Effective Team and Performance Management
This article is intended to evaluate the case study on Electron Corporation and highlights main key points pertaining to team building as well as enhancing the effectiveness of team productivity, established team environment and performance. Building of teams and effectiveness of team performance can be derived from various primary attributes (Zaccaro & Klimoski, in press). Teams are firstly needed to successfully contribute their individual efforts because their certain needs and responsibilities will form the basis of the collective success of the team. Secondly, since teams need to operate in complicated and ever changing organizational environments, they need to tackle multiple organizational team characteristics such as conflicting agendas, load of greater information, swift changes in the situations as well as enhanced dynamic changes (Zaccaro, Rittman & Marks 2001).
A small overview of the company includes; Electron is a small manufacturing organization established in 1997 in North of England. It manufactures components for telecommunication division. It employs 150 people along with 90 people in the manufacturing division. It was originally a department of a huge telecommunication organization and the Electron’s team bought the component manufacturing section as a portion of an outsourcing plan presented by the parent company in 2007. Electron has acquired both full time and part-time employees. In 1990s, its management realized that the company was striving for increasing competition and innovation in the industry. So in order to enhance their competition in the market, they have found the need of a more proficient and effective production procedures while emphasizing on enhancing organization’s culture, customer services, improved performance and responsibility and loyalty towards teamwork.
However, the subsequent sections of the assignment involve literature review which will cover the benefits and dysfunctions of teamwork. The Tuckman’s (1965) model of team building is also been employed in relation to the case study which demonstrates how teams must be efficiently formed. Whereas, the last sections will demonstrate the conclusion of the study as well recommendations on how to enhance the team performance more effectively and the steps that need to be taken for creating a subtle team environment.
Literature Review
The use of teams seems to provide several advantages; they may not be the most appropriate tactic for all types of organizations and not all of the organizations face similar and all challenges imposed by the teams. The influence of teamwork (both optimistic and pessimistic) is dependent upon several features such as company’s culture and environment, efficiency of team leadership, company’s efforts etc. Primarily, a team can be described as a small group of people along with a set of performance objectives, who are responsible to a common goal and the attitude they carry themselves mutually responsible (Katzenbach & Smith 1993). This definition explains that organizational teams should be of a manageable size and all of the team members should be accountable to achieve the shared team objectives. Moreover, all of the team members should be mutually responsible towards their activities and the results of those activities.
The Enticement of Working with Teams
The power of team work roots from several factors particularly when teams are employed. Various researchers demonstrated that teams are increasingly being employed as a response to ever increasingly global marketing competition (Heap 1996; Roufaiel & Meissner 1995; Sundstrom, De Meuse & Futrell 1990). Because of this increase in competition, it is also viewed that catering niche markets is also a growing concern. Since, electron emphasizes on enhancing organization’s culture, customer services and improved productivity; as a result, Electron manufacturers not only need to compete on cost but also strive to compete on innovation by establishing distinctive goods and services that could not be countered by the other rivals in the market. However, this will originate a problem where the company is not supposed to rely on mass production as well as economies of scale in the industry.
Most organizations still believe that working with teams is the only answer to this problem (just as Electron did). In their view teams are the source to optimize company’s innovation as employees have increased self-sufficiency, increased involvement and autonomy for making decisions (Harvey, Millet & Smith 1998). The employees no longer need to be guided about what is required to be done. In fact, they are provided with the objectives or develop objectives along with their team leader and then give autonomy to choose the best way in order to accomplish those objectives. Additionally, organizational innovation can also be optimized if teams are able to provide other enticements to the organization the situation in which they operate.
For instance, firstly, teams can optimally utilize human resources since they permit companies to achieve access to a person’s knowledge and capabilities (IRS Employment Review 1995). Albeit, the enhanced intricacy of the companies means that not all the managers know everything regarding each and every facet of the company’s operations. In this circumstance, it is important to utilize knowledge and capabilities of the employees/teams. Secondly, teams can be utilized to optimize company’s learning as employees are capable to design best strategies being suited to their work objectives (Wageman 1997). Thirdly, Teams are also capable to enhance individual’s performance levels and his/her efficiency, thereby establishing a synergy (Katzenbach & Smith 1993). Finally, team work is greatly associated with various numbers of objectives, tasks and additional accountability for each member of the team, which in turn resulted in enhanced job satisfaction, employee motivation and more work commitment. This will also result in lower employee turnover and absenteeism, thus, decreasing company’s costs and enhancing company’s knowledge base (Kirkman & Shapiro 1997).
Dysfunctions or Challenges Accompanied Teamwork
The employment of teams is primarily a change to an organization as well as a developmental procedure. Thus, teams can be easily affected to any challenge that might emerge during an organizational change. Particularly, resistance among employees may occur when they are needed to work along with other employees who are unfamiliar to them. In this way, teams are more likely to have broken established social relationships. This has already done in the Electron when huge number of new employees was hired and was integrated into one of the Electron’s teams. Those workers were new to their team’s values and consensus where they exerted greater challenge to the already existed relationships among the older employees.
In accordance to Bettenhausen (1991), one way to cope this problem is by forming teams. Building of teams will enhance group productivity by enhancing communication, minimizing conflicts and establishing greater bonds and commitment among all the working team members. Resistance among employee can also occur as a result of other factors. For instance, teamwork may need job enlargement where each team member is required to perform his/her conventional role along with his/her team role (IRS Employment Review 1995). In this circumstance, it is essential to minimize their certain responsibilities or to change the structure of their rewards or compensation.
Besides job enlargement, team work is also coherent with autonomy, ownership and additional commitments. Managers frequently perceive that employees must participate in decision making instead of simply being directed of what needs to be done. However, this might be true for certain situations but not for all situations. This will, in turn, may resulted in employee job dissatisfaction, increased employee turnover and/or reduced work productivity. The similar case is also viewed in Electron, when it hired new employees on temporary basis and let the managers to decide who must be hired on as full-time employee. Those workers initially were also unfamiliar with the team procedures and were expected by the managers to know the team’s values and conform and act accordingly to their team’s norms. Teams at Electron started exerting their concertive control over the new individuals which as a result new employees began controlling themselves and those norms and values become rationalized rules for the new members. There is no simple solution for catering such problem; however, training or changing positions can be probable within the company.
Other associated problems with “empowered teams” originate when there is a lack of trust in the team when they are no longer trusted enough to participate in decision making. This will result in teams and organizations losing full potential to accomplish their desired objectives. The situations in which teams are needed to seek consent before executing any idea or timeliness, ownership is likely to reduce. Organizational innovation will also decrease as teams are compelled to suggest ideas that will be likely to accept (Nahavandi & Aranda 1994). Moreover, team members may also perceive that their management is paying insincere respect to their proposed ideas of teamwork which will certainly result in reduced employee morale.
It is also viewed that when teams are involved in making decisions, they take more time than the system they reinstate. This is also needed where team coordination is required and where team members are independent. This issue can be partly cope by the formation of the team, but this also requires continuous training and development of groups teams. Such kind of training can be specifically appropriate for the new hired staff as there may be no established procedures for them to follow. Also, for effective teams, there must be strong coordination among them (Harvey, Millet & Smith 1998). Similarly, the lack of participation in decision making and coordination among employees for building of more strengthened team culture is seen in Electron’s eight teams (red, blue, white, green, silver, aqua, purple and yellow). This is due the fact that the older and long tenured employees have tried to impose strict concertive rules and procedures to conform to the group norms.
In case of organizational environmental changes and developmental initiatives, culture of the organization and environment must also be considered. It must not be perceived that the objectives and values of the individuals are similar to those of their management or congruent even across the entire organization. The attitude of individuals towards teams will demonstrate the success of those teams. If teams need to be executed more successfully, the extension of already existed values must be there (Carr 1992). Therefore, Electron when working with teams also demand shift in attitudes that a company may turn to it when it wants to accomplish a cultural shift, for instance, when it becomes more quality or customer oriented (IRS Employment Review 1995).
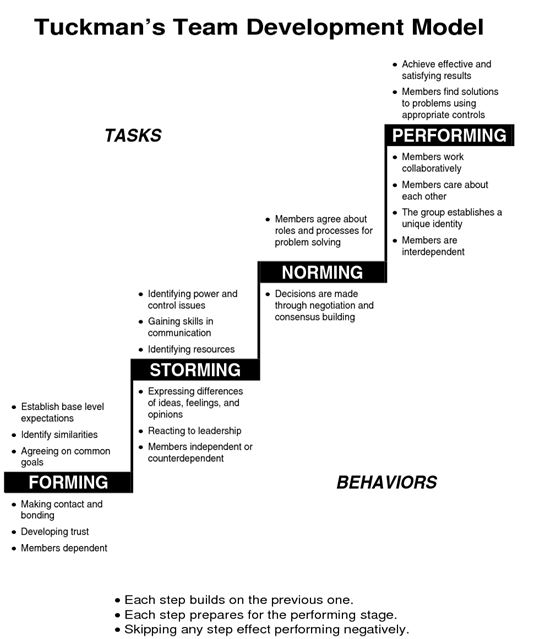
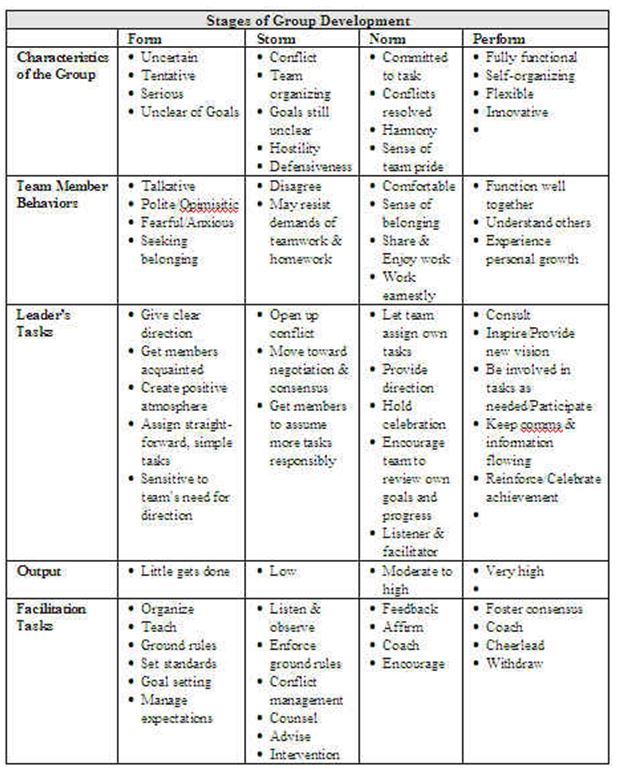
Five Team Development Phases as Proposed by Bruce Tuckman
This model as proposed by Bruce Tuckman (1965) tends to highlight and guides the areas where teams can be successful and/or become failure to achieve desired team goals. For forty years, Tuckman’s classical model of team development delivers ease and new perceptions to managers to either charge to run a team or attempt to function within a team while assuring each member that they are not alone and that the uneasiness is a normal part of the team journey towards an efficient and pleasant unit. Tuckman speculates that these stages are essential and unavoidable. In order for the Electron teams to grow, to face the hurdles, to cope up with the problems, to search for solutions, to organize work and to deliver desired outcomes; these five phases can be elaborated as follows.
Phase One: Forming
In this first phase of team building, Electron teams must be formed. Where the attitude of the individual is driven by the desires which are likely to be accepted by the other individuals and prevent any controversy or conflict. Solemn problems and attitudes are prevented and people are required to concentrate on their busy work routines. Individual members also try to gather knowledge regarding each other, regarding the scope of the task and how to reach it. This phase is considered to be an easy stage but prevention of controversies and conflicts mean that not much objective is actually accomplished. The teams will together meet and learn about various opportunities and confront and then agree on objectives and start to tackle the tasks and objectives. Members of the team will quite behave autonomously.
Each team member must concentrate on his/her team leader by accepting the leader’s guidance and authority while maintaining a respectful distant association with other individuals. At this phase, the leader must open two way communications and be ready to reply any of the queries that may come on his/her way; limitations, potency and vulnerabilities must also be tested including those related to the leader.
Phase Two: Storming
Each Electron group then will enter into the next stage where different ideas for competition are considered. The teams address distinct issues such as what kind of problems they need to solve, how they must function autonomously as well as mutually with each other and which leadership model they must accept to follow. Each team member will have the privilege to confront others’ ideas and perceptions. In most cases storming is solved more quickly while in others, most of the teams never leave this phase (this depends on the maturity of the team). Most team members concentrate on the ins and outs to dodge the problems. This second phase is essential for the teams to grow which could be controversial, distasteful and often excruciating to the team members who are opposed to the conflicts. Tolerance of each team member must also be emphasized because without patience, teams will likely to fail.
This stage can be proved destructive for the teams if they are permitted to go out of control. Managers/supervisors of the teams might be more accessible but need to be directive in their professional and decision making attitudes. The teams therefore, will solve the problems and differences and contribute more comfortably with one another. In this way, they cannot be judged and can share their stand points and ideas easily with each other.
Phase Three: Norming
At this phase of team building, Electron managers will set one objective and one mutual plan for the team to accomplish. Some of the members will be motivated to give up their certain ideas in order for the team to effectively function. At this phase, each team member feels his/her commitment to the team and has the aspiration to work towards the success of the team’s objectives.
Phase Four: Performing
It is probable for certain teams to reach to this stage. The high performing teams can be able to work as one unit as they able to identify best approaches to get their job done mutually, comfortably and without irrelevant controversy or the requirement of any external management because they become motivated and knowledgeable by this stage. When the members of the Electron teams are now skilled, independent and experienced, they can tackle the process of decision making without the burden of any supervision (however, supervisors are also directive and participative at this stage but team make more appropriate decisions). The Electron teams must pass through this stage several times because of the global and organizational dynamic changes.
Phase Five: Adjourning (and Transforming)
This stage involves un-forming the groups which sometimes create a sense of loss often feel by the team members. This stage will include ‘dissolution’ which leads to the end of the Electron team members’ roles and responsibilities, the accomplishment of objectives and minimization of reliance. This procedure can be traumatic specifically when the dissolution is not planned. Thus, team members must be acknowledged at this phase that at the successful achievement of the productivity levels and outcomes, teams will be dissolved and that new teams will emerge for new targets.
Conclusion
In order to execute and sustain teams to operate effectively within the organization, sufficient organizational changes are required to be considered as well as various issues required to be catered. Those changes not only influence team members but also the responsibilities and commitments of the supervisors and managers, the organizational framework, work procedures and techniques and employees’ social bonds. That’s why due to the dynamic environmental changes, Electron manufacturers also face multiple challenges which occur as a result of teams’ implementation. However, it is also evident that in case of teams’ implementation, various organizations will not opt for going back to their prior organizational frameworks (IRS Employment Review 1995). Consequently, it is also seen that teams, in spite of the emerging challenges, are capable enough to offer several advantages to firms in the long run.
In case of Electron manufacturers, new hired team members were unknown of the team’s values, norms and consensus that proved greater challenge to the already existed relationships among the older employees. Moreover, managers were also expecting that each new member must be familiar with the procedures and norms of the groups to act accordingly and conform themselves to those groups. However, besides the implementation of their concertive procedures and motivating employees (by providing them rewards), Electron teams still lacking certain key aspects which formed the basis of a strengthened team. Such as two way communication, participation of employees in decision making, lack of trust among team members, sharing of opinions and ideas among each other to resolve any critical issue regarding production and enhancement of work performances and employees’ morale.
Thus, as a result of this, Bruce Tuckman’s (1965) model of team building is employed in the context of Electron manufacturers. According to his model, teams are to be developed step by step by ensuring performance effectiveness in each team building phase. This model consists of five stages i.e. forming, storming, norming, performing and adjourning. This can be concluded as Electron must forge its eight teams in a manner such that each individual must know his/her accountability, change his/her attitude according to the organizational culture so that teams will effectively function with minimum conflicts and controversies (forming). Second, teams must be encouraged to share their wide scope ideas and opinions and can confront the other’s ideas for making better decisions and improved productivity (storming).
Third, Electron managers must establish one objective and direct the team to mutually accomplish the objective which enhances the members’ sense of responsibility towards the team success (norming). Forth, when Electron’s team members become more experienced and capable enough, they will be able to make decisions without any supervisor which in turn, gives employees more autonomy, understanding of each other’s roles, increase employee social relationships, enhance their morale as well as enhance work productivity (performing). Finally, when the production target is successfully achieved, teams will be terminated at the final stage so that new teams will be developed to achieve new production targets with the passage of time and make the organization subtle to dynamic industrial changes with the help of new teams’ formation.
Recommendations
Following are some of the recommendations that can be further considered for making organizational teams more strengthened and intensified.
- In accordance to Tuckman’s strength deployment inventory (SDI) model, employees must be nurtured with the help of managers without directing rewards in return. They must be motivated to enhance their self-worth by accomplishing tasks and other significant orders.
- Fulk, Bell & Bodie (2011) also employed Tuckman’s five stages of team development to enhance team performance. According to them, the first stage ‘forming’ must also involve hiring and selecting right individuals at the right time who also possess the qualities of solving critical problems, controversies, communication gaps, decision making, setting of plans and goals and organizing tasks within teams.
- At the second stage ‘storming’, managers must anticipate to unexpected events that are likely to lead the whole team to the conflicts which are likely to arise as a result of differences in opinions, styles of working and priorities. The managers must be vigilant to take all those conflicts into consideration and encourage teams to take appropriate and productive actions towards mitigating those conflicts.
- The third stage ‘norming’ must involve working with teams with specific as well challenging goals and those goals must be present in writing. Here team performance can be enhanced if teams revisit their initial goals, clarification of the goals and the commitments towards those goals.
- At the fourth stage ‘performing’, managers must monitor their teams ‘objectives and their feedback on a regular basis in order to enhance teamwork. That feedback must be timely basis as well as concrete to be acted upon.
- At the final stage ‘adjourning’ the team members instead of felling a sense of loss, team members must be expected to enjoy their success resulted in successful completion of the task.
Bibliography
Bettenhausen, K.L. (1991) ‘Five Years of Group Research: What Have We Learned and What Needs to be Addressed’, Journal of Management, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 345-381.
Carr, C. (1992) ‘Planning Priorities for Empowered Teams’, Journal of Business Strategy, vol. 13, no. 5, p. 43-47.
Fulk, H.K. (2011) Team Management by Objectives: Enhancing Developing Teams’ Performance. Journal of Management Policy and Practice, 12(3), 17-26.
Heap, N. (1996) ‘Building the Organisational Team’, Industrial and Commercial Training, vol. 28, no. 3, pp.3-7.
IRS Employment Review (1995) ‘Key Issues in Effective Teamworking’, no. 592, pp. 5-16.
Katzenbach, J.R. & Smith, D.K. 1993, The Wisdom of Teams, McKinsey & Company, New York.
Kirkman, B.L. & Shapiro, D.L. (1997) ‘The Impact of Cultural Values on Employee Resistance to Teams: Toward a Model of Globalised Self-Managing Work Team Effectiveness’, Academy of Management Review, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 730-757.
Nahavandi, A. & Aranda, E. (1994) ‘Restructuring Teams for the Re-engineering Organization’, Academy of Management Executive, vol. 8. no. 4, pp. 58-68.
Performance Coaching Training (2010) Bruce Tuckman’s Forming, Storming, Norming & Performing Team Development Model.
Roufaiel, N.S. & Meissner, M. (1995) ‘Self-Managing Teams: A Pipeline to Quality and Technology Management, Benchmarking for Quality, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 21-37.
Sundstrom, E., De Meuse, K.P. & Futrell, D. (1990) ‘Work Teams: Applications and Effectiveness’, American Psychologist, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 120-133.
Teambuilding Solutions (2011) Strength Deployment Inventory (SDI).
Wageman, R. (1997) ‘Critical Success Factors for Creating Superb Self-managing Teams, Organisational Dynamics, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 49-60.
Zaccaro, S. J, Rittman, A.L & Marks, M.A (2001) Team Leadership. The Leadership Quarterly, 12, 451-483.
Appendix A