The Adoption Rate of E-Mobile Banking is an Impact of Customers’ Acceptance of Information Technology in the Banking Sector
The information and telecommunications industry had been a key enabler of productivity across the societies and economies. The IT innovation is not only a significant contributor to the economies of a state, but also towards the growth of the industries. In the present days, banking industries have felt the influence of the telecommunications by a margin among other industries. The emerging information technology trends in across states had been a concern of the researchers. Precisely, m-banking services have had an uptake as the banking industry have enhanced access of service with convenience and ease to use cell phones. This thesis study is aimed to an extensive provide research on the most influencing factors affecting adoption of the technology in banking industry. In this case therefore, the research will place focus on the m-banking services in Australian banking sector (Drennan et al., 2009). The study incorporates Technology Acceptance Model to derive a conceptual framework in order to address its objective and research questions. In this study, data will be gathered from literature reviews and analysts, questionnaires, and interviews. The collected information from interviewing 40 respondents through a survey questionnaire will be used to compare and provide discussion on the factors influencing m-banking adoption rate. Data analysis methods will include weighted mean calculation, for analyzing the questionnaire data, and regression method to test the correlations and significance of factors influencing adoption rate of m-banking.
Chapter One: Background Of The Study
Banking industry in the contemporary world has been intensive users of technologies. Since its emergence, technologies have rendered essential roles to industries to deliver quality products and services. Particularly, their essence had risen from financial technologies such as information and telecommunications across nations. In comparison of the recent IT and telecommunications services with those provided in early 1970s, it is clear that, there had been a complete transformation of technology acceptance and adoption rate in banking industries. This way, there had been numerous researches as an area of interest to scholars, managers, and scientist to explore as the apparent world has taken a new face of technology (Drennan et al., 2009).
This research paper, therefore, places attempt to further past research basing on the past theoretical views of technology acceptance model.
Research topic
The adoption rate of e-mobile banking is an impact of customers’ acceptance of information technology and telecommunications innovation in the banking sector.
Statement of the problem
The adoption rate of any advancement of technology is not guaranteed that it will translate into consumer adoption. However, consumers’ acceptance and their willingness to adopt new technology have been evidence to be a crucial aspect to the banking industry. This is especially in implementation of new product development and marketing. In which technology diffusion is partially determined whether potential users accept and adopt the technology employed.
Significance of the study
Not only scarce research on the technology acceptance and adoption had been a hindrance to the banking sector, but also a limit to managers to understand the priorities of the formation of intentions to accept and adopt mobile e-services. Precisely, this research study focus on the factors affecting technology acceptance model as proposed by Fred Davis. It seeks to expand research on the significance of the factors affecting TAM. This knowledge helps stakeholders in realizing the prevailing environment and its trends in the subject sector.
Objectives of the study
Primary objective
- To determine the significance of the factors affecting adoption of m-banking industry.
- To determine the significance of the factors influencing technology acceptance model.
- To understand consumer behaviors influence on the product development and marketing.
- To understand better on how adoption of m-banking has impacted financial services in the banking industry.
- To offer recommendation towards designing of effective m-banking marketing strategies.
- Do the potential customers perceive the relevance of the e-mobile banking?
- Do the potential customers perceive mobile e-service easy to use?
- Does the cell phone banking influence users attitude towards adoption.
- Does the intention to adopt the e-mobile banking influence consumer behavior.
Chapter Two: Literature Review
Internet mobile banking
Internet banking and mobile banking are both essential subsets of e-banking services. According to Lassar (2005, p. 177), internet banking can be defined as an electronic system that allows potential customers to perform various banking services electronically through bank’s website. It is an internet features which in the present day; mobile phones have been provided web surfing capabilities. It is an apparent trend of adoption of new mobile phones technologies that can enable users to access internet through their hand-held devices. The mobiles phones capabilities are enhanced by the wireless application protocol (WAP) cell phone banking with a similar inter-face to internet banking. Only that, the hand-held device is supported by the GPRS, WAP, EDGE, or 3G.
Internet mobile banking had been a fundamental change in the banking sector in the recent years. It is evidenced by the consumer movement from the conventional branch banking into more stand-alone banking services via electronic delivery channels than office branch. However, following the acceptance and intention to adopt new technology Chan (2001, p.10); modified the initial definition of mobile banking. His argument posits that mobile internet banking is an electronic transaction service via bank’s website by using a computer a computer and a modem to access internet. It is a field of study that researchers have considered the influence and the adoption of e-mobile banking. according to Suoranta & Mattila (2004, p. 364).typical e-mobile banking users will continue to use the wired channel while the current users of the automated bill payment and the branch offices will be shifted to mobile phone banking.
This way, cell phone banking users, cannot be drawn from the heavy internet banking users probably, because, they will continue using internet banking. Besides, he posit rationality for banks not to invest convincing its regular internet users to adopt a new electronic, but they should or rather attempt to enable potential customers outside this segment to be interested with the advantages of mobile phone banking. Precisely, the relevant performance of the new technology should be inessential issue of concern to the banking industry influence a change in accordance to customers on taste and preference.
Technology acceptance model
The initials steps required for adoption of the emerging information technology had been a hindrance of banking performance. It involves establishing which purpose the intended new system will address and what functionality the bank requires. This way, for any e-portfolio system the bank need to establish which one size fits all; corresponding to a series of standard functionalities (Zhang, et al., 2007).
Technology acceptance and its usage had been a focal point in a wide range of research studies. In this case, TAM application enabled understanding of conceptual issues related to the e-portfolio use. In which several theoretical models have been applied to provide sufficient study on user acceptance and usage behavior of emerging information technology trends. Several studies, including Roger’s diffusion theory, Theory of Planned Behavior, and Theory of Reason Action (TRA) gave inception of the Technology Acceptance Model. TAM has emerged to be preferable model that represents the preceding theories of technology usage through the profound beliefs related to the perceived usefulness and its ease of a technology. The previous researches have shown the powerfulness of TAM over other theories of the as a basis to explain the variance in systems use (Davis, 1989).
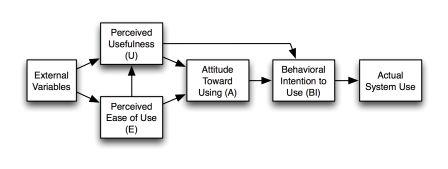
(Pearlson& Saunders, 2006) argues that, the use of TAM is predicted on the decision on or rather attention of individuals having control whether or not they accept the use of the system. The factors in the model are perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use and the attitude towards the usage of the system and adoption. The behavioral intention to use by the potential customers is the essentials factor that draws whether the users will actually utilize the information technology introduced. This way, the firm may draw critical decisions-making to enhance its performance especially in the banking sector (Ajzen& Fishbein, 2000).This theoretical view, therefore, derives the of propositions below;
Technology Acceptance Model and study of e-mobile banking
The mobile services convenience and promptness to customers had been growing concerns to academic researchers. Accordingly, a past growing body of academic research has examined the determinants of the cell phone banking acceptance and its utilization (Arora et al., 2011),.
Dillon and Morris (1998, p.5) portrays the technology acceptance as the demonstrable willingness of individuals within a group to employ IT for the designed task as intended to support. Basically, the research investigated the instrumental influences involving beliefs on how to utilize technology. This way, it results in the objectives hence improvements in the performance. (Thompson, et al., 2006) argue that non-instrumental factors may be limiting factors on the acceptance of the technology. However, the TAM posits that, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of utility are the fundamental detriment that influences an individual behavioral intention (Hu et al. 1999).
According to Laurin and Lin (2005, p. 878) research; it extended the technology acceptance model. Their perspective towards understanding of the behavioral intention to the utility of the mobile banking survey was conducted in Taiwan included the perceived credibility, perceived self-efficacy and the perceived financial costs in m-banking context (see figure 1).In their research, they revealed that, all stated factors have effects on the behavioral, and the perceived credibility is evidenced to be the most contributing factor to intention. However, on later study to generalize their earlier m-banking acceptance model, Wang, Lin and Laurn (2006) adopted an extended constructs. That is perceived usefulness had a significant contribution followed by the perceived ease of usage contributed behavior attention.
Another study by Cheong and Park (2008) carried out research on reluctance factors of the Korean’s to adopt m-banking services. In addition to the conventional TAM factors included additional constructs; facilitating conditions and the switching barriers. The findings in the research show that facilitating conditions affluence the positively the intention to use m-payment, whilst switching barriers negatively affected the behavioral intentions. Besides, Gu et al., (2009) research in Korea examined the determinants of the mobile banking. The authors introduced another factor; it considered trust as an additional key construct of the behavioral intention to utilize an introduced technology. In addition to self-efficacy, social influence, facilitating conditions, system quality, structural assurance, familiarity with the bank, and calculated-based on trusts were indicated as the key constructs of behavioral intentions. However, perceived usefulness and ease to use were the most contributing factors on behavioral intentions.
Another stream of research in developing countries was carried out to understand the socio-economic and technological impacts of m-banking adoption. Research placed study that m-banking in developing countries is considered as a complimentary service offered by the banking industry. It is considered an alternative of ATMs and internet banking. However, important criteria such as convenience and ease to use seemed to be important when they consider adopting m-banking. The appeal for the cell phone banking in developing countries revealed that influence on the convenience may be less than accessibility and affordability due to the network quality connection, coverage, and costs (Donner and Tellez, 2008). However, Laforet and Li (2005) investigation in developed countries; examined consumer behavior, motivation, attitude, and cultural influence on the m-banking in China. In the findings, customers in China do not attach much importance on m-banking convenience but perceived risks and technological skills are the most influential factors.
Lastly, Sripalawat et al. (2011) carried out to examine positive and negative factors influencing m-banking acceptance in Thailand. The research considered subjective norms, self-efficacy, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease to use as the positive factors. Contrary, the study considered device barrier, lack of information, perceived risk, and financial costs as the negative factors. Their findings not only revealed that positive factors are the most influential than negative factors, but also subjective norms to be the most influential amongst positive factors.
Conceptual framework
The conceptual framework deduces its constructs from the past literature reviews as from chapter two. The study basis is from the extended Technology Acceptance Model by of Luarn and Lin (2005). Its shows the factors which influence the adoption of cell phone banking. The constructs suggests that the technology user adoption of a new information system fundamentally determined by two factors; perceived usefulness and the perceived ease of use of the system. In addition, perceived credibility, efficacy and financial cost also affects the behavioral intentions of users to adopt m-banking. The model in this case, therefore, states the gaps between the past literatures reviews and the current study.
Conclusion
The successful marketing of the new technology remains one of the crucial aspects of banking industry that employs technology to satisfy customers across border. However, it places challenges when addressing the factors that influence potential customer’s decision to adopt the newly introduced technology. It requires better understanding on behavioral intentions to accept new technology. Specifically, the influence of beliefs of the existing technology moderates its adoption necessary another technology. This way, the study will gain better understanding through the past tentative literature reviews and followed by empirical research amongst customers. Besides, the study will provide extensive information to the field of marketing with possible strategies to m-banking.
Chapter Three: Methodology
This chapter provides discussion on the methodologies and various data collection techniques. These techniques will be employed as demanded by objectives of the study. The research methods were designed owing to the objectives of the study. For this reason, therefore, the strategies which the paper will use are to determine the major significance of the factors affecting adoption rate of mobile banking (Bryman, 2012).
Research approach
Philosophical approaches enable planning of the research design and the choice of methodology. It provides guide in choosing appropriate research methods regarding to the research objectives and research questions. In accordance, they follow research design choice, performance, assessment of design and the research quality. Besides, they are approaches which provides guide of the choices available from epistemology and ethnology as well (Johnson, 2000). Regarding ethnology, the paper will use realism paradigm to address the hypothesis of the study. This way the paper will adopt realism of factors affecting significantly the behavioral intentions to adopt mobile banking in Australia. On the other hand, the paper will use objectivity as its epistemology approach to base on the assumptions to deduce results without biasness. The researcher, therefore, will carry out the study in a neutral state to address the objectives successfully (Bryman, 2012).
The overview of the research methodology which the study will employ involves three-layer approach (see figure 2). It provides aims of developing an experimental framework to study the empirical findings. It incorporates a combination of both the primary and secondary data necessary to validate the study accordingly. This way, the paper will be able to test null hypothesis about a specific factor influence on the m-banking adoption (Saunders et al., 2012). The hypotheses derive form from the TAM literature review and interview data collected are as below.
- H 1: perceived usefulness has a significant influence on the m-banking adoption rate
- H 2: Perceived ease of use has a significant influence on the m-banking adoption rate
- H 3: Perceived credibility has a significant influence on the m-banking adoption rate
- H 4: Perceived self-efficacy has a significant influence on the m-banking adoption rate
- H 5: Perceived financial cost has a significant influence on the m-banking adoption rate
Justification of the research methods
Basing the research actual need, qualitative and quantitative analysis will be used. The study sought to choose both techniques because it will employ to determine the significance of the specific factor on m-banking. It will therefore include the weighted mean average and regression analysis of the primary data. Amongst the techniques which will be used, the study will prefer interviews to be most appropriate to facilitate survey questionnaires effectively.
Questionnaire design
Technology Acceptance Model accommodated the banking industry analysis. Accordingly, it make it best-suited theoretical framework to study the factors affecting cell phone banking. The model will refer to the significance of the factors to determine behavioral intentions of the potential customer to adopt it. This way in provided a conceptual framework to address the hypothesis as it involves lots of internet participant of varied dimensions such as the customers, suppliers and other stakeholders. To improve on the validity and credibility, the study will paper will use both closed and open-ended questionnaires: in which questionnaire form will contain demographic questions, ratings for the constructs influencing m-banking adoptions, and throws open questions to try cover in summary any factor beyond the listed ones (Oppenheim, 2000).
Data collection
Primary data collection
In order to identify the significance of the key factors affecting the adoption of m-banking in Australia banking industry, respondents from top three bank’s respondents will be selected. This will be the primary source to form the null hypothesis to be tested in the study. The selection is based on the assumption that these respondents understand the nature of the industry banking services especially m-banking. This way, will ensure the result will fit into the context of the study. Besides, the data collection method will follow the questionnaire design mentioned above (see section 3.3).
Secondary data collection
Apart from the past literature reviews, the study will also use secondary method to source information from the bank managers. It will obtain answers regarding significances of factors affecting m-banking by processing questionnaires avenues such as the number subscribers, m-banking frequencies and customers’ satisfaction feedback messages. Similarly, it will access data from the bank’s customer care desks data concerning the subject matter of the study covering the limited range of two years; the past year of 2013 and to the current records of 2014 (Matthews et al., 2010).
Face-to-face interviews Justifications
Face-to-face interview technique had been most preferable over the past years to date. Researchers, analysts and journals had found it effective for empirical studies. Since it develops life participation in which the informant feels he or she is involved. Hence, attains a sense of ownership of the study too. Put simpler, it is an in-depth direct and a repeated face-to-face interaction between the researcher and the informant. This way, it enables the respondent to share freely and openly their opinion about the subject of the study regarding their experience, attitudes and lifestyles. Therefore the research will be in a position to uncover the respondent’s situations, attitudes and experience effectively (Oppenheim, 2000).
Besides, interviews will be used to draw opinions of the respondents. The interview methods will include Face-to-face interviews which is the preferable over email, and in-world interviews.
In-world interview justifications
In-word environment is a recent times innovations which enables internet users to engage in a virtual environment through avatars. It is more like face-to-face social interaction but it is computer mediated communications feature which participant may as well interact through live chats. This is a marketing platform which banking industry places their products advertisement in an immersive environment such as online gaming, videos and so forth. Perhaps it is adopted for some reasons to embraces the Second Life way of doing things in 21st century. In this case, therefore, the study will engage respondents online through in-world interviews at ease. It is a technique which is essential especially respondents are unavailable to participate in face-to-face interviews.
Email interviews justifications
These are research interviews essentially conducted in rare occasions. Mostly, it is applied in case where the respondent is unavailable at the time of or uncomfortable in having face-to-face interviews. It is a rare instance that considers time constrains in which respondents will participate via email. The researcher will forward mail with semi-structured questions expected to be replied within a period of one week. All the respondents will be assumed that they are computer literate and had access of internet. This is because they on the expectations of the study that if they are using m-baking therefore are computer literate. However, email-based might raise confidentiality, deception and consent, otherwise, resolved to provide confidentially and identity protection (Bryman, 2012).
Sample and sampling size
In order to achieve the desired objectives, sampling strategy is important to be used especially, where qualitative approach is intended to be used. According to this study, the target population will be Australian top three bank’s customers. It will consider thirty respondents between the age of eighteen and seventy five. The study target pre-assumes that the population is the actual customers of the bank with access to the internet, computer literate, bank account and the uses m-banking services (Davies, 2007).
Random sampling method will be employed for the sample selection from the identified banks. This will be a necessary method for the study in order to avoid selection bias. It will create an opportunity in conducting the survey at neutral state for the sample population. The pilot-testing of the model will be conducted prior the study in order to ascertain the strategy performance, reliability and validity.
Methods of data analysis
Data analysis is a logic way of understanding and interpretation of the collected data. It includes two processes; analytical process where the data will be collected, categorized, compared, and integrated. Whilst interpretation process of analyzed employed circularly while making out sense out of the analyzed data (Hassan, et al. 2013). Since the study seeks determine the significances of the factors affecting adoption of m-banking in Australia, it triggers the need to employ statistical method of analysis. Therefore, it will incorporate two methods of data collection;
Weighted mean for the questionnaires
The results of the closed-ended questions will be assessed using TAM constructs significance. They will be scale from 1 to 5; strongly disagreed scores 1, disagree scores 2, neutral scores 3, agree scores 4 and strongly agree will equate 5 scores. To analyze the results obtained from the informants, the weighted mean score will be calculated accordingly. Similarly, open-ended questions will be analyzed at a personal interpretation, but at a neutral state rating the significance of the defined factors of adoption in ranks.
Least square method regression analysis
A least square multiple linear regression will be used to assess the correlation between the predators among the five independent variables and the m-banking adoption intention. This way, their variance will be used to in behavioral intentions to adopt m-banking will be therefore used to analyze the factor’s significance will be ranked accordingly (Smith, 2011).
Validity, Reliability and Ethics
Qualitative research is considered to execute reliability and the credibility of the study. Ethnology choice of realism will enable the stability of the study in conjunction with epistemology positivism approach. Positivism will be essential to deliver a neutral interpretation or measures without bias of the open-ended questionnaires. Use of repeatedly random sampling method and in-depth interview reviews also contributes the reliability of the research study.
While the reliability concerns the consistency of the scores results validity concerns, how the results will be interpreted. Validity will concern how well the study results place support of the theory or the constructs of the research paper. Accordingly, the collection data and analysis techniques will be pilot-tested prior the actual research. Besides, the constructs validity will be assessed by means of convergent and discriminant validity as well. That is, comparison of the similarity of results from different instrument of data analysis methods used.
Considering ethics, the paper will ensure the study will not cause any harm to the respondents by ensuring; their consensus to be part of the study contributors via interviews prior commencement of the study. Secondly, explaining the benefits of the study and guaranteed confidentiality in the procedures. This way, the research will provide their protection rights to respondents accordingly (Walliman, 2010).
References
Ajzen, I. & Fishbein, M. (2000). Attitudes and the attitude-behavior relation: Reasoned and automatic processes. In W. Stroebe & M. Hewstone (Eds.), European review of social psychology(pp. 1-33). John Wiley & Sons.
Arora V. and Vamvakidis A., (2011), “China’s Economic Growth: International Spillovers.China & World Economy”, 19: 31–46.
Bhatti, T. (2007). Exploring Factors Influencing the Adoption of Mobile Commerce. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 12(3), 1-13.
Bryman A., (2012) Social Research Methods, 4th Edition, Oxford University Press,
Cellular-News, (2011), Mobile Banking Surges as Emerging Markets Embrace Mobile Finance.
Davies, M.B. (2007) Dong a successful research project: Using Qualitative or Quantitative Methods, Palgrave MacMillan .
Davis, F. D. (1993). User acceptance of information technology: System characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 38(3), 475-487.
Dillon, A. & Morris, M. (1998). From “can they” to “will they?”: Extending usability evaluation to address acceptance. In E. D. Hoadley & B. Izak (Eds.), Proceedings Association for InformationSystems Conference. Baltimore, MD.
Drennan, Judy, and Wessels, Lisa. 2009. An investigation of consumer acceptance of M-Banking in Australia.
Easterby-Smith, M., Thorpe, R. and Lowe, A. (2002), Management research: An introduction, 2nd ed., London: Sage.
Ellen, P.S., Bearden, W.O., & Sharma, S. (1991). Resistance to Technological Innovations
Ferro, Enrico. 2010. Handbook of research on overcoming digital divides constructing an equitable and competitive information society. Hershey: Information Science Reference.
Ghauri, P. & Gronhaug, K. (2010). Research methods in business studies. 4th ed., Pearson.
Great Britain. (1997). Electronic commerce. London, DTI.
Hassan, Z., Nareeman, A., & Pauline, N. (2013). Impact of CSR Practices on Customer Satisfaction and Retention: An Empirical Study on Foreign MNCs in Malaysia. Available at SSRN.
Infocomm Development Authority of Singapore, (2011), Statistics on Telecom Services for 2011.
Johnson, P. (2000) Understanding management research: An introduction to epistemology, London: Sage.
Kim, H.W., Chan, H.C., & Gupta, S. (2007). Value-based Adoption of Mobile Internet: An Empirical Investigation. Decision Support Systems, 43(1), 111-126.
Kuo, Y.F., & Yen, S.N. (2009). Towards an Understanding of the Behavioral Intention to Use 3G Mobile Value-added Services. Computers in Human Behavior, 25(1), 103-110.
Luarn, P., & Lin, H.H. (2005). Toward an Understanding of the Behavioral Intention to Use Mobile Banking.
Matthews, B., Ross, L. (2010) Research Methods: A proactical guide for the social sciences, 3rd ed., London: Longman.
Mattila, M. (2003). Factors Affecting The Adoption Of Mobile Banking Services. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 8(1), 149-160.
Ópez, J. R., Walkenhorst, P., & Diop, N. (2009). Trade competitiveness of the Middle East and North Africa: policies for export diversification. Washington, D.C., World Bank.
Oppenheim, A. (2000) Questionnaire design, interviewing and attitude measurement, 3rd ed., London: Continuum.
Pearlson, K. E., & Saunders, C. S. (2006). Managing & using information systems: A strategic approach. John Wiley & Sons.
Rao, S., & Troshani, I. (2007). A Conceptual Framework and Propositions for the Acceptance of Mobile Services. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 2(2), 61-73.
Ryan, B., Scarpens, R., and Theobald, M. (2002) Research Methods & Methodology in Accounting and Finance (2nd Ed). ISBN Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Saunders, M., Thornhill, A., Lewis, P. (2012) Research Methods for Business Students. London: FT Prentice Hall.
Smith, M. (2011) Research Methods in Accounting, 2nd Edition, SAGE Publication.
Sripalawat, J., Thongmak, A., & Ngramyarn A. (2011). M-banking in Metropolitan Bangkok and a Comparison with Other Countries. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 51(3), Tole of Self-efficacy and Performance Satisfaction. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 19(4), 297-307.
Walliman, N (2010) Research Methods: The Basics, 4th ed., London: Routledge Publications.
Wang, Y.S., Lin, H.H., & Luarn, P. (2006). Predicting Consumer Intention to Use Mobile Service. Information Systems Journal, 16(2), 157-179.
Wang, Y.S., Wang, Y.M., Lin, H.H., & Tang, T.I. (2003). Determinants of User Acceptance of Internet Banking: An Empirical Study. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 14(5), 501-519.
Zhang, S. X., Olfman, L. & Reetham, P. (2007). Designing eportfolio 2.0: Integrating and coordinating web 2.0 services with eportfolio systems for enhancing users’ learning. Journal of Information Systems Education, 18(2), 203-214