the main issue to ensure that customers are convenient and fast as well as to ensure the parties secrecy and safety to a transaction that requires a complete electronic systems of trading (Caudill and Murphy, 2000).
Conclusion
It can be concluded that e-commerce is mainly considered as the products selling and buying over the internet, but any transaction which is solely accomplished through electronic systems can be called as e-commerce. The concepts of m-commerce and e-commerce is playing a great role in today’s retail businesses, as people utilising mobile devices for their transactions and purchases are regularly increasing around the globe. However, the e-commerce is not free from several securities, ethical and legal issues, due to the unauthorised use, destruction, alteration and access over the retailers’ site. The fraudsters are continuously looking to take benefit of online shoppers, who are liable of making novice errors.
Some common mistakes that leave customers at risk include shopping on insure websites, leaving the devices open to viruses and providing too much sensitive or personal information. Therefore, the online retailers are require to apply proper ethical standards to their online transactions and selling practise, in order to gain customers trust and offer them safe and secure shopping method. It is because all the business aspects are greatly affected by ethics. Also, it creates impact on the brand image and subsequently the advertising, marketing and selling functions of the business. Thus, in order to keep up and increase revenue with growing mobile uses and online shopping behaviours of customers, the sellers needs to consider code of conduct related to m-commerce operations.
References
Caudill, E.M. and Murphy, P.E., 2000. Consumer online privacy: Legal and ethical issues. Journal of Public Policy & Marketing, 19(1), pp.7-19.
De Silva, G.H.B.A., 2015. Determinants of Online Buying Behavior.
Fulgoni, G.M. and Lipsman, A., 2016. The Future of Retail Is Mobile. Journal of Advertising Research, 56(4), pp.346-351.
Jones, M.A., 1999. Entertaining shopping experiences: an exploratory investigation. Journal of retailing and consumer services, 6(3), pp.129-139.
Kenney, M. and Pon, B., 2011. Structuring the smartphone industry: is the mobile internet OS platform the key. Journal of Industry, Competition and Trade, 11(3), pp.239-261.
Kim, Y.K., 2002. Consumer value: an application to mall and Internet shopping. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 30(12), pp.595-602.
Kumar, H., 2016. Mobile Commerce Trends to Buy Into. The Experience, M-Commerce.
Massoud, S.L., n.d. Ethical and Legal Issues in E-Commerce.
McDermott, J., 2014. The future of retail in 5 charts.
Mehra, J., 2015. E-commerce: Opportunities and Challenges. The International Journal of Business & Management, 3(1), p.182.
Mennecke, B.E. and Strader, T.J. eds., 2003. Mobile commerce: technology, theory, and applications. IGI Global.
Niranjanamurthy, M. and Chahar, D.D., 2013. The study of e-commerce security issues and solutions. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 2(7).
Rigby, D., 2011. The future of shopping. Harvard Business Review, 89(12), pp.65-76.
ROTENBERG, M., BUTLER, A., MCCALL, G., HORWITZ, J. and HUSBAND, D., 2003. Electronic Privacy Information Center.
Sadeh, N., 2003. M-commerce: technologies, services, and business models. John Wiley & Sons.
Saha, D. and Mukherjee, A., 2003. Pervasive computing: a paradigm for the 21st century. Computer, 36(3), pp.25-31.
Siau, K., Ee-Peng, L. and Shen, Z., 2001. Mobile commerce: promises, challenges, and research agenda. Journal of Database management, 12(3), p.4.
Smith, C., 2014. THE E-COMMERCE REPORT: Mobile Is Giving Traditional Retailers A Chance To Bounce Back These Holidays.
Tauber, E.M., 1972. Why do people shop. The Journal of Marketing, pp.46-49.
Tilson, D., Sorensen, C. and Lyytinen, K., 2012, January. Change and control paradoxes in mobile infrastructure innovation: the Android and iOS mobile operating systems cases. In System Science (HICSS), 2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on (pp. 1324-1333). IEEE.
Wang, Y.D. and Emurian, H.H., 2005. An overview of online trust: Concepts, elements, and implications. Computers in human behavior, 21(1), pp.105-125.
Other Relevant Blog Post
I do hope you enjoyed reading this post on the evolution of M-Commerce. There are many other titles available in the IT Dissertation Collection that should be of interest to information technology and computer science students and information technology professionals. There are many dissertation titles that relate to other aspects of information technology such as Network Security, Information Systems, ERP, Software, IT Infrastructure, Programming, Telecommunications, eLearning, eCommerce, Wireless Networks and Systems Analysis. It took a lot of effort to write this post and I would be grateful if you could share this post via Facebook and Twitter. Feel free to add your thoughts in the comments section. Thank you.