MBA Operations Management
MBA Operations Management students will learn that in business there are always individuals that are responsible for the managerial and supervisory activities. For a business to operate in the most efficient and conducive manner, the mode of operation needs to be advanced and even overseen by someone else. The research described these individuals as managers. The core objective of all the business or organizations is always to maximize profit. For these to take places, all the operations of the firm need to be correctly managed. Each business is managed through various business functions in which each function is responsible for managing a certain aspect of the business and as I had said earlier the core objective of all businesses is to provide the correct and appropriate requirement to the customers by offering goods and services (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). The president or the CEO of a company is faced with a daily marketing, operational, financial and information tasks. Marketing is a sector responsible for the generation of customer demand, sales and understanding customer’s wants and needs. Finance is responsible for the management of capital investments, the flow of cash and current assets. The information sector, on the other hand, is in charge of the constant stream of information in and out of business. The operating divisions are responsible for the management of the goods and services (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998).
Importance of MBA Operations Management
Therefore it is imperative for the manager to equally distribute the available resources in the business so has to ensure all the sectors are covered. Some of the cited sources will agree with my line of thought if I argue out that all the areas of management are to be treated evenly since they depend on each other. However, in this essay, we are going to discuss a lot about operational control answering all the questions in short subtopics. The essay will begin with the introduction to the body and finally to the conclusion.
Describe the Role of Operations Management in the Firm and How This Role Can Lead To Competitive Advantage and Profitability
Operating management by definition refers to act of administering business practices to establish a high level of efficiency in business (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons & Bordoloi, 2008). The method involves the conversion of labor and other factors of production into goods and services that are efficient enough to raise a maximum profit. An MBA Operations Management team has the duty to identify which of the factors of production best suits the company. They also work under a close surveillance and ensures that the cost of production is achieved once the products have been sold. Modern researchers refer to the task of being an operating manager as one of the hardest and the primary duty of an organization. Despite having other sectors, operation management forms the main reason why a business was created. It involves a lot of functions such as planning, coordination of activities, organizing and planning all the resources as they are channeled to goods and services as the end product.
A few scholars also argue that being that operating management has a management function; it, therefore, means that it can also be involved in managing equipment’s, people and technologies that are needed in the production process (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998). Operation management includes two very core aspects or rather two terms that need to be wee understood before engaging into being an enterprise manager. The two terms are the supply chain management and the logistics both of which will be covered in the MBA Operations Management module.
MBA Operations Management student will learn that the two terms act as the foundation for the business management and to out compete other competitors; one is expected to understand what exactly is meant by the terms. Take for example following the trends of supply and chain management globally; this will enable the team to strategies accordingly thus meeting the customers demand. While in logistics, it is critical to understand the use of resources in a cost effective way since there has been a trend where the resources are scarce, and the demand of the customers is skyrocketed (Cases & Case, 2004).
Often writers and employers confuse the skill required for efficient operation management and those that are needed in the logistics and supply chain management (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons & Bordoloi, 2008). One of the abilities that would be much appreciated is the consummate organizational skills. The completed organizational skills enhance efficiency and drive the productivity to another level as well. One must be able to understand the operations and coordination of activities in the firm to show effectiveness. However, operational management is a broad spectrum sector in a business and when well managed can lead to a lot of advantages to the firm. The scopes of executive management include decision making. Decision making involves making decisions on what type and kind of goods to be produced and with quick decision-making process the entire production process will be efficient and fast thus creating a lot of profits (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007).
Adding on the objective of the operation system, a complete operational objective must aim at a competitive advantage (Krajewski, Ritzman & Malhotra, 1999). A business or an organization is considered to have a competitive edge when its profitability is greater than the average profitability of the other competing companies of the same set of customers – This will be explained in the MBA Operations Management module. This can be achieved by emphasizing on specific areas of operation with the intent of meeting the client’s request. A good operating management should be able to perform the following; adaptability advantage, reliability advantage, and service delivery advantage. Through these, the company can make significant profits and become more efficient as expected.
Discuss Systems To Take Advantage Of Capital, Location, And Labor Differences So That Profits Are Maximized. MBA Operations Management
MBA Operations Management students will appreciate that the core objective of every organization is to make a profit and to minimize the cost of production. However, in the market as per the general information, we get that some specific companies often perform better than others (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). This happens due to the difference in various points of concentration, especially during the production process. Companies differ in labor, capital, and their locations and this can lead to an advantage of a particular company against another. This variance in the factors of production is the reason why we have a best-performing company and another one that performs poorly. Therefore, every company has invested in specific systems that will fully exploit the potential of these factors of production thus favoring them. Operation management also plays a very general role of logistics during the system establishment (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998).
Research covered in the MBA Operations Management module indicates that many successful companies apply the system of specialization of labor to help to maximize their profits (Cases & Case, 2004). Employees often have strengths and weaknesses, and those that are encouraged to yours their strengths are more loyal and engaged. Remember specialization does not only apply in the case of employees, but it also uses to material resources.
The best thing about specialization is that the workers get to choose what they love to do according to their ability and natural aptitude and this gives them the opportunity to perfect those skills thus saving a lot of production time. This prevents the delays that are created by the continuous shifting of workers from one point to another. Through this specialization, a company can make good use of his laborers thus increasing the profit levels. Labor specialization system works hand in hand with the division of labor in a company (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons & Bordoloi, 2008). This will ensure that the duties are only performed according to the line of interest. Material specialization will mean that a particular material will be developed and adapted for a specific use.
On a regional basis, each region will produce the products that they are best suited. This can be applied to both locational and capital systems – This will become apparent on the MBA Operations Management module. A combination of material specialization and human specialization can lead to a maximized efficiency (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). Capital systems can also be used to ensure that there is adequate and abundant production in the firm.
Through the use of capital goods, it will enable the producers to produce more efficiently and surplus output. The company’s capital should be invested in short term avenues that can translate excess profits within the shortest time, in this way we will be able to out compete effectively in the market. Priority is also another factor that needs to be considered especially when distributing capital in the business. Activities that have a real history on profit maximization are to be considered the first. On location of the company and its effects to profit maximization is also important as well. Location of the company should be based on specialization and distribution of raw materials (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998). The movement of raw materials to the company should be profitable, and the same applies to consumer’s accessibility to the firm. In other words, the location of the company should be close to the market as well as the raw materials thus reducing unnecessary cost.
Outline how planning the operations system takes place and how international considerations are integrated into planning
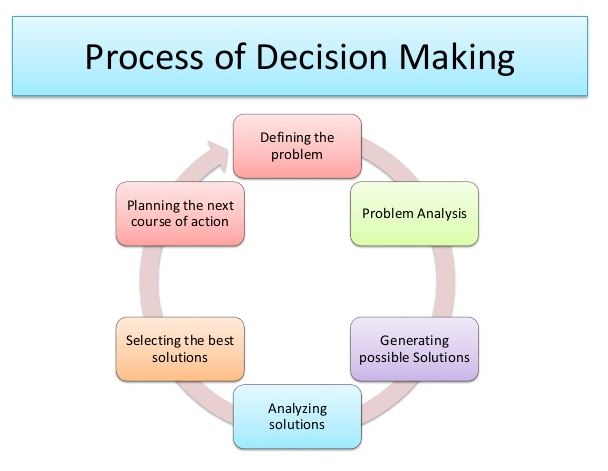
As discovered in the MBA Operations Management module, planning can be defined as the process of analyzing, researching, anticipating and influencing change in society (Wacker, 1998). Various pieces of literature indicate that before an action is executed, it is important to draw a plan to avoid things falling apart as it was not planned. Therefore it is very healthy to plan for activities in a business environment before their execution. Planning is a role that is left for the managers and the executives to perform in a healthy business climate. Moreover, many other activities are incorporated in planning. A strategic planning of the operation can communicate what the institution is striving to become and it also maps the necessary step that is needed to get to the target. In the past, the operational plans of a company used to take an entire ten years but today companies even plan year by year (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons & Bordoloi, 2008).
MBA Operations Management graduates state that planning is a procedures activity that involves gradual processes for the plans to be approved and exhibited appropriately. First, the vision of the organization needs to be stated and used as guidance during planning (Krajewski, Ritzman & Malhotra, 1999). The vision statement is approximately two to three sentences that spell out the intentions of the company; it shows how far the organization is willing to strive and reach. It is important to understand the organization right before the vision is created. At this point is important to create the image within the international standards that doesn’t violate any business law of operation. The next step in planning is to write the mission statement – This has been covered in the MBA Operations Management module through the year. Mission statement unlike the vision statement, explains what the organization exists and the path it will take to achieve its vision. Business wise, the mission statement is usually shorter than the mission statement.
A similar process is used in the construction of the mission statement. However, in the mission statement is where many people display false information. This is common with the organizations that deal with illegal products. The third process in planning is to perform a gap analysis. Gap analysis involves the comparison between the current operational situation and the vision of the company. This stage requires a lot of innovativeness and future oriented individuals. This is because there is need to compare the current situation and what the business hopes to be (Cases & Case, 2004). This process is much involving as it requires a collection of data and information outside the firm. The gaps that need to be examined include financial differences, customer relation, market share and internal systems.
Formulation of goals is the fourth step in the planning process. The goal can either be short term or long term. In many occasions, they are always referred to as SMART goal (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998). The goals need to be implemented right from the managerial level to the employee level. Lastly, monitoring the progress of the plans. The goals should be followed in every quarter of the business year. This is usually done by inquiring from those who are responsible in such areas. The above processes are inclusive of other minor steps that are also of importance in the process of planning. The international laws are always considered when an organization is planning. Ethical consideration at an international level, morals, and other core values are also applicable (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). During the operational planning, another important thing is the consideration of the international laws that govern all the business activities in the globe.
Describe some of the quantitative tools and techniques of Operations Management and how these are applied to formulate solutions to business problems.
In an organization, managers and the CEO always rely on their experiences in making decisions. However, in some situations, they would like to know what exactly the number saying is (Schmenner & Swink, 1998). In such circumstances, there is need to use quantitative methods especially when it involves an era of big data. The method, therefore, has been used by several operational analyzed to provide evidence that can guide in managerial, distribution, marketing, and personal decisions. The method also helps the executive team to predict what is expected to happen in future. This does not mean that the qualitative methods are point blanks, but they are also preferred in an individual situation. The manager is supposed to convert the inputs that are inclusive of the factors of productions into outputs (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons & Bordoloi, 2008). The quantitative techniques and tool include regression analysis, linear programming, factor analysis, data mining and descriptive data analysis.
Descriptive Data Analysis
This process involves the use of pie charts, maps, graphs, frequency tables, histograms, control charts, run charts and Ishikawa diagrams. They are used to analyze mainly the descriptive data in the production process. Research indicates that this can be achieved by entering the data into software like EXEL, STATA, SPSS and other software used for the analysis (Cases & Case, 2004). This method can be used to identify the problems realized in the business and attended to accordingly.
Regression Analysis
This is a traditional method that is mainly used by economists and the operational analysis; regression involves the use of complex statistical equations that help to predict the future output and maybe find out the cause of the past problem. This can significantly benefit the business. The products of the regression equation are known as the predictors or the dependent variables. Research indicates that economists and businesses have used the regression formula to estimate effects of advertisement expenses in companies (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998). Though the utilization of this method, we can determine the correlation between two products in the business.
Linear Programming
All organizations and companies are faced with the problem of scarce resources. This usually calls for a selective allocation of resources, and this often gives the manager a little bit of challenge. Linear programming, a conventional technique of management analysis and operational research (Schmenner & Swink, 1998). This is a mathematical program that helps us determine how to achieve optimum outcomes. It is also indicated that it can help in manufacturing and transport analysis.
Factors Analysis
This method is used to survey data and group statistical data accordingly. It explores all the avenues to find out the correlations and relationships (Krajewski, Ritzman & Malhotra, 1999). For example, the method can be used by market researchers to analyzed data on consumer’s consumption habits. This will then help the organization with the product knowledge as they will be able to determine what quantity they should produce.
Data Mining
Research indicates that this method has grown over the years. It is used to analyze a large amount of data. This has been used by big business like the Amazon to monitor consumer’s behavior.
Discuss business situations for which tools of Operations Management can be applied.
According to recent scholars, operation management involves directing and managing the physical and technical functions of an organization (Cases & Case, 2004). The skills and tools are used in the development, manufacturing, and production processed in the operation sector. The tools are used in the below-explained processes and will be covered off in the MBA Operations Management module:
Project Management
Project management is a common factor in both large and small companies, and it often takes a lot of time to plan. From the accessing the supplies and delegating the employees to all the shipment cost and all the activities involved in the manufacturing of the products. The project management tools can be used in an organization to strategically plan creates a budget, salaries, overhead costs and every detailed information about the business. The spreadsheet can be used to manage all the activities and track areas not covered (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007).
Quality Control and Inspection
Assessment of the products is a significant activity in the manufacturing process. Assessment is important because it will enable the business to track whether it has met its goals or not. Additionally, assessment should form part of the regular management process to ensure the project is completed (Wacker, 1998). Literature shows that it is always healthy to criticize the outcome and even establishes other realistic expectations.
Equipment Maintenance Policy
Depreciation is expected in any business and therefore maintained is expected as well. The equipment should, therefore, be regularly checked to ensure they are still in a position to function effectively. For example in a vehicle company, the cars are expected to be continuously serviced when the time arrives (Chase, Aquilano & Jacobs, 1998). Computers and hardware needed to be checked for virus and cleaned to ensure a stable functionality. The maintenance calendars can be created by the operation tools and equipment.
Product Scheduling
This is also another instance in which the tools can be effectively applied. Manufacturing companies complete their product arrangements to get them from the product establishment to the respective point of sales to the consumers. This can be done using plan long range projects. The process is usually effective especially when the company is dealing with a significant number of customers (Cases & Case, 2004).
Explain how control of operations must respond to changes in the international economy.
Today’s economy is far much different from the economy of the olden days (Krajewski, Ritzman & Malhotra, 1999). The globally economy changes gradually day by day and these calls for a relatively positive response from every organization that is associated with the international trade. In a business environment, it is the duty of the managing director responsible for the operation to ensure that the company adapts to the changing global economy. From the financial perspective, organizations are intentioned at making high profits, and therefore it should vary its price with the world’s market price. Through this method, it will be able to secure a large section of the consumers (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons & Bordoloi, 2008). In other words, the operation must respond effectively to the change in prices of goods and services.
Control of process must also meet the consumer’s demand on an international scale. The quantity and quality of good should meet the customer’s demand. The service team must ensure that they manipulate the consumers into buying their products without going into loss. This can be done by forming business merges and also ensuring that a lot of awareness is created (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). The company should also be in a position of responding to the technological changes in the international market. Recruiting young and innovative minds to handle the technological shifts in the organization. This can also be advanced through training the worker on how to cope up with the constant changes in the body.
Conclusion
MBA Operations Management students will learn and appreciate that operation management forms the center of many organizations has it is characterized by several functions including planning, staffing, and production. Through the correct exhibition of duties, it can lead to the creation of a lot of profits. Through specialization, excellent location and use of capital goods, an organization can make a lot of benefits depending on the available resources. However, for this to occur appropriate operational tools such as linear programming should be used to predict the future outcomes in the organization. Such tools are always essential in project management and even in quality assessment.
References
Cases, T., & Case, F. (2004). MBA Operations Management.
Chase, R. B., Aquilano, N. J., & Jacobs, F. R. (1998). Production and operations management. Irwin/McGraw-Hill,
Fitzsimmons, J. A., Fitzsimmons, M. J., & Bordoloi, S. (2008). Service management: Operations, strategy, and information technology (p. 4). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Krajewski, L. J., Ritzman, L. P., & Malhotra, M. K. (1999). MBA Operations management. Singapore: Addison-Wesley.
Schmenner, R. W., & Swink, M. L. (1998). On theory in operations management. Journal of operations management, 17(1), 97-113.
Stevenson, W. J., & Hojati, M. (2007). MBA Operations Management (Vol. 8). Boston: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Wacker, J. G. (1998). A definition of theory: research guidelines for different theory-building research methods in operations management. Journal of operations management, 16(4), 361-385.
Other Relevant Blog Posts
MBA Dissertation PDF Examples University
Business Forecasting Predictions MBA
Recommended Reading For MBA Operations Management Students
- Operations Management for MBAs by Jack R Meredith and Scott M Shafer
- Handbook of Decision Analysis (Wiley Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science) by Gregory S. Parnell PhD and Terry Bresnick MBA
- Operations and Supply Chain Management for MBAs by Jack R. Meredith and Scott M. Shafer
- Operations Management by Prof Nigel Slack and Prof Alistair Brandon-Jones
I hope you enjoyed reading this post on MBA Operations Management. There are many other titles available in the business management and MBA dissertation collection that should be of interest to MBA students and academic professionals. There are many dissertation titles that relate to other aspects of business such as strategy, leadership, international business, mergers and acquisitions to name a few. It took a lot of effort to write this post and I would be grateful if you could share this post via Facebook and Twitter. Feel free to add your thoughts in the comments section. Thank you.