Explain the Importance of the Micro-Economic Environment to Business Organizations
Business in a literal term is collective work of bunch of people with similar interests in production of goods and services for trading purpose at any market and draws some monetary reward for this whole exercise”. There are so many factors which effect the business organizations one of them is the Micro-Economic environment. This type of environment basically related to the analysis of small area or the marginal aspects of the any organization. The factors which are analyzed in micro economic environment are as following:
- Characteristics of organization’s human resource and their ability to manage the organization are analyzed.
- Both types of customers (major and minor) are evaluated.
- Dig about the means of generating money by organization.
- Information is gathered about the suppliers of raw material and their network.
- Analysis of local communities , competitors and their business performance is conducted (Hiriyappa,B, 2008)
From above discussion if we conclude that Micro-Economic environment has direct relation to any business organization then it would not be wrong and we are going to discuss the effect of Micro-Economic environment on the performance of any company that how these micro economic environment affect the performance of any company. The company which would be under discussion is Vodafone which falls in the services sector. Vodafone is included in one of the leading companies in communication sector which is providing services in 30 countries and having partnership networks in over 40 countries. Customer count is 360 million in the world and it is 19 million only in United Kingdom. Vodafone started working on 1 January 1985 at London. Vodafone is having more than 8,000 employees in UK. Until 2013 Vodafone was earning £429 million profit.
Micro economic Environment Importance for Business
Micro-Economic environment is very important for business organizations as it could be said that it is complementary for the business organizations because micro economics studies the basic factors which affect the individual business like consumer behavior, market environment, competition in the market and demand and supply forces prevalent in the market place. For the better understanding and explanation of effects of Micro-Economic environment on business organization it is necessary to discuss it which the help of a case study on Vodafone in terms of services. If Vodafone wants to deliver its services in certain country or area then it has to apply certain Micro-Economic principles in order to check the feasibility of business environment in that area. First of all Vodafone has to evaluate the market environment whether market of that particular area is feasible for that kind of business or not.
Micro-Economic environment also includes the environment of the marketplace which is further subdivided into location and governmental policies. Vodafone has to check whether these both factors are in harmony with their business policies or not. They have to check how much tax and other duties they have to pay if Vodafone starts business in that particular country. Micro-Economic environment also include the location for setting up the office for starting business. Vodafone has to find place where it can target its potential customers easily and customers could have easy access to their services. I deal location could be any business hub where lots of offices are located and have to use the telecommunication services on daily basis and want any company with fastest service, better signals, voice quality and internet services.
Survey of other communication networks working in that country would also help the Vodafone to identify how much competition it has to face if it set up their business at any place.
So identification of Micro economic environment is very important for any business organization if it has to do or start new business at any particular place. Regular survey of the micro economic environment also helps the organizations to do their SWOT analysis and keep pace with the ever growing business in the market (Ejim Esther, 2014).
Business Objectives and Behaviour Analysis
In managerial economics the basic purpose of business organization is to maximize the profit of organization. So in economics terms profit maximizes when certain condition of marginal revenue equals the marginal cost (MR=MC) is met. Diagram below is the analysis of changing circumstances which effect the business objective of profit maximization in an imperfectly competitive market in other words monopoly. Profit maximization is considered most important objective of any business when dealing in any type of market whether competitive, oligopolistic, or monopolistic.
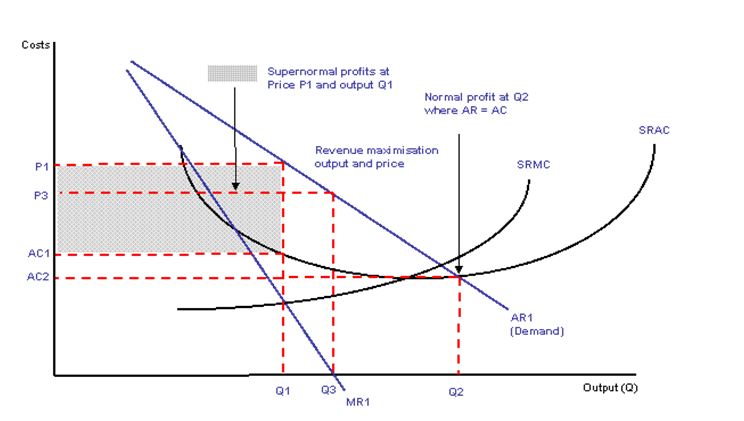
There are different objectives ahead of any organization and they also affect the performance of organization in certain ways.
Satisfaction Behavior
This kind of behavior is adopted by the business organizations to set and minimum but acceptable level of revenue and profit collection for business for example a firm has set a certain amount for sale growth or return on any capital which it is acceptable for firm if they get it in case of minimum revenue and profit. In other words it is could be called as the scale for measuring profitability of firm.
Optimization of Sales Revenue
Revenue of any business organization is considered maximum when the certain assumption is fulfilled which is Marginal revenue (MR) = 0.
Managerial Satisfaction
Williamson opined to increase the utility of managerial level through high revenue from sales of firm, a good share achieved in market or through output targets are included in all this.
Constrained Sales Revenue Maximization
Managers would give shareholders free hand to design a constraint which could be minimum profit gaining constraint in order to support their shares worth.
Every business has its own paradigms and at profit maximization level every business organization operates in separate way. If business behavior is summarized then few things are kept in mind while taking decisions such as competitors’ reaction towards policies made by particular organization. Local demands and competitions from rivals make it necessary to give managers authority to set the prices.
Diagram illustrates that how change in objectives affects the business in terms of price and output (Samuelson, 2010).
Market Structures Impact on Business Organizations
Business organizations are categorized on the basis of market structure in which these are serving. Various variables are induced in market which determine its structure and affect the organization’s business working in that market. Variables are costs, mutual dependence, free entry and exit etc (Baumol, 1982; Colton, 1993). Following are the different type of market structure and these variables act under any of these types.
- Perfect competition: Gives liberty to many sellers of same product to enter in the market.
- Monopolistic Competition: There are lots of sellers in market but also offering different products.
- Oligopoly: limited number of sellers but products could be same or different.
- Monopoly: Only one seller ruling the market.
Market structure has very profound impact on the business organizations because it has direct effect on different business dynamics such as motivations, opportunities, and business organizations’ decisions. This basic theme of analysis of market structure’s impact on business organizations is to study these effects separately and make the market more predictable for business organizations (McNulty 1968; Broaddus, 1991).
In order to study the impact of market structure on the business organizations, it is very important to define market because product substitutability is important task performed by the market structure which is very key element in the working of any organization (Broaddus, 1991). But any economist from Adam Smith to onwards is not able to crack this hard nut.
Through market structure analysis business organizations become able to predict market and act accordingly in order to generate more revenues and compete with their rivals. Market structure analysis also helps business organizations to keep pace with the changing dynamics and challenges of market.
In case of mobile network performance Vodafone increased its mobile network speed up to Mbps which shows that Vodafone is on track of achieving their target of 3Mbps. Vodafone held maximum market share in year 2013 too according to analysis of its relative market share performance report. Vodafone has increased their dividend up to 7% consecutively three years. Revenue collection was not much satisfactory in year 2013 as it remained -1.9% and £40.9 billion in case of services which was less than last year (Vodafone annual report 2013).
References
Hiriyappa, B. (2008) Strategic Management for Chartered Accountants, New Age, pp 3, 30 Micro-Economic Environment.
Ejim, H (2014) What Is the Relationship between Micro-Economics and Business? Wise Geek Micro-Economic Environment
Samuelson, (2010) Micro-Economics and the Micro-Economic Environment 19th edition, McGrawhill
Baumol, W J., (1982). Contestable Markets: An uprising in the Theory of Industry Structure. American Economic Review (March): 1-15.
Colton, R D. (1993) Consumer Information and Workable Competition in Telecommunications, Journal of Economic Issues 27(3) (September):775-792.
McNulty, P, J. (1986) Economic Theory and the Meaning of Competition Quarterly Journal of Micro-Economic Environment (November: 639-656.
Broaddus, A (1991) The Structure of the Market for Banking Services. Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Monthly Review Micro-Economic Environment (November): 35-42
Vodafone Group Plc (2013) Annual Report for the year ended 31 March 2013, the way ahead Introducing Vodafone 2015”.
Office of National Statistics, 2013, Statistical bulletin: Gross Domestic Product Preliminary Estimate, Q2 2013.




