Business Management Essay Topics
Below you will find a great range of business management essay topics for you to purchase. These business management essay topics are here to help inspire you in creating your own Business essay or assignment. Our sample business management essay topics will prove helpful in formulating your own dissertation topic, objectives, literature review, methodology and analyses. Our sample Business essays are an ideal tool for any student struggling to start their own business management essay topics.
Business Management is an essential part of any organisation and there are many elements of Business Management. By browsing our collection of business management essay topics, you will get ideas for your Business essay through the following Business subjects: Global Business, Business Strategy, Corporate Social Responsibility, Change Management, Project Management, Organisational Behaviour, Leadership, Globalization, Strategic Management, Entrepreneurship, Technology and Innovation Management. We hope you find the business management essay topics you are looking for.
Click Here To View Business Management Essays
MBA Change Management Assignment: Snap-on Incorporated. For an organisation to remain competitive, flexible in changing market conditions and at the forefront of their particular market segment, change has become an essential part of the management process. Change does not necessarily have to form part of the day-to-day operations once a particular activity has been agreed. However, to prevent as little disruption to normal business practices as is completely necessary the resultant effect of the change must form part of the organisations longer term, three to five year, strategy. Snap-on Incorporated is a global leader and developer of automotive diagnostic solutions and, over the last several years, has been faced with stiffening competition and the threat of new entrants from diverse markets. Snap-on Incorporated has throughout this time been reorganizing its facilities in order to sustain these challenging times and prepare itself for long term growth. It is now time to review how the recent change activities have aligned Snap-on Incorporated to ensure long-term success. [2,000 words]
Management Theory: Conflict Is An Essential Part Of Management. Conflict is a state of mind. It has to be perceived by the parties involved. If two or more parties are not aware of a conflict, then no conflict exists. This broad definition encompasses conflicts at different levels within an organisation. Conflicts are based upon differences in interest and values, when the interests of one party come up against the different interest of another. Parties may include shareholders, managers, departments, professionals and groups; while conflict issues can include dividends, control and wage levels. [2,300 words]
Management Theory: Analysis Into Approaches & Evolvement Of Management. There are a number of management theories that have emerged and evolved over the years. The importance of management theories didn’t materialise until the Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries. The growth of large organisations with high concentrations of people and resources in one area created a need for co-ordination and organisation which highlighted the need for management [3,300 words]
High Quality Business Management Essay Topics For University Students
Management Theory: An Evaluation of Taylor and McGregor’s Management Theories. Organisational theories develop from different backgrounds, experiences, and way of life and through unique set of frameworks, which in retrospect offer new perspectives to old conceptions and theoretical frameworks. Organisation theory can be defined as the study of the structure, functioning and performance of organisations; and the behaviour of groups and individuals within them [4,000 words]
Change Management: Human Relations & Organisational Behaviour. Change is an organizational reality. External forces for change include the marketplace, government laws and regulations, technology, labour markets, and economic changes. Internal forces of change include organizational strategy, equipment, the workforce, and employee attitudes. Changes within an organization need a catalyst. Managers can serve as change agents by becoming the catalyst for change in their units and by managing the change process. People who act as catalysts and assume the responsibility for managing the change process are called change agents. Any manager can be a change agent. A no manager can also be a change agent. Internal managers who act as change agents may be more thoughtful and possibly more cautious. As change agents, managers initiate change because they are concerned with improving their organization’s effectiveness [1,700 words]
Keep Scrolling Down For More Business Management Essay Topics
Demand Chain Management. Demand chain management can be seen as a further development to the existing supply chain management theory. Demand chain is essentially a concept that focuses more on the market need than on the efficiency of supplying the product. This concept is becoming more relevant as manufacturers strive to be more competitive by adopting mass customization approach [3,000 words]
Analysis into Knowledge Management. There are major obstacles to the management of knowledge. The most important one is the people in the organisation. Knowledge is in people’s heads and therefore, without them there would be no flow of knowledge. People can be obstacles to knowledge management if they do not seek advice and learn from others; this could be because of psychological reasons such as pride or maybe because the environment is not the one that encourages a flow of the knowledge [2,000 words]
Vast Collection of Business Management Essay Topics
Management Theory: Managing Diversity within the Organization. Diversity within the workplace has certainly increased over the last decade, being a key issue among organizations of today. This paper will identify and discuss some of the important issues when managing diversity within the workplace. The paper will also document numerous key challenges that managers face regarding workplace diversity. Key strategies to overcome such challenges will be employed. Finally, some important opportunities and benefits that arise as a result of workplace diversity will be examined [2,000 words]
MSc Procurement Management: Managing Relationships & Multicultural Negotiations. The reform and open door policies initiated by the Chinese Government through its Ten Year Programme for Social and Economic Development in 1978 has led the country to unprecedented economic growth. The key strategy that was adopted by the Chinese in order to accelerate these reforms was to attract foreign investment frequently in the form of joint ventures. These joint ventures are often complex processes and should not be underestimated by foreign executives. Specific consideration must be given to the negotiation process at which time difficulties such as language, cultural differences and political barriers will develop [3,000 words]
Best Business Management Essay Topics For University Students
MBA Strategic Management: A Strategic Appraisal of Vodafone. The aim of this report is to appraise Vodafone’s current strategic direction and choices with a view to making relevant recommendations on options for future direction. Vodafone appears to be at crossroads strategically, it has reached what may be termed a mature stage as a company and investors are applying increasing pressure due to what they see as under performance by the company. Includes PEST, SWOT, BCG Matrix, Ansoff Matrix and KSF analysis [17,000 words]
We Have A Large Collection of Business Management Essay Topics
MBA Project Management: Analysis of the Success of the Channel Tunnel. The purpose of this report is to determine whether the Channel tunnel project was a success or a failure as a project management exercise. Based on the supporting documents and investigation into the project the following report will identify key aspects of project management, fundamental to any project succeeding, and if these have been applied. Necessary recommendations at the end of this report will support any findings. Initial reports would support the decision that this project was a failure due to the fact of it costing twice the original planned budget, the final product being delivered several years late, loss of life during the project life cycle and numerous well documented failures of rolling stock and significant lapses in security arrangements [2,000 words]
Business Management: Low Costs Airlines – What Impact Have They Had On Tourism? The report will look at how, and in what way, low cost airlines affect tourism. While air travel was once a luxury only the rich could afford, the entry of more airlines serving the busiest and most profitable routes has caused airfares to plummet. Some of the airlines that will be analysed are Buzz, Go, Ryan Air, and EasyJet. These are well known low cost airlines [1,600 words]

Analysis into Organisational Behaviour. Hackman’s model identifies a causal link between group effectiveness and factors related to the task, group composition, managerial support and processes of the group. The implication is that when these factors are favourable, the result will be a greater level of group effectiveness, determined by such outcomes as the acceptability of the output, meeting of team members’ needs and the continuity of the group. The model asserts that challenge, complexity and interdependence are requisite task characteristics for maximum group effectiveness for the sake of efficiency and succinctness, it will be assumed henceforth that this is the ultimate objective and justification for recommendations proposed [3,000 words]
Contemporary Management Theory: Analysis into Customer Relationship Management (CRM). The management of customer relationships has changed in the past decade. Previously, organisations had a very personalised relationship with customers that can be referred to as ‘one-to-one’ relationships. It was argued that companies were able to do this -at the time -due to their refined customer base, where they were able to customize products to suit individual needs and tastes. As a consequence, customers remained satisfied and loyal. In the mid 20th century, however, product availability increased substantially and so changed the way organisations have relationships with customers. Evidently, companies lost the uniqueness of this relationship and the ability to track customers’ ever changing needs and wants. Presently, however, organisations are very much looking to regain this one- to-one exchange, to establish loyalty in a very competitive market place. Subsequently, a new phenomenon of customer relationship management (CRM) has been introduced. This includes the management’s guidelines that are needed to develop the long-term relationship between organisations and customers, which they crave. The initiation of this management issue has sparked criticism however, where its application has been described as ‘just another buzzword’. Yet other theorists have contradicted this idea and denoted it as ‘the holy grail’ [8,000 words]
Where Can I Find Business Management Essay Topics?
Using relevant theories, discuss critically the validity of the contention that the motivation for staff to work well depends on more than a high salary and good working conditions. All people who work within an organisation need to maintain a level of motivation for a company to exist. Organisations are required to be financially viable, and the staff they employ are needed to ensure that this occurs – if these members of staff carry no motivation, then the company for which they work will incur major problems. What I intend to do, is to analyse proposed theories on this subject, in order to establish what it is that provides worker motivation, and which providing factors need to be considered [2,500 words]
Marketing Communications Strategy: Analysis Into Marketing Communications of Sainsbury’s. Sainsbury’s main objective is to increase sales to retain their number one spot in the supermarket industry within the UK. Sainsbury’s goal to achieve their objective is by delivering an improved quality shopping experience for its customers with high quality products for low prices. Sainsbury’s are trying to gain back the customers that they have lost in the past years. Today Sainsbury’s are competing against the major leaders of the supermarket industry. These include Tesco who happens to be the market leader in the UK, ASDA which Wal-Mart took over and also happens to be the market leader in the world, and Morrison’s which is also a well-established supermarket retailer [2,000 words]
Browse Our Business Management Essay Topics
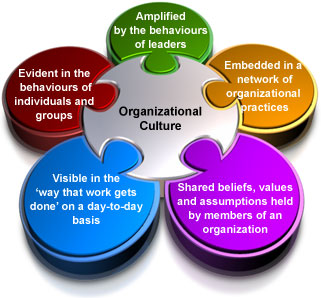
International Management: Management Styles In India. This MBA essay discusses about the organisational culture of India and than compare its culture with cultures of UK and Japan. It will be done with the help of different models. Like human civilisation, where they have a set of values, beliefs, traditions and behaviours, which define the way the people live on day to day basis, every organisation have its own culture, which defines the ‘way the things are done here’. These cultures are mainly influenced by the society or country, these organisations are operating in. India is an emerging market in the global market, therefore most of the management researchers are trying to figure out the kind of management and leadership styles that are used in India and which can be useful for foreign corporations to be used in India. These researchers have found that the westernised management styles can not be used in India because of its history and family oriented business [2,500 words]
Global Advertising: Ford Fiesta Project. This project focuses on the Ford Motor Company and its take on advertising. The project aim is to analyse competitive advertising in the car manufacturing industry. In 2005 Ford came third in the world ranking of car makers behind General Motors and Toyota. Ford has exited for over 100 years and has managed to penetrate global markets on a large scale and is thus recognized worldwide as a leading brand. Nonetheless, Ford itself, aside from its sister brands, is not positioned in the premium market. In fact, the main advert that we have selected portrays Ford’s Fiesta Zetec Climate, which is priced from £8,995. Similarly, prices for Ford cars in the UK range from just over £7,000 for 3-door hatchbacks up to £20,000 for 7-seaters with vehicle (mainly vans) prices ranging from £10,000 to £23,000, which clearly positions Ford in the affordable prices market [2,300 words]
Top 50 Business Management Essay Topics
MBA Project: Market Analysis Of LG Consumer Durables & Dealer Development In India. Before the liberalization of the Indian economy, only a few companies like Kelvinator, Godrej, Allwyn, and Voltas were the major players in the consumer durables market, accounting for no less than 90% of the market. Then, after the liberalization, foreign players like LG, Sony, Samsung, Whirlpool, Daewoo, and Aiwa came into the picture. Today, these players control the major share of the consumer durables market. Consumer durables market is expected to grow at 10-15% in 2007-2008. It is growing very fast because of rise in living standards, easy access to consumer finance, and wide range of choice, as many foreign players are entering in the market [10,000 words]
MBA Project: Analysis Into The Major Segments In The Indian Retail Market. The retailing sector of India can be split into two major segments. They are the informal and the formal retailing sector. The informal retailing sector is comprised of small retailers. For this sector, it is very difficult to implement the tax laws. There is widespread tax evasion. It is also cumbersome to regulate the labour laws in this sector. As far as the formal retailing sector is concerned, it is comprised of large retailers. Stringent tax and labour laws are implemented in this sector. If the retail industry is divided on the basis of retail formats then it can be split into the modern format retailers and the traditional format retailers. The modern format retailers comprise of the supermarkets, Hypermarkets, Departmental Stores, Specialty Chains and company owned and operated retail stores. The traditional format retailers comprise of Kiranas, Kiosks, Street Markets and the multiple brand outlets. The retail industry can also be subdivided into the organized and the unorganized sector. The organized retail sector occupies about 3% of the aggregate retail industry in India [10,000 words]
Strategic Business Management Essay Topics
Project Management and Control & IT Project Management Methodologies. IT project has deliverables: a delivery date and a budget, and each stage of the project lifecycle carry its own risks. Since IT projects are often difficult to estimate and manage, the project should not be allowed to go from one phase into the next until a formal Risk Assessment has been performed, in order to achieve deliverables and expectations and to meet with user’s satisfaction. Risk assessment can take place at any stage and during any time of the project lifecycle, though the sooner the better. In this paper risk management and assessment in the early stages of IT projects will be discussed, along with methodologies on project management that will help ensure that a project start off with a reasonable chance of being successful. Emphasis will be on the TenStep methodology [3,500 words]
Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurial Behaviour. There is a common understanding that entrepreneurs in general can be stereotyped, however all entrepreneurs are different, and subsequently the reasons for why they initially start their businesses is unique to each of these individuals. Due to this it does not exist any valid general agreement on what the definition of what an entrepreneur is. Likewise, there exists multiple differences within social entrepreneurs. What is clear, however, is that social entrepreneurs differ from other entrepreneurs in their mission of creating superior social value for their clients. In today’s society, the common consensus of improving the world through social responsibility and environmental accountability seem to attain growing importance. We are increasingly becoming more educated in terms of the augmented social needs in our integrated world, and therefore social entrepreneurship is attracting an increased amount of talent, money and attention from multiple sectors [5,000 words]
Keep Scrolling Down For More Business Management Essay Topics
Leadership: Donald Trump & Sir Richard Branson. The chosen leaders of our team are Donald Trump and Sir Richard Branson, each possessing extraordinary leadership skills, allowing them to soar high in their respective enterprises and succeed. They are among the most prolific brand builders in the world, irrepressible businessmen whose corporate empires are created in the image of their over sized personalities. Donald Trump and Richard Branson continue to extend the reach of their personal brands to remote corners of consumerism which is fueled in part by their showmanship. They are a study in contrast: Donald Trump, the boastful, button-downed, grim Yankee deal maker who has ridden the real estate boom and his personal myth making to phenomenal business success; Sir Richard, the toothy British adventurer who sprouts new businesses as quickly as the hairs of his bushy goatee [4,500 words]
Global Business Management Essay Topics
Methods for Managerial Decisions: Application of Inferential Statistical Tests in Quality Control. Technology is moving forward with contactless products. Contactless products allow the consumer to purchase without a human intervention while using electronic technology to make purchases or payments. The most valued part of this new technology is that the consumer is apt to use this type of ‘card’ more often, thereby increasing the credit card company’s revenues. “Issuers hope contactless technology will help them convert the mostly cash payments at such locations into card transactions. The magnetic strip will remain on the cards for now for larger purchases [2,000 words]
What is Six Sigma? Six Sigma has been sweeping the business world with remarkable results to the bottomline of many organizations since its adoption in the late Eighties, driving breakthrough improvements in product and service quality. Today Six Sigma as a business strategy has been proved to be successful in reducing costs of poor quality, improving cycle times of various processes, eliminating errors or defects from processes, enhancing customer satisfaction and so on. So what is Six Sigma? [2,500 words]
University Business Management Essay Topics
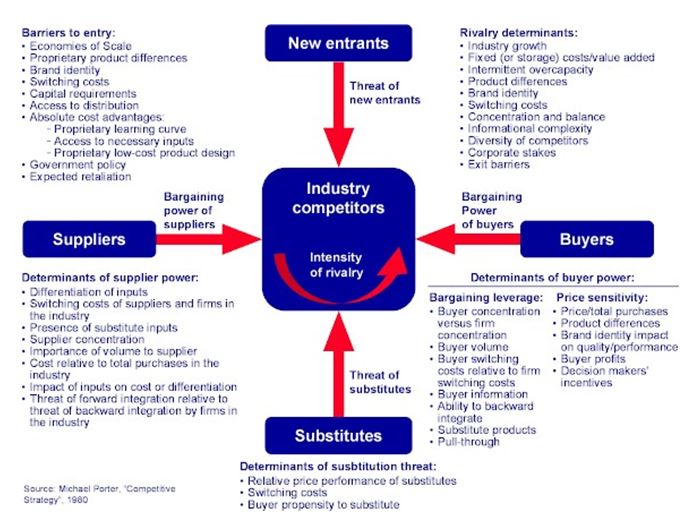
Porters 5 Forces – The BBC. Knowledge of the environment in which a firm operates is vital for it to work at full efficiency and achieve its goals. The BBC was the first national broadcasting organisation and was founded on 18 October 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company Ltd; it was subsequently granted a Royal Charter and was made a publicly funded corporation in 1927. The corporation produces programmes and information services, broadcasting globally on television, radio, and the Internet. The stated mission of the BBC is “to inform, educate and entertain” (as laid down by Parliament in the BBC Charter); its motto is “Nation Shall Speak Peace Unto Nation”. In this paper, I will analyze issues facing the BBC using Porter’s 5 forces [2,500 words]
Business Analysis – Lidl. Question 1: Use the model of input/output procedure and critically analyse the importance of managing resources and identify the techniques that have been applied to deliver Lidl’s outputs. Question 2: Discuss and provide the evidence of Lidl’ main operation performance objectives to remain competitive in retail industry? Question 3: Apply Slack, Chambers and Johnston’s adaptation or Parasuman’s SERVQUAL Model to discuss how quality gaps can be diagnosed; and evaluate how Lidl’s quality planning and control can be improved by understanding any gaps evident from your examination of customers/operation domains [2,000 words]
Undergraduate and Postgraduate Business Management Essay Topics
Critically evaluate a B2B organisation of your choice – Yahoo. In this report it is my aim to critically evaluate a B2B organisation in order to gain a sound knowledge of the business, the area it operates in and also to be able to make recommendations in how the organisation can improve. Typically B2B organisations tend to be out of the spotlight of customers, as it is there nature to operate business to business. Examples of these kinds of organisations include IBM, EMAP and obviously more well known Microsoft. They operate on a grand scale within the B2B sector and are obvious choices when discussing B2B organisations [2,500 words]
Business Operations: AAPL vs. DELL. Over the years many businesses and corporations has been changing PC’s to Mac because they found that Mac was much easier to use and user friendly and smooth in just about every way, and due to lack of services provided by the Dell customer care services, if they had a problem they would call it a nightmare because it would just take almost forever for them to get something done, unlike Apple services which is known to be excellent and fast. Apple Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries design, manufacture, and market personal computers, portable digital music players, and mobile communication devices, and sell various related software, services, peripherals, and networking solutions. Dell Inc, was founded in 1984 and is headquartered in Round Rock, Texas, together with its subsidiaries, engages in the design, development, manufacture, marketing, sale, and support of computer systems and services worldwide [2,500 words]
Keep Scrolling Down For More Business Management Essay Topics
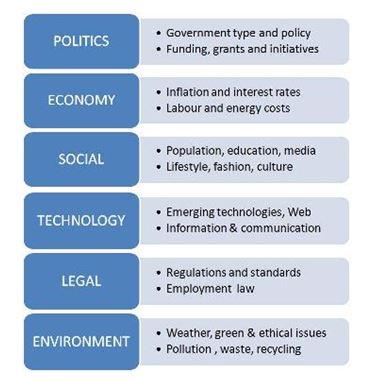
MBA Global Business Context: Retail Banking Industry; Focusing on the Changes in the Market Industry and Cross Border Restructuring. For the past ten years a serious changes have been occurring in the banking industry. Significant transformations can be noticed in the financial sector market structure due to the mergers and acquisitions. Decrease in credit institutions operating in the Western Europe and noticeable increase in concentration and competition. Additionally the total value of assets increased in all examined countries. Western Europe market as a whole saw an increase of almost 100% in the asset value. The total number of operating banks declined to around 7000 institutions, a decline of 30% during the time period. The concentration ratio increased in majority of the countries with Estonia and Netherlands holding the biggest CR5 ratios. The number of micro and macro environmental factors contributed to the changes in the industry. The most influential and therefore important were political factors, including changes in regulations and policies regarding consolidation in the banking sector. Economic, Social and Technological factors were less effective with economic growth being the most influential force [2,800 words]
Global Business: With Reference to Business Fortunes, Compare and Contrast the Economies of India and China. In this assignment, I will be investigating India’s and China’s background and comparing their economies to develop an understanding of their position in the world economy and how it was achieved. In addition, I will be looking at the differences in their economic growth as well as problems both countries may encounter as they try to become the world’s leading economies. My assignment will be supported by books such as The Business Environment by Ian Worthington and Chris Britton as well as the internet. The key indicators which affect the economy are growth, population and gross domestic product [1,500 words]
MBA Business Management Essay Topics
Global Business: Russia’s Accession to the WTO Discuss Barriers and Opportunities of This Entrance. Russia’s entrance in the World Trade Organization is very actual issue today and this is very important for Russian business and economic environment. This issue is important also for the other countries which are members of the WTO, because World Trade Organization’s main objective is to develop and facilitate open international trading system and adjudicate trade disputes between or amongst member nations. As the Georgia is the member of the WTO it is very important for us, whether Russia will enter this organization or not. The main purpose of our project is to discuss positive and negative consequences for Russia that might result from entering the WTO, will they gain much by entering this organization or they will not. We will discuss why President Vladimir Putin made it a top priority to enter the World Trade Organization [3,000 words]
We Offer Example Business Management Essay Topics
Managing Culture using Hofstede’s 5 Cultural Dimensions & Trompenaar’s 7 Cultural Dimensions. Power Distance means the less powerful members of organizations accept and expect that power is distributed unequally. In high power distance countries, such as India, Mexico and South Korea, employees always accept and obey superior therefore the organization’ structure is centralized and tall. On the other hand, the structure of low power distance countries, for instance Finland, Ireland and Austria, is flat and decentralized. Universalism versus Particularism, universalism search for general rules and applies judgment to every circumstance. While, particularism look for finding exemption and judgments are influenced by relationships and environments [3,500 words]
MBA Project: Management People and Organisations Assignment Employment practices at A & B. In order to fully understand the marketing directors proposal, a situation analysis technique known as SWOT” has been used to identify the salient points. Also, underpinning my theory is the HRM “Warwick Model”. Influencing factors of Warwick Model: (a) More clearly illustrates the effect of external forces. For example; the political, technical, competitive and economic climates on internal decision-making. (b) Recognises the influence, internal culture, leadership and structure has on business strategy and the HRM context. (c) Acknowledges the effect that work systems, reward systems and employee relations have on the ability to deliver business strategy. (d) Supports the view that the workforce is a valued resource and key to the organisational development [3,000 words]
Supply Chain Management & Logistics Strategy. Identify and critically evaluate the major supply chain issues of conventional volume car manufacture and explain how these issues had been addressed by the Smart Concept and Logistics at MCC. The smart car is definitely one of the best innovations of the hundred years. It is usually the simplest businesses on this planet that generates profit while materializes ecological safeguarding visions. The smart car is definitely an ideally little auto that is made from synthetic whole body panels as well as a strengthened metal covering, which suggests less energy and heavy-industrial substances necessary in the process of producing them. The best characteristic in this auto is its superb fuel gas consumption. Quite simply, the smart car is petrol useful, which will not, just helps the car owner reduce your bills gasoline, but additionally minimizes the Carbon dioxide release from shedding the gasoline, for that reason tremendously contributes to the safeguarding of our environment [2,500 words]
Keep Scrolling Down For More Business Management Essay Topics
A Strategic Analysis of United Parcel Service (UPS). United Parcel Service (UPS) is one of the oldest and most successful courier companies in the world. It was founded in the year 1907 and started as a messenger company in the United States of America. Sine their humble beginnings UPS has grown from strength to strength to a $36 billion dollar corporation. UPS is a multinational company and is one of the world’s most recognized and admired brands around the globe. They are also one of the largest package delivery companies in the world and a major competitor of FedEx and DHL in supply chain management operations. Every day, they manage the flow of goods, funds, and information in more than 200 countries and territories worldwide [5,500 words]
International Trend Analysis – The Evolution of Green Cars. Change is a phenomenon that affects all aspects of life. In the business sector, change determines the directions taken by business venture. The survival of any business venture is largely dependent on how the sector responds to change. There are trends in a business environment that acts as indicators of the possible events in a sector. The current automobile industry is a product of trends in the world social economic front for the last century. The car has become an integral part of modern society and therefore subject to the changes in every society. Source of energy to the automobile engine has been subject to different market trends. The history of the car is characterized by shifts from the steam driven engine where coal was the major energy source to use of oil [4,000 words]
International Business Management Essay Topics
MBA Change Management Assignment – Leadership challenges to the communication silos in business organizations. Overcoming numerous barriers in organizational communication is one of the major challenges for managers in business organizations. In business literature, a silo is defined as an organizational entity that resembles as an information container working as a communication barrier to other organizational entities. The objectives of the current study are to investigate the communication silo and its cause and impact on Royal Greenland and to provide suggestions to overcome this barrier. The method of the research is qualitative where a cumulative method of data collection and analysis were followed. It has been found that Royal Greenland lack of a proper corporate culture, and the communication silo existed in every corner of the organization, where the senior managers were actively involved [6,000 words]
Analysis of Apple Inc. business Strategic Unit (iPad unit) Apple is an American-based multinational company that deals in the sale and design of personal computers, computer software plus a range of hand-held gadgets. Apple Inc. is best known for its hardware products branded as Macintosh. Started in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Apple has grown to become one of the current day’s iconic designers of consumer electronics. Although Apple deals in a wide range of products, the company treats every product line in a unique way. Each product of Apple is treated as a standalone business unit. This report singles out the Ipad product of Apple Company and analyses this business unit in terms of its strategic competitive position, its external environment and the value addition proponent of its strategic position. This report is based on the UK market [3,000 words]
Case Study of the Strategy Adopted by Japan Airlines Corporation. By external and internal analysis as well as SWOT analysis, the report points out the strength and weakness of JAL, analyses the opportunities and threats of JAL, and puts forward the three key strategic issues confronted by JAL, i.e, financial crisis, lack of capital, overdue liabilities and the inability to maintain sustainable development; the decrease in attendance due to external factors such as economic crisis and security issues, etc; redundant organization structure, low efficiency in operation, high human resource cost, all of which lead to heavy burden on the JAL. By Ansoff Matrix analysis, the report puts forward the three strategic options faced by JAL: market penetration, market development and diversification. By comparative analysis, the report indicates the adoption of market penetration strategy would be the optimal choice for JAL and there are two issues to be resolved if JAL adopts market penetration strategy [3,000 words]
More Business Management Essay Topics Available
MBA Operations Management Essay. Operational Management is a subject which applies for every organization as well as for individuals, from accomplishment of organizational goals to run the day-to-day operational activities. In this report author will discuss an operational issue which face by a leading Sri Lankan financial institute. And currently they are experiencing some bottleneck effects along their lending process and it started to cause long delays which lead to unsatisfied customers, time waste as well as frustration among staff members. Through this report author will describe what the causes for process constraints are and propose a set of recommendations and processes with the use of operational management theories to overcome these issues [4,500 words]
Critically evaluate the extent to which the growth strategies of large MNCs in China are affected by local institutions. The paper examines the ways in which indigenous Chinese firms are competing with FDI influx in China and how MNCs operating in China are trying to come out victorious in face of such stiff competition. International Marketing is a subsystem of marketing that thrives on the interaction of nations since it involves business transactions across the borders and is therefore grossly transnational in nature. These transactions help turn geographical boundaries into frontiers and therefore influence the world markets immensely. Since most developed nations are slowly turning towards a more and more services sector centric economy, and the retail sector being one of the foremost of the industries dominating the services sector across the world, international business cannot afford to do away with the impact that the retail sector has made on the economy [2,500 words]
Total Quality Management (TQM). This paper examines critical factors of TQM Implementation in most popular electronics companies, Samsung and Apple. Various levels of researches have been made to evaluate the performance, predictions, workouts and requirements not only for company’s personal growth but also for customer’s satisfaction. This research paper covers Total Quality Management of two giant companies representing their quality control system against their software whether it’s mobile or relative product. Need of SQA is quite demanding today as it involves 100% end user’s satisfaction where there are most likely chances of deficiencies, bugs and problems in software area nowadays [4,000 words]
Leadership Challenges to the Communication Silos In Business Organizations. Overcoming numerous barriers in organizational communication is one of the major challenges for managers in business organizations. In business literature, a silo is defined as an organizational entity that resembles as an information container working as a communication barrier to other organizational entities. The objectives of the current study are to investigate the communication silo and its cause and impact on Royal Greenland and to provide suggestions to overcome this barrier. The method of the research is qualitative where a cumulative method of data collection and analysis were followed. It has been found that Royal Greenland lack of a proper corporate culture, and the communication silo existed in every corner of the organization, where the senior managers were actively involved [5,500 words]
Keep Scrolling Down For More Business Management Essay Topics
IKEA Business Strategy. IKEA is Swedish furniture emporium. Nowadays, IKEA has become the largest furniture and household goods emporium in the world, the range of products IKEA offers focuses on better design and function at a lesser price. It offers smart home furnishing solutions for all areas of a house. The brand caters to the likes and needs of different people; for those who prefer a romantic touch, to the minimalist and everyone in between. In order to give the people a better everyday life, IKEA asks the customer to work as a partner [5,000 words]
Analysis of the internal and external business environment of Vodafone. Vodafone Group is among one of the world’s largest mobile communications companies by revenue operating in over 30 countries across the globe providing a range of communications services including mobile voice, messaging, data, and fixed broadband. The company has its operations in the United Kingdom, Continental Europe, The United Stated (under the name Verizon), Asia Pacific, Africa and the Middle East through its subsidiaries, investments, joint ventures and associates. In this report, I aim to analyze the business and management of Vodafone UK with the help of a number of models and theories to understand the internal and external environment of the company. Porter’s Diamond Model, PESTEL Analysis, Value Chain Analysis, Global Environmental Analysis and Porter’s Five Forces Analysis [4,000 words]
High Quality Business Management Essay Topics
Business and Project Management. This individual report discusses in detail the association between business objectives, programs, computer systems projects and benefits realisation. The next section discusses how a business can be organised for taking advantage of project management methodology and a PPSO (Programme and Project Support Office) for achieving the business strategy. Next part focuses on the safety management system which is incomplete without the predictions of the risk management done by proper research. These both terms are often considered as independent but these are linked together. Further the associated project structures required for implementing a project management methodology such as PRINCE2 and a review of the stages, processes and components necessary as well as how quality is discusses in detail in the project [3,000 words]
Strategic Management In Government and Voluntary Organisations. Government and nonprofit organization encounter the problem of strategic management most of the time during their operations to curb the problem it is very crucial to have better understanding of it true sense and meaning. Strategic management is defined as successful achievement of organizational goals stem from development of competent edge in the industry by the allocation of resource available at disposal and a comprehensive analysis of internal and external industrial environment in order to carve the strategies and all this is found as blessing of strategic management by managers [4,500 words]
PDF Business Management Essay Topics
Oxfam Case Study. Oxfam is a name today internationally acclaimed for their humanitarian services. The non-governmental organisation today consist of seventeen Oxfam organisations all working together in ninety-four countries around the world. The key mandate of Oxfam is an organisation, which strives to get solution to the looming poverty experienced in some countries as well as find solution also for issues, which the organisation considers as injustices globally. The organisation has been successful since they work with communities and together form a strong lobby group, which then influence those in power to ensure the poor get a chance to improve their lives through their voices. The entire different organisation under Oxfam all work in unison globally, which allows the overall organisation to achieve its objectives better [3,000 words]
We have more Business Management Essay Topics available
Other Relevant Blog Posts
Business Management Strategies
MBA Dissertation PDF Examples University
Click Here To View Business Management Essays
If you enjoyed reading this post on Business Management Essay Topics, I would be very grateful if you could help spread this knowledge by emailing this post to a friend, or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook. Thank you.