Standardization versus Adaptation Debate in International Marketing
In the international business market field, standardization versus adaptation debate is not new, where thus far researchers have not agreed on which strategy is effective to be adopted in international market. Taking a business into international market and successfully selling its products and services can attract a range of challenges. For many years, many multinational corporations make costly mistakes when trying to sell to the global consumers or audience. Such mistakes are mainly described by a lack of awareness of the role and contributions of adaptation and standardization in international markets. This paper seeks to analyse the issues of adaptation (customization) and standardization (global strategy) within international marketing strategies and proposes specific approaches that can help companies compete efficiently and effectively within these global setting.
Available Evidence
Since the start of the 1980s, globalization issue has developed significantly and critical to modern businesses. Globalization has helped in reducing the differences between countries. Both international of businesses and an increasing level of globalization have had a significant impact on how businesses plan and view their global marketing strategy (Wang & Yang, 2011). As a result, various research studies have been done on whether companies need to standardize or adapt certain behaviours in international market. As these multinational businesses start to market their products and services in foreign markets, one important strategic decision is whether to change the marketing strategies and mix to match the unique aspects of each local market or whether to adopt a standardized marketing mix (people, promotion, place, price, product, process management, and physical evidence) and a single marketing strategy in all international markets (Vrontis & Thrassou, 2007)
One consideration shows that markets are becoming more integrated, increasingly more global and similar and consider that the main element to business survival is its capability to standardize. In contrast, the other consideration identifies the challenges in adopting a standardized strategy, and thus, supports market adaptation or customization. Nevertheless, evidence proposes that following adaptation or standardization strategies depends on the positioning and dimensions present in respective international market.
Standardization versus Adaptation
Based on some studies, followers of standardization consider that there is an integration of cultures with the same customer demand and environmental demands across the world. They also state that trade barriers are being reduced and advancements in technology, where multinational companies reveal global integration in their strategies. Under standardization, providing a single strategy for the international market, along with standardizing the marketing mix components, can enable constancy with customers and also reduce costs. Brei, et al (2011) state that businesses managed effectively have shifted away from customizing their products to serving internationally standardized items that are low priced, reliable, functional, and advanced. Brei, et al (2011) further state that businesses can attain long-term success through focusing on what customers need instead of being afraid of the particulars of what customers think they might need.
In contrast, followers of international adaptation strategy focus on the significance of customization. The key base of the adaptation strategy is that when a business enters an international market, it needs to reflect on all environmental aspects, constraints, and factors, such as societies, cultures, different laws, taste, education, occupations, race, climate, and language (Akgün, et al., 2014). Nonetheless, studies have reported significant source of constraints that may be challenging to measure, for example, customs, manners, attitudes, values, religion, aesthetics, education, and cultural variations originated in history, along with variations in legal systems, economics, wants, and needs. Vrontis and Thrassou (2007) stated that multinational corporations need to realize how they should alter their whole marketing strategy and include how they order, distribute, and sell to match the new international or local market demands. It is also very vital to adjust the marketing strategy and mix to fit local preferences and tastes, customer non-equivalent requirements, and special market needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardization
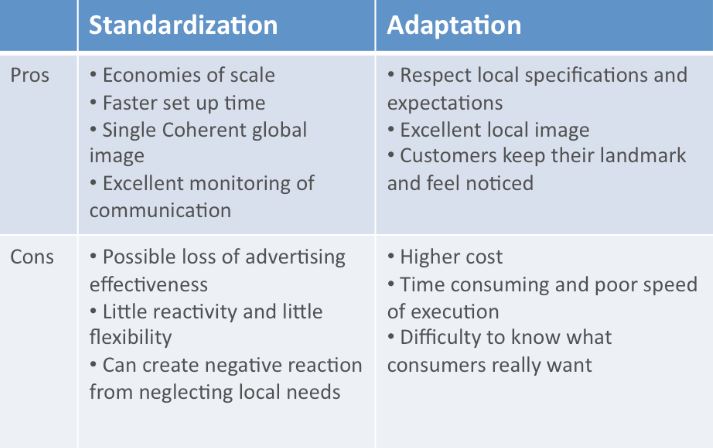
Global uniformity and standardization have various benefits. First, customers can anticipate similar quality level of any particular brand in all outlets across the globe. Moreover, Hise and Choi (2013) posit that standardization facilitates positive consumer perceptions towards certain product. If companies that have a strong reputation and brand identity decide to follow the standardized approach, they will certainly gain success. In a global setting, positive word-of-mouth can imply an improvement in sales. Another benefit embraces cost reduction that provides the economies of scale (Hise & Choi, 2013). Selling huge amounts of non-adapted, same product and purchasing certain constituents in bulk may help in reducing the cost-per-unit.
Other benefits linked to economies of scale consist of reduced investment costs, marketing operational costs, and enhanced research and development. Additionally, standardization is a rational strategy in an era in which trade barriers are diminishing. Adopting a standardized approach assists multinational businesses to direct their emphasis on a uniformed marketing mix particularly concentrating on one single product or service, enabling adequate space for quality improvement. By focusing on one single uniformed product, employees will be trained to improve the product quality, which enables manufacturers to make equipment and technological investment that can protect the quality of the standardized product being served.
Nevertheless, standardization poses a range of shortcomings. Aforementioned, different international markets mean different consumer’s preferences. As a result, selling or offering one unified item poses lack of uniqueness. This enables competition to acquire bigger market share through adjusting their products to fit the need of a certain segment or market. Given that different markets have varied tastes and needs, by adopting the standardized strategy, businesses can become more at risk. One company example is Walmart’s failure when it entered international markets (Kim, 2008). Walmart encountered various challenges when it entered foreign markets such as Japan, South Korea, Brazil, and Germany as it realized that its recipe for success in the US (a huge set of merchandise, inventory control, and low prices) did not actually activate the same level of success in foreign markets with shoppers with varied habits and own discount chains. The key problem for the retail giant was that the company tried to inflict its values globally. Particularly, Walmart’s incident is Germany, where the company lost large sum of dollar as of 1998, has become an example or reference point for how not to expand internationally.
Another disadvantage is that it relies mainly on economies of scale. In nature, companies that are global often engage in manufacturing in various countries. This may also pose a great problem because some countries adopt trade barriers such as the EU and the US (Dimitrova & Rosenbloom, 2010). For such a case, adaptation is predetermined. However, even though the standardization strategy is more used, its adoption is not absolute. Standardization approach raises the performance of a firm. Nevertheless, this is only true for businesses where competition occurs in a global range, such as perfumes, luxury goods, fashion, electronics, consumer durables, among others. In such cases, similar product may be sold across all markets. In contrast, there are other sectors where this same action does not apply and thus, this needs to be considered.
Moreover, consumer non-durables, such as food products, are highly responsive to variations in national habits and tastes, making the companies to consider some adjustments to fit different markets. For instance, Unilever realized a greater opportunity among Indian low-income consumers who intended to purchase personal care products and high-end detergents, but might not afford them. To respond to this, Unilever produced a low-cost packaging product and various other alternatives that enabled it to provide radically cheaper alternatives. According to Theodosiou and Leonidou (2003), such a flexibility not only increase a new market for the business, but enabled also it to produce brand loyalty that customers benefit from it when their income increased and might afford higher-end products from similar manufacturer.
There are some questions which most businesses in the international market expansion need to answer: what products do we aim to standardize? And do we standardize distribution channels, pricing, marketing communications, product support and customer service? The answer to such questions need to either all adapted or all standardized.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Adaptation
Customization is also commonly considered an adaptation. Moreover, product adaptation is more applicable in the case in which: (1) there is an intense competition, compelling differentiation of products; (2) there is a considerable variations in consumer wants and needs; and (3) to meet essential host country requirements, including legal, technical, and packaging issues. These are also essential reasons for product adaptation and modification; literacy, customer lifestyle, and consumer’s income level.
The key arguments towards implementing adaptation approach is that it entails the individual approach as it enables the company to be aware of the preferences, wants, and needs of each market or consumer. Followers of adaptation strategy credibly support the idea that there is a considerable variation in consumer’s lifestyle, political system, regulations and rules, economic condition, culture, and consumer belief and values across the globe. Such elements need to be reflected on for the success of the company (Hussain & Khan, 2013). The application of adaptation marketing strategy supports the companies to gain an increased competitive advantage. In addition, the ultimate aim of a business needs not to be the cost reduction using standardization, but the actual long-term corporate profitability through improved sales attributable to the enhanced use of the differing consumer needs globally.
Poturak & Duman( 2014) assert that the followers of standardization does not possess the conventional knowledge of contemporary marketing. Irrespective of various arguments of improved consumer homogeneity, various studies have reported that consumers are becoming progressively more complex or diverse and do not essentially intend to substitute quality over price. Moreover, product modification or adaptation approach will results in a boost in sales volume of the company in international market; by highly meeting the wants and needs of the consumers, but reflecting on the competing companies; and by also retention of the current customers through frequently updating the product.
There are also certain drawbacks of product adaptation or modification of different marketing strategy, including duplication of the practices across the company and additional cost needed for the promotional practices. In this strategy, the company will need extra resources for research and development. The increased costs are attributable to defender fights and developments, which are also more risky. Moreover, companies may lack knowledge and experience regarding the technical elements of the different products and understanding on how to market a product (Hossain & Yazdanifard, 2015). This strategy also promotes decentralization of management.
Most Appropriate Strategy
These two strategies emerge to be coherent, logical, and rational, outlining the benefits that a company intending to expand internationally can acquire through implementing either strategy. When an international company puts forth all its efforts of the extreme side of either strategy, it normally becomes incoherent and unfeasible. The point is that marketing for international companies is not based on either of the two opposite strategies, since both strategies are probably to coexist, even in similar multinational company, brand, and product line (Rocha & Silva, 2011).
Vrontis and Thrassou (2007) stated that standardizing some components of the marketing mix, while adapting other components to differing market conditions is required. Adaptation and standardization should not be considered an ‘all or nothing’ proposal; rather it should be considered a matter of degree. For instance, diversity across various countries and markets does not enable whole standardization. Nevertheless, Schilke, et al. (2009) opines that higher cost associated to adaptation can limit the application of adaptation strategy. Wei and Yazdanifard (2014) focus on three factors to analyse adaptation and standardization practices: transferability of competitive advantage; homogeneity of various consumers’ reponse towards the marketing mix; and similarities in the level of economic freedom.
Schilke, et al. (2009) point out that even in markets or countries with the same cultures, such as across the EU, there are variations in customer wants and needs. In addition, they state that standardization will be effective when the customer response homogeneity and the level of sameness in economic freedom are higher, with easily transferable competitive advantages. Components of both strategies need to be integrated so that it can enable international companies to achieve desirable success. Acquiring the benefits of both strategies needs various firms to not only standardize different components of marketing strategies and marketing mix, but to implement also adaptation when needed with the aim of meeting the evident market needs (Batraga & Pūķe, 2015).
McDonald’s Case Study
An example of a major corporation that has been able to demonstrate the benefits of both adaptation and standardization strategy is McDonald’s. With around 35,000 restaurants in around 120 countries globally, McDonald’s competently manages its franchise system, providing an outstandingly reliable branding and customer experience, while also enabling for locally appropriate service and menu differentiations in segments or markets globally. Moreover, all advertisements are provided in twelve different languages, characterizing the tailored products organized to each region or market (Vignali, 2001). McDonald’s launched the McArabia (a flatbread sandwich product) in 2003, to its outlets in the Middle East. In addition, in India, it launched the McVeggie, while introducing EBI-Fillet-O shrimp in Japanese markets.
The company also selects convenient locations for its franchises, which include local neighbourhoods, airports, and malls. Such marketing strategies have proven to be efficient, showed by the company’s 8% increase in profit margins within the last five years. Nonetheless, McDonald’s has placed various efforts to improve them using the latest marketing practices in regards to the 7Ps. The company has started to modernize its eateries, shifting from a plastic-appearance to a more wood and brick design with the aim of sustaining a modern image (Yeu, et al., 2012). McDonald’s has also chosen to “re-image” its business operations in their advertisements through integrating a hip-hop theme with young generation icons such as Lee Hom and Justin Timberlake in China as a way of attracting young people. Moreover, this company has started to serve healthier foods (e.g. oatmeal), provided consumers are highly health conscious.
Conclusion on Standardization versus Adaptation
The regular topic in international marketing is whether multinational firms need to plan for adapted or standardized marketing strategy is immensely debated in scholarly setting and is a major issue to all multinational firms and marketing individuals. Followers of standardized strategy state that the international market has become homogenized and thus, these firms can market their commodities similarly across the globe. Using similar approaches will lead to higher margins and reduced costs. On the contrast, followers of the adaptation strategy focus on the evident differences between the markets of various countries and markets, particularly those for consumer goods, and favour adopting global differentiated marketing initiatives
This paper listed some advantages and disadvantages of every strategy, suggesting that the solution to an effective market strategy lies between these two extreme strategies. Firms can promote a strong international marketing strategy with the relevant structure, attitude, and operating behaviours that attain an effective and efficient balance between standardization versus adaptation approaches. Companies intending to expand internationally need not to treat the world as one singular market. Rather, they should initiate market research and establish their customers, and their wants and needs.
References
Akgün, A. E., Keskin, H., & Ayar, H. 2014. Standardization versus Adaptation of International Marketing Mix Activities: A Case Study. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 150(15), pp.609–618.
Batraga, A., & Pūķe, I. 2015. Integrating Standardization versus Adaptation in International Marketing Strategies: Companies in Latvia. Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference, pp.27-36.
Brei, V., D’Avila, L., Camargo, L., & Engels, J. 2011. The Influence of Adaptation and Standardization of the Marketing Mix on Performance: a Meta-Analysis. BAR, Curitiba, 8(3), pp.266-287.
Dimitrova, B., & Rosenbloom, B. 2010. Standardization Versus Adaptation in Global Markets: Is Channel Strategy Different? Journal of Marketing Channels, 17(2), pp. 157-176.
Hise, R., & Choi, Y.-T. 2013. Are US companies employing standardization versus adaptation strategies in their international markets? Journal of International Business and Cultural Studies, 1-29.
Hossain, A., & Yazdanifard, R. 2015. Which One of Standardization or Customization Works the Best When It Comes to Online Marketing? American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 5, pp.45-52.
Hussain, A., & Khan, S. 2013. International Marketing Strategy: Standardization versus Adaptation. Management and Administrative Sciences Review, 2(4), pp.353-359.
Kim, R. 2008. Wal-Mart Korea: Challenges of Entering a Foreign Market. Journal of Asia-Pacific Business, 9(4), pp.344-357.
Poturak, M., & Duman, T. 2014. The Role of Marketing Standardization versus Adaptation Strategies on Managers’ Satisfaction with Export Performance: Proposal of a Conceptual Framework. European Journal of Economic Studies, 10(4), pp. 252-262.
Rocha, T. V., & Silva, S. C. 2011. The Standardization versus Adaptation Dilemma: The Case of an American Company in Brazil. Internext – Revista Eletrônica de Negócios Internacionais da ESPM, 6(1), pp.63-83.
Schilke, O., Reimann, M., & Thomas, J. 2009. When Does International Marketing Standardization Matter to Firm Performance? Journal of International Marketing, 17(4), pp. 24–46.
Theodosiou, M., & Leonidou, L. 2003. Standardization versus adaptation of international marketing strategy: an integrative assessment of the empirical research. International Business Review, 12, pp.141–171.
Vignali, C. 2001. McDonald’s: “think global, act local” – the marketing mix. British Food Journal, 103(2), pp.97 -111.
Vrontis, D., & Thrassou, A. 2007. Adaptation versus standardization in international marketing – the country-of-origin effect. Innovative Marketing, 2(3), pp.7-20.
Wang, X., & Yang, Z. 2011. Standardization or Adaptation in International Advertising Strategies: The Roles of Brand Personality and Country-Of-Origin Image. Asian Journal of Business Research, 1(2), pp.25-36.
Wei, S., & Yazdanifard, R. 2014. Comparison on the Impact of Standardization and Adaptation on International Marketing. Journal of Research in Marketing, 3(1), pp. 250-259.
Yeu, C., Leong, K., & Tong, L. 2012. A Comparative Study on International Marketing Mix in China and India: The Case of McDonald’s. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 65, pp.1054–1059.
Other Relevant Blog Posts
Example Marketing Dissertations
Brand Management Reputation Marketing
Did you find any useful knowledge relating to the impact of standardization and adaptation on International Marketing in this post? What are the key facts that grabbed your attention? Let us know in the comments. Thank you.