HR Metrics and Workforce Analytics
In the current business environment where competition and technological advancement is on the rise, it is imperative for the HR function to be on the forefront in enhancing the success of the business. One of the ways in which the HR function can help improve the work-ability of the business is by ensuring the workforce and the activities that relate to it bring the maximum returns to the company. As such it is pivotal to use the HR metrics and job analytics to track the return on investments channeled to the workforce. In the recent past, organizations have realized the importance of a balanced scorecard for the HR department (Smith, 2013). It is through this score card that the organizations have adopted the use of HR metrics and job analysis to measure the efficiency and the effectiveness of the workforce and use this information in decision-making.
One of the reasons that have led to an increased interest in HR metrics is the use of the data obtained from the metrics and job analytics towards improving the effectiveness of the company. The data obtained from the metrics acts as a basis in which the management can make major decisions for the improvement of the company and achieving the company’s goals. As such, the data acts as a thermostat that can measure the current situation and use the information in decision-making (Smith, 2013). Since the workforce comprises a major asset to the company, it is critical to ensure that decisions based on HR have facts that back them.
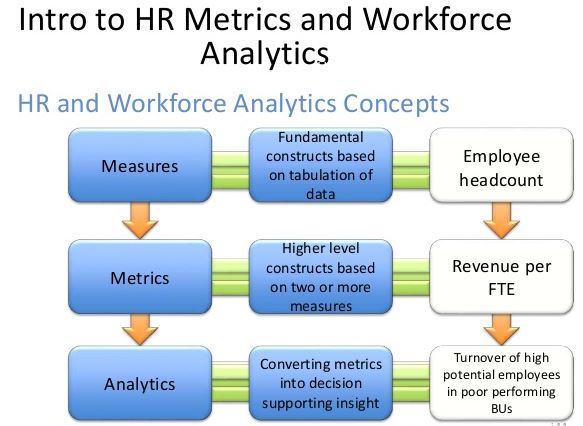
Additionally, organizations have realized that the use of technology in analyzing the HR function has the ability to save time and resources. Essentially the human resource department has the obligation of ensuring that the value of money and time spent in HR activities has major returns for the company. Therefore, it is their duty to provide the management with essential information that they can use to make decisions based on efficient use of the organization’s time and money (Sullivan, 2003). Using the HR metrics and job analytics, the HR department is able to track down the changes and trends in the workforce variables. Further, organizations can monitor the effectiveness of the activities based on people, process, and productivity. Thus it becomes easy to measure the value of time and money spent by the organization in the HR department.
The cost of HRIS is usually a debatable issue among organizations. However, it is important to realize the benefits that come with the use of HRIS in the HR department. For instance, when the HR uses the metrics and job analysis to analyze the cost per hire, the organization gets the facts on the amount it is using to hire. As such, it gives the organization the opportunity to find out whether the amount of money used in hiring is spent on the right people. In essence using the job analytics during the hiring process saves the company the situation where it could hire the wrong people for the job and consequently reducing the turnover rate in the organization (Sullivan, 2003). Primarily this justifies the cost of HRIS.
Additionally, the HR function spends the highest money in most organizations in terms of pay and allowances. Therefore, it is imperative for the organizations to ensure that they reap the most from the services offered by the workforce. Through the use of HRIS, the department can account for the training ROI in which the company spends money (Sullivan, 2003). The training returns on investment ensure that there are maximum financial gains from a training function to the employees. Without the use of this HRIS the company may make losses in training.
It is a significant loss to lose a valued employee by the organization. Therefore, it is important for the organization to have a functional HRIS that keeps track of the employees’ performance and improvements (Smith, 2013). For instance, using the manual employee tracking system may be compromised due to the human nature of being faulty. Such instances may lead to increased turnover and talent mismanagement. Thus a good HRIS saves the company all these losses.
References
Smith, T. (2013). HR analytics. Create-Space Independent Publishing Platform
Sullivan, J. (2003). HR metrics, the world-class way. Peterborough, NH: Kennedy Information.
Other Relevant Blog Posts
Best HRM Dissertation Topics For University Students
IHRM Human Resource Management
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to HR metrics and workforce analytics in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.
